INFORMATION:
IU researchers discover new potential for functional recovery after spinal cord injury
2021-03-05
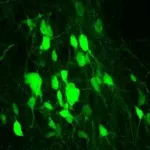
(Press-News.org) Researchers at Indiana University School of Medicine have successfully reprogrammed a glial cell type in the central nervous system into new neurons to promote recovery after spinal cord injury--revealing an untapped potential to leverage the cell for regenerative medicine.
The group of investigators published their findings March 5 in Cell Stem Cell. This is the first time scientists have reported modifying a NG2 glia--a type of supporting cell in the central nervous system--into functional neurons after spinal cord injury, said Wei Wu, PhD, research associate in neurological surgery at IU School of Medicine and co-first author of the paper.
Wu and Xiao-Ming Xu, PhD, the Mari Hulman George Professor of Neuroscience Research at IU School of Medicine, worked on the study with a team of scientists from the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center. Xu is also a primary member of Stark Neurosciences Research Institute, where he leads the Indiana Spinal Cord and Brain Injury Research Group.
Spinal cord injuries affect hundreds of thousands of people in the United States, with thousands more diagnosed each year. Neurons in the spinal cord don't regenerate after injury, which typically causes a person to experience permanent physical and neurological ailments.
"Unfortunately, effective treatments for significant recovery remain to be developed," Xu said. "We hope that this new discovery will be translated to a clinically relevant repair strategy that benefits those who suffer from a spinal cord injury."
When the spinal cord is injured, glial cells, of which there are three types--astrocyte, ependymal and NG2--respond to form glial scar tissue.
"Only NG2 glial cells were found to exhibit neurogenic potential in the spinal cord following injury in adult mice, but they failed to generate mature neurons," Wu said. "Interestingly, by elevating the critical transcription factor SOX2, the glia-to-neuron conversion is successfully achieved and accompanied with a reduced glial scar formation and increased functional recovery following spinal cord injury."
The researchers reprogrammed the NG2 cells from the mouse model using elevated levels of SOX2--a transcription factor found inside the cell that's essential for neurogenesis--to neurons. This conversion has two purposes, Xu said: generate neurons to replace those lost due to a spinal cord injury and reduce the size of the glial scars in the lesion area of the damaged tissue.
This discovery, Wu said, serves as an important target in the future for potential therapeutic treatments of spinal cord injury.
The partnership between the laboratory of Chun-Li Zhang, PhD, professor at UT Southwestern Medical Center, and Xu's laboratory at IU School of Medicine greatly benefited the research, Xu added, by offering complementary expertise in neuronal reprogramming and in spinal cord injury, respectively.
"Such a collaboration will be continued between the two laboratories to address neuronal remodeling and functional recovery after successful conversion of glial cells into functional neurons in future," Xu said.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Blind trust in social media cements conspiracy beliefs
2021-03-05
PULLMAN, Wash. - The ability to identify misinformation only benefits people who have some skepticism toward social media, according to a new study from Washington State University.
Researchers found that people with a strong trust in information found on social media sites were more likely to believe conspiracies, which falsely explain significant events as part of a secret evil plot, even if they could identify other types of misinformation. The study, published in the journal Public Understanding of Science on March 5, showed this held true for beliefs in older conspiracy theories as well as newer ones around COVID-19.
"There was some ...
Small volcanic lakes tapping giant underground reservoirs
2021-03-05
Boulder, Colo., USA: In its large caldera, Newberry volcano (Oregon, USA) has two small volcanic lakes, one fed by volcanic geothermal fluids (Paulina Lake) and one by gases (East Lake). These popular fishing grounds are small windows into a large underlying reservoir of hydrothermal fluids, releasing carbon dioxide (CO2) and hydrogen sulfide (H2S) with minor mercury (Hg) and methane into East Lake.
What happens to all that CO2 after it enters the bottom waters of the lake, and how do these volcanic gases influence the lake ecosystem? Some lakes fed by volcanic CO2 have seen catastrophic ...
How does your brain process emotions? Answer could help address loneliness epidemic
2021-03-05
Research over the last decade has shown that loneliness is an important determinant of health. It is associated with considerable physical and mental health risks and increased mortality. Previous studies have also shown that wisdom could serve as a protective factor against loneliness. This inverse relationship between loneliness and wisdom may be based in different brain processes.
In a study published in the March 5, 2021 online edition of Cerebral Cortex, researchers at University of California San Diego School of Medicine found that specific regions of the brain respond to emotional stimuli related to loneliness and wisdom in opposing ways.
"We were interested ...
Humans evolved to be the water-saving ape
2021-03-05
DURHAM, N.C. -- When you think about what separates humans from chimpanzees and other apes, you might think of our big brains, or the fact that we get around on two legs rather than four. But we have another distinguishing feature: water efficiency.
That's the take-home of a new study that, for the first time, measures precisely how much water humans lose and replace each day compared with our closest living animal relatives.
Our bodies are constantly losing water: when we sweat, go to the bathroom, even when we breathe. That water needs to be replenished to keep blood volume and other body fluids within normal ranges.
And yet, research published March 5 in the journal Current Biology shows that the human body uses 30% to 50% less water per ...
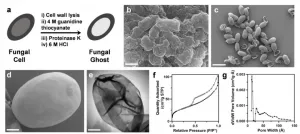
'Fungal ghosts' protect skin, fabric from toxins, radiation
2021-03-05
The idea of creating selectively porous materials has captured the attention of chemists for decades. Now, new research from Northwestern University shows that fungi may have been doing exactly this for millions of years.
When Nathan Gianneschi's lab set out to synthesize melanin that would mimic that which was formed by certain fungi known to inhabit unusual, hostile environments including spaceships, dishwashers and even Chernobyl, they did not initially expect the materials would prove highly porous-- a property that enables the material to store and capture molecules.
Melanin has been found across living organisms, on our skin and the backs of ...
Putting a protein into overdrive to heal spinal cord injuries
2021-03-05
Using genetic engineering, researchers at UT Southwestern and Indiana University have reprogrammed scar-forming cells in mouse spinal cords to create new nerve cells, spurring recovery after spinal cord injury. The findings, published online today in Cell Stem Cell, could offer hope for the hundreds of thousands of people worldwide who suffer a spinal cord injury each year.
Cells in some body tissues proliferate after injury, replacing dead or damaged cells as part of healing. However, explains study leader END ...
Outcomes, mortality among adults hospitalized with COVID-19 at US medical centers
2021-03-05
What The Study Did: The objectives of this study were to examine the characteristics and outcomes among adults hospitalized with COVID-19 at U.S. medical centers and analyze changes in mortality over the initial six months of the pandemic.
Authors: Ninh T. Nguyen, M.D., of the University of California, Irvine Medical Center, in Orange, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.0417)
Editor's Note: The article includes ...
Racial/ethnic disparities in autism
2021-03-05
What The Study Did: Survey data were used to estimate changes in racial/ethnic disparities in rates of autism spectrum disorder among U.S. children and adolescents from 2014 through 2019.
Authors: Z. Kevin Lu, Ph.D., of the University of South Carolina in Columbia, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.0771)
Editor's Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
INFORMATION:
Media advisory: The full study is linked to this news release.
Embed ...
Health care use among undocumented patients
2021-03-05
What The Study Did: Researchers examined the association of increased anti-immigrant rhetoric during the 2016 presidential campaign with changes in the use of health care services among undocumented patients.
Authors: Joseph Nwadiuko, M.D., M.P.H., M.S.H.P., of the University of Pennsylvania Perelman School of Medicine in Philadelphia, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.0763)
Editor's Note: Editor's Note: The article includes conflicts of interest and funding/support disclosures. Please see the article ...
Neurologic involvement in children, adolescents hospitalized in US for COVID-19 or multisystem inflammatory syndrome
2021-03-05
What The Study Did: In this study, many children and adolescents hospitalized for COVID-19 or multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children had neurologic involvement, mostly transient symptoms. A range of life-threatening and fatal neurologic conditions associated with COVID-19 infrequently occurred. Effects on long-term neurodevelopmental outcomes are unknown.
Authors: Adrienne G. Randolph, M.D., of Boston Children's Hospital, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamaneurol.2021.0504)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest ...