Diagnosis of genetic condition could help patients stop smoking and prevent lung disease
Estimated 40,000 smokers in Ireland with condition are undiagnosed
2021-03-03
(Press-News.org) New research shows that people diagnosed with a genetic condition, called alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency (AATD), are far more likely to stop smoking and therefore prevent the development of lung disease.
The study, led by researchers from RCSI University of Medicine and Health Science, is published in COPD: Journal of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease.
It is estimated that 265,000 people on the island of Ireland are affected by either severe or moderate AATD, but the vast majority of people with AATD have not been diagnosed.
Previously, it was assumed that only people with severe AATD were at risk of lung disease. Recent Irish research has shown that people with the far more common moderate form of AATD are also at risk of lung disease if they are smokers.
With the smoking rate in the general population in Ireland at 17%, this means there are approximately 45,000 current smokers with either severe or moderate AATD who are at increased risk of lung damage due to cigarettes. According to the latest figures from the national targeted detection programme for AATD based at RCSI Beaumont Hospital, 90% of these smokers with AATD remain undiagnosed.
The researchers surveyed patients enrolled in the National AATD Registry with a questionnaire relating to demographics, parental smoking history, personal smoking history, AATD awareness and personal medical history.
Of the 293 respondents, 58 reported being smokers at the time of their AATD diagnosis. Their subsequent reported quit rate was 70.7%.
"Our study has shown that those who receive a diagnosis of alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency are far more likely to stop smoking. We hope this study will lead to increased testing for AATD, with more people being diagnosed and choosing to stop or completely avoid smoking in order to prevent lung disease from developing," said Dr Tomás Carroll, senior lecturer at RCSI and the study's corresponding author.
"People with AATD who use electronic cigarettes are also potentially at risk, but more research is needed."
The research also found that people who reported having a parent who smoked were far more likely to become smokers themselves. Those with a parent who smoked were 84% more likely to smoke than those who did not.
For a diagnosis of AATD, a simple blood test is available in most large hospitals in Ireland that can identify those who need further testing. The more precise definitive test is provided for free by Alpha-1 Foundation Ireland as part of a HSE funded national targeted detection programme.
INFORMATION:
More information on how to get tested can be found at http://www.alpha1.ie or by calling (0)1 8093 871.
AATD results from a deficiency of the alpha-1 antitrypsin protein, which is made by the liver and protects tissues in the body from being attacked by its own enzymes. It is a genetic condition that can cause lung, liver and skin disease.
With 1 in 25 people in Ireland carrying a defective alpha-1 antitrypsin gene, AATD is much more common in Ireland than in most other countries. AATD is one of the most common genetic conditions in Ireland.
About RCSI University of Medicine and Health Sciences
Ranked number one globally for Good Health and Well-being in the Times Higher Education (THE) University Impact Rankings 2020, RCSI University of Medicine and Health Sciences is an international not-for-profit university, with its headquarters in Dublin.
RCSI is exclusively focused on education and research to drive improvements in human health worldwide. It is among the top 250 universities worldwide in the THE World University Rankings (2020) and its research is ranked first in Ireland for citations. RCSI has been awarded Athena Swan Bronze accreditation for positive gender practice in higher education.
Visit the RCSI MyHealth Expert Directory to find the details of our experts across a range of healthcare issues and concerns. Recognising their responsibility to share their knowledge and discoveries to empower people with information that leads them to better health, these clinicians and researchers are willing to engage with the media in their area of expertise.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-03
Lithium-ion battery fire hazards are extensive worldwide and such failure can have a severe implication for both smartphones and electric cars, says the head of the group and Professor in the Department of Electrochemistry at St Petersburg University Oleg Levin. 'From 2012 to 2018, 25,000 cases of catching fire by a wide range of devices in the USA only were reported. Earlier, from 1999 to 2012, only 1,013 cases were reported. The number of fire incidents is increasing as is the number of the batteries being used,' he said.
Among the main reasons why lithium ion batteries catch fire or explode are overcharging, short circuit, and others. As a result, the battery is overheated and the battery ...
2021-03-03
Semaglutide, an injectable medication taken once a week, offers a nonsurgical way to reduce weight and treat obesity. It could help the more than 70 million adults in the United States who struggle with this chronic condition, says Ildiko Lingvay, M.D., M.P.H., M.S.C.S., professor of internal medicine and population and data sciences at UTSW and lead author of the study, published today in The Lancet.
People with diabetes benefit greatly from weight loss, yet they have a much harder time losing weight compared with those without diabetes, Lingvay says. This ...
2021-03-03
WEHI researchers have uncovered a process cells use to fight off infection and cancer that could pave the way for precision cancer immunotherapy treatment.
Through gaining a better understanding of how this process works, researchers hope to be able to determine a way of tailoring immunotherapy to better fight cancer.
Led by Dr Dawn Lin and Dr Shalin Naik and published in Nature Cell Biology, the research provides new insight into the way cells adapt to fight infection.
This research lays the foundation for future studies into the body's response to environmental stressors, such as injury, infection or cancer, at a single cell level.
At a glance
WEHI researchers have studied dendritic ...
2021-03-03
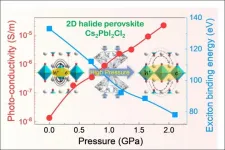
HPSTAR scientists Dr. Songhao Guo and Dr. Xujie Lü report three orders of magnitude increase in the photoconductivity of Cs2PbI2Cl2 from its initial value, at the industrially achievable level of 2 GPa, using pressure regulation. Impressively, pressure regulating the 2D perovskite's excitonic features gains it 3D compound characteristics without diminishing its own advantages, making it a more promising material for photovoltaic and photodetector applications. Their study is published as a Cover article in the latest issue of the Journal of the American Chemical Society.
Two-dimensional (2D) halide perovskites have recently emerged for photovoltaic and optoelectronic ...
2021-03-03
In a report summary released today Thomas McAndrew, a computational scientist and assistant professor at Lehigh University's College of Health includes probabilistic forecasts of the impact of vaccines and variants on the U.S. COVID trajectory over the next few weeks. The goal of the report, says McAndrew, is "to support public health officials, infectious disease modeling groups, and the general public"
Report highlights:
A consensus of 91 forecasters predicts that the B.1.1.7. variant will be found in 42% of all genetic sequences with an S-gene mutation in the first two weeks of March and in 72% in all sequences between ...
2021-03-03
Researchers have captured the first detailed images of newborn babies' lungs as they take their first breaths.
The research, led by the Murdoch Children's Research Institute (MCRI) and published the American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, provides a breakthrough in understanding the events around a baby's first breath, why healthy babies cry at birth and provides clues to improving preterm babies' survival chances and long term health outcomes.
About 10 per cent of newborns, and almost all preterm infants, need resuscitation because their lungs do not properly fill with air at birth (a process called lung aeration). Despite ...
2021-03-03
New research from UBC finds that higher life satisfaction is associated with better physical, psychological and behavioural health.
The research, published recently in The Milbank Quarterly, found that higher life satisfaction is linked to 21 positive health and well-being outcomes including:
a 26 per cent reduced risk of mortality
a 46 per cent reduced risk of depression
a 25 per cent reduced risk of physical functioning limitations
a 12 per cent reduced risk of chronic pain
a 14 per cent reduced risk of sleep problem onset
an eight per cent higher likelihood of frequent physical activity
better psychological well-being on ...
2021-03-03
If you've ever swatted a mosquito away from your face, only to have it return again (and again and again), you know that insects can be remarkably acrobatic and resilient in flight. Those traits help them navigate the aerial world, with all of its wind gusts, obstacles, and general uncertainty. Such traits are also hard to build into flying robots, but MIT Assistant Professor Kevin Yufeng Chen has built a system that approaches insects' agility.
Chen, a member of the Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science and the Research Laboratory of Electronics, has developed insect-sized drones with unprecedented dexterity and resilience. The aerial robots ...
2021-03-03
Green tea supplements modulate facial development of children with Down syndrome
A new study led by Belgian and Spanish researchers published in Scientific Reports adds evidence about the potential benefits of green tea extracts in Down syndrome. The researchers observed that the intake of green tea extracts can reduce facial dysmorphology in children with Down syndrome when taken during the first three years of life. Additional experimental research in mice confirmed the positive effects at low doses. However, they also found that high doses of the extract can disrupt facial and bone development. More research is needed to fully understand the effects of green tea extracts and therefore they should ...
2021-03-03
Imagine a robot.
Perhaps you've just conjured a machine with a rigid, metallic exterior. While robots armored with hard exoskeletons are common, they're not always ideal. Soft-bodied robots, inspired by fish or other squishy creatures, might better adapt to changing environments and work more safely with people.
Roboticists generally have to decide whether to design a hard- or soft-bodied robot for a particular task. But that tradeoff may no longer be necessary.
Working with computer simulations, MIT researchers have developed a concept for a soft-bodied robot that can turn rigid on demand. The approach could enable a new generation of robots that combine the strength and precision of rigid robots with the fluidity and safety of ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Diagnosis of genetic condition could help patients stop smoking and prevent lung disease
Estimated 40,000 smokers in Ireland with condition are undiagnosed