Corona: Nearly half of the population has already gotten tested
50 weeks BfR Corona Monitor: Interim results shows trends in the perception of the pandemic
2021-03-09
(Press-News.org) According to the current BfR-Corona-Monitor of the German Federal Institute for Risk Assessment (BfR), 43 percent of the respondents have already had themselves tested for the virus. The survey, which has been conducted regularly for almost a year now, documents how the population is dealing with the situation, what they are doing to protect themselves and how they are informing themselves about the current events. "For 50 weeks now, our survey has provided insights into the current situation and its development," says BfR-President Professor Dr. Dr. Andreas Hensel. "Over time, we see that the vast majority of the population is implementing the key protective measures."
BfR-Corona-Monitor as to 2-3 March 2021:
https://www.bfr.bund.de/cm/349/210302-bfr-corona-monitor-en.pdf
Regarding the measures ordered to contain the coronavirus, the current mood is very mixed. For example, 84 percent of the respondents support the cancellation of events, 92 percent think the distance regulations are appropriate, and 91 percent think the same about the mandatory use of masks. For months, these regulations have been quite consistently accepted by the population. Other measures, however, have been losing support over the past few weeks. For example, approval for the closure of shops has dropped to 37 percent - at the beginning of January it was at 61 percent. In the current survey, about half of the respondents approve of the closure of restaurants, and 60 percent approve of the closure of cultural institutions. Similar values were last seen in the surveys at the beginning of December. After that, approval had initially risen.
Proximity to other people is still assumed to be the primary source of infection. Currently, around two-thirds of respondents rate the probability of contracting the disease through proximity to others as high. By comparison, at the beginning of the pandemic about a year ago, this figure was at 81 percent. Overall, it can be seen over time that the transmission of the coronavirus via objects such as door handles or toys is now considered less likely than a year ago. The perception of the possibility of an infection via pets, on the other hand, remains fairly constant. The values vary, with minor outliers, between 6 and 10 percent.
INFORMATION:
What happens next?
The BfR-Corona-Monitor will continue in March. The survey will continue to be carried out every two weeks and will comprise around 1,000 people at a time.
The BfR has published FAQs on the topic of coronavirus:
https://www.bfr.bund.de/en/can_the_new_type_of_coronavirus_be_transmitted_via_food_and_objects_-244090.html
About the BfR-Corona-Monitor
The BfR-Corona-Monitor is a recurring (multi-wave) representative survey of the German population's perception of risks from the novel coronavirus. Every week between 24 March and 26 May 2020, around 500 randomly selected people were asked by telephone about their assessment of the risk of infection and their protective measures, among other things. Since June 2020, the survey is continued every two weeks with about 1,000 respondents each. A summary of the data is regularly published on the homepage of the German Federal Institute for Risk Assessment. More information about the method and sample can be found in publications about the BfR-Corona-Monitor.
About the BfR
The German Federal Institute for Risk Assessment (BfR) is a scientifically independent institution within the portfolio of the Federal Ministry of Food and Agriculture (BMEL) in Germany. It advises the German federal government and German federal states ("Laender") on questions of food, chemical and product safety. The BfR conducts its own research on topics that are closely linked to its assessment tasks.
This text version is a translation of the original German text which is the only legally binding version.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-09
PLYMOUTH MEETING, PA [March 9, 2021] -- New research in the March 2021 issue of JNCCN--Journal of the National Comprehensive Cancer Network from Mass General Hospital Cancer Center, Harvard Medical School, and Dana-Farber Cancer Institute finds muscle mass (quantity) correlated with survival, while muscle radiodensity (quality) was associated with symptom burden, healthcare use, and survival in patients with advanced cancer undergoing an unplanned hospitalization. The researchers also found nearly two-thirds of the patients in that population had significant muscle loss ...
2021-03-09
BUFFALO, N.Y. -- New research from the University at Buffalo suggests that breast cancer patients who drink sugar-sweetened beverages regularly are at increased risk for death from any cause and breast cancer in particular.
Compared to women who never or rarely drank non-diet soda, those who reported drinking non-diet soda five times or more per week had a 62% higher likelihood of dying from any causes, and were 85% more likely to die from breast cancer specifically. The findings were published online ahead of print March 2 in Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers & Prevention, a journal of the American Association for Cancer Research.
Research on soda and breast ...
2021-03-09
Researchers at Uppsala University have developed a digital self-test that trains users to assess news items, images and videos presented on social media. The self-test has also been evaluated in a scientific study, which confirmed the researchers' hypothesis that the tool genuinely improved the students' ability to apply critical thinking to digital sources.
The new tool and the scientific review of it are part of the News Evaluator project to investigate new methods of enhancing young people's capacity for critical awareness of digital sources, a key component of digital literacy.
"As ...
2021-03-09
Philadelphia, March 9, 2021--Combining computational mining of big data with experimental testing in the lab, researchers at Children's Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP) have identified RNA editing events that influence gene expression and, in turn, the phenotypic manifestation of that expression. In analyzing so-called A-to-I RNA editing, in which the adenosine of an RNA molecule is chemically modified into an inosine, the researchers describe how a single nucleotide change by RNA editing can have large downstream effects. The findings were published today in Genome Biology.
"Millions of A-to-I RNA editing sites have been identified across the human transcriptome, but the functions of most RNA editing ...
2021-03-09
If travel to distant stars within an individual's lifetime is going to be possible, a means of faster-than-light propulsion will have to be found. To date, even recent research about superluminal (faster-than-light) transport based on Einstein's theory of general relativity would require vast amounts of hypothetical particles and states of matter that have "exotic" physical properties such as negative energy density. This type of matter either cannot currently be found or cannot be manufactured in viable quantities. In contrast, new research carried out at the University of Göttingen gets around this problem by constructing a new class of hyper-fast 'solitons' ...
2021-03-09
Researchers have demonstrated that a slimy, yet tough, type of biofilm that certain bacteria make for protection and to help them move around can also be used to separate water and oil. The material may be useful for applications such as cleaning contaminated waters.
In the journal Langmuir, North Carolina State University researchers reported the findings of an experiment in which they used a material produced by the bacteria Gluconacetobacter hansenii as a filter to separate water from an oil mixture.
"It's really remarkable to think that these little bugs can make this stuff that is so perfect in many ways," said Lucian Lucia, the study's corresponding author and an associate professor of forest biomaterials and chemistry at NC State.
The biofilm the bacteria make and ...
2021-03-09
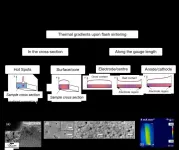
Flash sintering is a ceramic processing technique which uses electric current to intensively heat the ceramic sample internally rather than using only external furnace heating. The process can lower ceramic processing temperatures and durations significantly, enabling ceramics to be co-processed with metals or other materials, and reducing energy use.
However, the process can result in low quality ceramics due to weaknesses caused by inhomogeneities in the microstructure.
The origins of these inhomogeneities caused by thermal gradients in the material during flash sintering have been studied by researchers ...
2021-03-09
Deforestation may cause an initial increase in malaria infections across Southeast Asia before leading to later decreases, a study published today in eLife suggests.
The results may help malaria control programs in the region develop better strategies for eliminating malaria infections and educating residents on how to protect themselves from infection.
Mosquitos spread the malaria parasite to humans causing infections that can be severe and sometimes deadly. In the area along the Mekong river in Southeast Asia, many residents hunt or harvest wood in the surrounding forests, which can increase their risk of infection. Yet recent outbreaks of malaria in the region have also been linked to deforestation.
"As countries in the region focus their malaria control ...
2021-03-09
As the fight against COVID-19 continues, scientists have turned to an unlikely source for a potentially effective treatment: tiny antibodies naturally generated by llamas.
While the world has welcomed the news of multiple vaccines against COVID-19, the search for effective treatments for those who contract the virus is ongoing. Now scientists are looking to what might seem to be an unlikely source: the South American llama.
Researchers are using the ultrabright X-rays of the Advanced Photon Source (APS), a U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) Office of Science User Facility at DOE's Argonne National Laboratory, to help turn naturally generated llama antibodies into potentially effective therapies against ...
2021-03-09
Every 12 minutes, someone in the United States dies of pancreatic cancer, which is often diagnosed late, spreads rapidly and has a five-year survival rate at approximately 10 percent. Treatment may involve radiation, surgery and chemotherapy, though often the cancer becomes resistant to drugs.
Researchers at University of California San Diego School of Medicine and Moores Cancer Center, in collaboration with Sanford-Burnham-Prebys Medical Discovery Institute and Columbia University, demonstrated that a new tumor-penetrating therapy, tested in animal models, may enhance the effects of chemotherapy, reduce metastasis ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Corona: Nearly half of the population has already gotten tested
50 weeks BfR Corona Monitor: Interim results shows trends in the perception of the pandemic