Meeting the meat needs of the future
2021-03-02
(Press-News.org) Tokyo, Japan - Humans are largely omnivores, and meat in various forms has always featured in the diet of most cultures. However, with the increasing population and pressure on the environment, traditional methods of meeting this fundamental food requirement are likely to fall short. Now, researchers at the University of Tokyo report innovative biofabrication of bovine muscle tissue in the laboratory that may help meet escalating future demands for dietary meat.
With global urbanization, the economics of animal husbandry are becoming unsustainable. From an environmental viewpoint, the land and water costs of modern mega-scale livestock farming are untenable, as are the greenhouse gas emissions and the overall toll on the planet. Additionally, ethical concerns against inhuman exploitation of lower species for food are increasingly being voiced.
To address future requirements, tissue engineering of cultured meat is under development at several centers worldwide. However, most biosynthetic meat products are amorphous or granular-like minced meat, lacking the grain and texture of real animal flesh. Mai Furuhashi, lead author, explains their novel process. "Using techniques developed for regenerative medicine, we succeeded in culturing millimeter-sized chunks of meat wherein alignment of the myotubes help mimic the texture and mouthfeel of steak. For this, myoblasts drawn from commercial beef were cultured in hydrogel modules that could be stacked allowing fusion into larger chunks. We determined the optimal scaffolding and electrical stimulation to promote contractility and anatomical alignment of the muscle tissue to best simulate steak meat."
Lead author, Yuya Morimoto, describes the synthesized product. "Our morphological, functional and food feature analyses showed that the cultured muscle tissue holds promise as a credible steak substitute. Breaking force measurements showed that toughness approached that of natural beef over time. Significantly, microbial contamination was undetectable; this has implications for cleanliness, consumer acceptability and shelf-life."
"Our method paves the way for further development of larger portions of realistic cultured meat that can supplement or replace animal sources," claims Shoji Takeuchi, senior and corresponding author. "However, there is a long way to go before lab-grown meat is indistinguishable from the real thing and hurdles concerning consumer acceptance and cultural sensibilities are overcome. Nevertheless, this innovation promises to be a green and ethical alternative to animal slaughter in meeting our need for dietary meat."
INFORMATION:
The article, "Formation of contractile 3D bovine muscle tissue for construction of millimetre-thick cultured steak" was published in Science of Food. at DOI: 10.1038/s41538-021-00090-7.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-02
In a world first, an international team of researchers has read an unopened letter from Renaissance Europe - without breaking its seal or damaging it in any way.
The research, published in Nature Communications, describes how an X-ray scanner used in dental research and 'virtual unfolding' allowed the interdisciplinary team to read the contents of a securely and intricately folded letter which has remained unopened for 300 years, while preserving its valuable physical evidence.
A highly sensitive X-ray microtomography scanner, developed at ...
2021-03-02
A volcanic eruption in the Galápagos Islands has given scientists a fresh insight into how volcanoes behave and provided vital information that will help to predict future hazards on the islands.
Irish scientists, based at Dublin Institute for Advanced Studies (DIAS) and Trinity College Dublin respectively, were members of an international research team from Ireland, United Kingdom, United States, France and Ecuador that made the discovery.
The research published today (02.03.21) in Nature Communications reveals the first ever detailed description of a volcanic eruption from Sierra Negra - one ...
2021-03-02
Hours before the 2018 eruption of Sierra Negra, the Galápagos Islands' largest volcano, an earthquake rumbled and raised the ground more than 6 feet in an instant. The event, which triggered the eruption, was captured in rare detail by an international team of scientists, who said it offers new insights into one of the world's most active volcanoes.
"The power of this study is that it's one of the first times we've been able to see a full eruptive cycle in this detail at almost any volcano," said Peter La Femina, associate professor of geosciences ...
2021-03-02
A large proportion of the benefit that a person gets from taking a real drug or receiving a treatment to alleviate pain is due to an individual's mindset, not to the drug itself. Understanding the neural mechanisms driving this placebo effect has been a longstanding question. A meta-analysis published in Nature Communications finds that placebo treatments to reduce pain, known as placebo analgesia, reduce pain-related activity in multiple areas of the brain.
Previous studies of this kind have relied on small-scale studies, so until now, researchers did not know if the neural mechanisms underlying ...
2021-03-02
In June 2019, an international team brought the complete skull of the 3.67-million-year-old Little Foot Australopithecus skeleton, from South Africa to the UK and achieved unprecedented imaging resolution of its bony structures and dentition in an X-ray synchrotron-based investigation at the UK's national synchrotron, Diamond Light Source. The X-ray work is highlighted in a new paper in e-Life, published today (2nd March 2021) focusing on the inner craniodental features of Little Foot. The remarkable completeness and great age of the Little Foot skeleton makes it a crucially important ...
2021-03-02
Publishing in peer-reviewed scientific journals is crucial for the development of a researcher's career. The scientists that publish the most often in the most prestigious journals generally acquire greater renown, as well as higher responsibilities. However, a team involving two CNRS researchers* has just shown that the vast majority of scientific articles in the fields of ecology and conservation biology are authored by men working in a few Western countries. They represent 90% of the 1,051 authors that have published the most frequently in the 13 major scientific journals in the field since 1945. ...
2021-03-02
WASHINGTON (Mar. 2, 2021) -- A report released today by the George Washington University Program on Extremism reveals new information about the 257 people charged in federal court for playing a role in the Jan. 6 attack on the United States Capitol. The report, "This is Our House!" A Preliminary Assessment of the Capitol Hill Siege Participants," also provides several recommendations aimed at combating domestic extremism.
The GW Program on Extremism tracked and categorized the people charged so far in the attack and the resulting report provides a preliminary assessment of the siege participants.
"The events of Jan. 6 may mark a watershed moment for domestic violent ...
2021-03-02
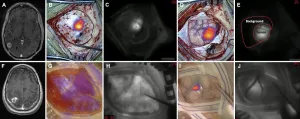
Charlottesville, VA (March 2, 2021). Researchers in the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania conducted a prospective cohort study utilizing their technique of delayed near-infrared imaging with high-dose indocyanine green (called "second window ICG" or "SWIG") in the identification of brain metastases during surgery. In this study, all metastatic lesions enhanced under near-infrared light with application of SWIG. The researchers compared near-infrared SWIG images obtained at the end of tumor resection with postoperative gadolinium-enhanced MRIs, considered the gold standard for imaging. The comparison demonstrated that SWIG can be used to predict the extent of gross-total resection and, ...
2021-03-02
Since 1970, bird populations in North America have declined by approximately 2.9 billion birds, a loss of more than one in four birds. Factors in this decline include habitat loss and ecosystem degradation from human actions on the landscape.
At the same time, enthusiasm for bird-watching has grown, with more than 45 million recreational participants in the United States alone. Now, researchers are looking into how to mobilize these bird enthusiasts to help limit bird population declines.
Enter bird-friendly coffee.
Bird-friendly coffee is certified organic, but its impact on the environment goes further than that: it is cultivated specifically to maintain bird habitats instead of clearing vegetation that birds and other animals rely on.
Researchers ...
2021-03-02
A new paper in Oxford Open Materials Science, published by Oxford University Press, presents low cost modifications to existing N95 masks that prolongs their effectiveness and improves their reusability post disinfectants.
The COVID-19 crisis has increased demand for respiratory masks, with various models of DIY masks becoming popular alongside the commercially available N95. The utility of such masks is primarily based on the size of aerosols that they are capable of filtering out and how long they can do so effectively.
Conventional masks like the N95 use a layered system and have an efficiency ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Meeting the meat needs of the future