INFORMATION:
An analysis of SARS-CoV-2 mutations in 1,000+ individuals from the UK
2021-03-09
(Press-News.org) An analysis of SARS-CoV-2 genome diversity in more than 1,000 people in the United Kingdom suggests that if viral mutations do arise, they can be transmitted in some cases but they rarely persist in subsequent transmissions. "Our observations indicate the within-host emergence of vaccine- and therapeutic-escape mutations is likely to be relatively rare," say the authors, "at least during early infection when viral loads are high." However, because mutations that can escape therapies like antibodies were identified, including in higher viral load samples, the authors encourage continued monitoring and vigilance, particularly as vaccines and therapeutics that put "pressure" on viruses to adapt are rolled out more widely. Most analyses of mutations in SARS-CoV-2 to date have been focused on mutations observed in individuals that represent the dominant variants. However, new mutations are emerging in infected individuals, too, and knowledge of the full underlying diversity of viruses in human hosts - how frequently they emerge, and whether they are transmitted - is important for understanding viral adaption and patterns of spread. To better characterize diversity in single human hosts, Katrina Lythgoe and colleagues used an RNA sequencing approach to analyze 1,390 SARS-CoV-2 genomes from 1,313 nasopharyngeal swabs sampled mostly from symptomatic patients in the UK who had gotten sick between March and June 2020 (the first global wave of infection). The authors observed only one or two variants in most individuals, but a few patients carried many variants. Most of these were lost at the point of transmission, though a small number initiated ongoing transmission and wider dissemination. Too, there were very few cases of virus transmission between households in the studied genomes. These results suggest that during early infection, mutations that can increase the virus's chances of escaping therapies rarely emerge and transmit. Even so, the authors did identify variants that can give the virus an advantage, including in high viral load samples. This indicates that naturally occurring variants would have the opportunity to spread as population selection pressure from vaccine rollout increases. The findings underline the need for continued monitoring, they say.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Modeling study examines impacts of one versus two doses of a COVID-19 vaccine
2021-03-09
While receiving just one dose of a two-dose SARS-CoV-2 vaccine tends to decrease infections in the short-term if it produces a strong immune response, it may increase the potential for the virus to "escape" therapies in the longer-term if one-dose vaccinal immunity is weak, reports a new modeling study "[O]ur work emphasizes that the impact of vaccine dosing regimes are strongly dependent on the relative robustness of immunity conferred by a single dose," the authors write. As COVID-19 vaccines have been distributed internationally, several countries including the United Kingdom and Canada have chosen to delay the second dose to increase the number of individuals ...
Pediatric emergency visits, hospitalizations down sharply during pandemic: study
2021-03-09
Amid the COVID-19 pandemic, children's hospitals across the United States have seen signification reductions in the number of children being treated for common pediatric illnesses like asthma and pneumonia, according to a new multicenter study led by Monroe Carell Jr. Children's Hospital at Vanderbilt.
Researchers at Children's Hospital found that 42% fewer children were being seen and hospitalized at 44 children's hospital across the U.S. for both respiratory and non-respiratory illnesses, with the most significant reduction seen in children under age 12. Hospitals saw a decline in the number of children seen or hospitalized for respiratory illness by 62%, while there was 38% reduction for non-respiratory illnesses.
The trend, ...
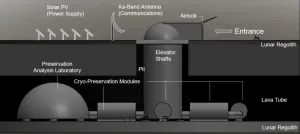
Engineers propose solar-powered lunar ark as 'modern global insurance policy'
2021-03-09
University of Arizona researcher Jekan Thanga is taking scientific inspiration from an unlikely source: the biblical tale of Noah's Ark. Rather than two of every animal, however, his solar-powered ark on the moon would store cryogenically frozen seed, spore, sperm and egg samples from 6.7 million Earth species.
Thanga and a group of his undergraduate and graduate students outline the lunar ark concept, which they call a "modern global insurance policy," in a paper presented over the weekend during the IEEE Aerospace Conference.
"Earth is naturally a volatile environment," said Thanga, a professor of aerospace and mechanical engineering in the UArizona College ...
Lower dose, less toxic radiopharmaceutical produces better outcomes
2021-03-09
Neuroendocrine tumours are cancers that begin in specialised cells called neuroendocrine cells. These cells have traits similar to those of nerve cells and hormone-producing cells. Neuroendocrine tumours, while rare, can occur anywhere in the body. Most affect the cardiothoracic region, eg lungs, appendix, small intestine, pancreas as well as the rectum. There are many types of neuroendocrine tumours: some grow slowly while others develop very rapidly.
Neuroendocrine tumors are characterised by abundant production of somatostatin receptor 2, a naturally circulating hormone that is an important target for scientists studying new treatment approaches.
Peptide Receptor Radionuclide Therapy (PRRT) is the most commonly used treatment for refractive ...
Study: Increase in taking HIV meds using Amazon Prime model
2021-03-09
Home delivery of HIV medicines in South Africa significantly increased viral suppression compared to those who received clinical care, according to a study by researchers at the University of Washington School of Medicine.
The study, conducted with Amazon.com guidance during COVID-19 restrictions in South Africa, showed that among study participants, paying a fee for home delivery and monitoring of antiretroviral therapy (ART) was highly acceptable in the context of low income and high unemployment, and improved health outcomes as a result.
The researching findings were ...
A new predictive model helps identify those at risk for severe COVID-19
2021-03-09
Researchers at the Buck Institute analyzed data from the COVID-19 Symptom Tracker app used by 3 million people in the United Kingdom, adding the use of immunosuppressant medication, use of a mobility aid, shortness of breath, fever, and fatigue to the list of symptoms and comorbidities that increase the risk for severe COVID-19. Results are published in the Journal of Medical Internet Research.
"Even though there are established risk factors for severe COVID-19 there are no good predictors that enable healthcare providers, or even those who have tested positive, to assess who should seek advanced medical care," says Buck Institute ...
Study reveals process to explain how maternal stress triggers idiopathic preterm birth
2021-03-09
TAMPA, Fla. (March 8, 2021) -- Preterm birth is a END ...
Bridge built between Kähler-Einstein and Chen-Ning Yang's Equations
2021-03-09
Recently, Prof. CHEN Gao from Institute of Geometry and Physics of the University of Science and Technology of China has made breakthrough in the field of complex differential geometry. Using mathematical invention, he buildt a new bridge between the relativity of Einstein and quantum mechanics. This work was published in Inventiones Mathematicae.
In the field of complex differential geometry, there are two crucial physical equations: the Hermitian-Yang-Mills equation, which became the standard model of quantum mechanics, and the Kähler-Einstein equation, which is closely related to relativity. To stably solve these two equations ...
Can chips replace animal testing?
2021-03-09
A team of researchers led by Professor Yaakov Nahmias, director of the Grass Center for Bioengineering at the Hebrew University of Jerusalem and founder of Tissue Dynamic, introduced a new technological approach that has the potential to rapidly develop new drugs without the need for animal experiments.
According to Professor Nahmias, "Drug development is a long and expensive endeavor that is defined by multiple failures. The main reason for this failure is that clinical experiments are ultimately based on minimal information gained from animal experiment which often fail to replicate the human response."
The primary animals used in drug development ...
Microchips of the future: Suitable insulators are still missing
2021-03-09
For decades, there has been a trend in microelectronics towards ever smaller and more compact transistors. 2D materials such as graphene are seen as a beacon of hope here: they are the thinnest material layers that can possibly exist, consisting of only one or a few atomic layers. Nevertheless, they can conduct electrical currents - conventional silicon technology, on the other hand, no longer works properly if the layers become too thin.
However, such materials are not used in a vacuum; they have to be combined with suitable insulators - in order to seal them off from unwanted environmental influences, and ...