INFORMATION:
About Mayo Clinic
Mayo Clinic is a nonprofit organization committed to innovation in clinical practice, education and research, and providing compassion, expertise and answers to everyone who needs healing. Visit the Mayo Clinic News Network for additional Mayo Clinic news.
Messenger RNA COVID-19 vaccines greatly reduce risk of asymptomatic COVID-19 infection, spread to ot
2021-03-11
(Press-News.org) ROCHESTER, Minn. -- Ten days after receiving a second dose of a messenger RNA, or mRNA, vaccine for COVID-19, patients without COVID-19 symptoms are far less likely to test positive and unknowingly spread COVID-19, compared to patients who have not been vaccinated for COVID-19. The Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna messenger RNA vaccines for COVID-19 are authorized for emergency use in the U.S.
With two doses of a messenger RNA COVID-19 vaccine, people with no symptoms showed an 80% lower adjusted risk of testing positive for COVID-19 after their last dose. Those are the findings of a Mayo Clinic study of vaccinated patients. These finding appear in the journal Clinical Infectious Diseases.
The authors say these findings underscore the efficacy of messenger RNA vaccines for COVID-19 to significantly limit the spread of COVID-19 by people with no symptoms who may unknowingly spread the infection to others.
The researchers retrospectively looked at a cohort of 39,000 patients who underwent pre-procedural molecular screening tests for COVID-19. More than 48,000 screening tests were performed, including 3,000 screening tests on patients who had received at least one dose of a messenger RNA COVID-19 vaccine. These screening tests were part of routine COVID-19 testing prior to treatments not related to COVID-19, such as surgeries and other procedures. Patients in the vaccinated group had received at least one dose of a messenger RNA COVID-19 vaccine.
"We found that those patients without symptoms receiving at least one dose of the first authorized mRNA COVID-19 vaccine, Pfizer-BioNTech, 10 days or more prior to screening were 72% less likely to test positive," says Aaron Tande, M.D., a Mayo Clinic infectious diseases specialist and co-first author of the paper. "Those receiving two doses were 73% less likely, compared to the unvaccinated group."
After adjusting for a range of factors, researchers found an 80% risk reduction of testing positive for COVID-19 among those with two doses of a messenger RNA COVID-19 vaccine.
The study was based on patients receiving screening tests between Dec. 17, 2020, and Feb. 8 at Mayo Clinic in Minnesota and Arizona and at Mayo Clinic Health System in Minnesota and Wisconsin.
Additional authors are Benjamin Pollock, Ph.D., co-first author; Nilay Shah, Ph.D.; Gianrico Farrugia, M.D.; Abinash Virk, M.D.; Melanie Swift, M.D.; Laura Breeher, M.D.; Matthew Binnicker, Ph.D.; and Elie Berbari, M.D. ? all of Mayo Clinic. Funding for the study was provided by Mayo Clinic.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Breast feeding mothers do not transfer COVID through milk
2021-03-11
A study conducted by researchers at the University of Rochester Medical Center (URMC) - in collaboration with several other universities - indicates that breastfeeding women with COVID-19 do not transmit the SARS-CoV-2 virus through their milk, but do confer milk-borne antibodies that are able to neutralize the virus.
The study, "Characterization of SARS-CoV-2 RNA, antibodies, and neutralizing capacity in milk produced by women with COVID-19," published on February 9 in the journal mBio - analyzed 37 milk samples submitted by 18 women diagnosed with COVID-19. None of the milk samples were found to contain ...
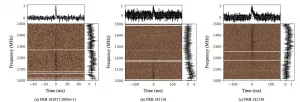
FAST captures distant fast radio bursts from the youth of universe
2021-03-11
Fast radio burst (FRB) is a kind of mysterious radio flashes lasting only a few thousandths of a second. Confirmed to be the cosmological origin in 2016, FRB has the potential to provide insights into a wide range of astrophysical problems.
Dr. NIU Chenhui from the team led by Dr. LI Di and Dr. ZHU Weiwei from National Astronomical Observatories of Chinese Academy of Sciences discovered three new FRBs with high dispersion measure from the massive data of the Five-hundred-meter Aperture Spherical radio Telescope (FAST).
Their findings were published in The Astrophysical Journal Letters on March 3.
The discovery indicated that these three FRBs happened billions of years ago when the ...
Lower risk of brain injury for at-risk infants whose mothers consumed pomegranate juice
2021-03-11
Intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR) is common and concerning, but few therapeutic options exist for pregnant mothers who receive this diagnosis. IUGR is a condition in which a baby in the womb is measuring small for its gestational age, often because of issues with the placenta, resulting in compromised or insufficient transfer of oxygen and nutrients to the growing fetus. The developing fetal brain is particularly vulnerable to these effects. One out of every 10 babies is diagnosed with IUGR, and infants with IUGR are at increased risk of death and neurodevelopmental impairment. ...
Marjoram supports health and weight gain in carps, say biologist from RUDN University
2021-03-11
Biologists from RUDN University suggested adding a marjoram-based supplement to the diet of common carp to support the growth of the fish and improve their resistance to bacterial infections. The results of the study were published in the Fish & Shellfish Immunology journal.
Cyprinus carpio is a type of large omnivore fish that grows 35-40 cm long in three to five years. 4 mln tons of carps were bred in aquacultural farms in 2010. Such farms protect natural populations of Cyprinus carpio while at the same time satisfying the market demand. However, as farmers strive for higher productivity, aquacultural farms become more and more crowded which leads to the lack of nutrients and harms the health of the fish. A team of veterinarians ...
Study suggests healthy ecosystems are vital in reducing risk of future deadly pandemics
2021-03-11
CABI scientist Dr Arne Witt has shared his expertise on invasive alien plant species as part of a new paper which argues that healthy ecosystems are vital in reducing the risk of future pandemics - such as coronaviruses (including COVID-19) - that threaten human health.
The paper - 'Land use-induced spillover: priority actions for protected and conserved area managers' - is published as part of a special issue by the journal PARKS entitled 'COVID-19 and Protected Areas: Essential Reading for a World Haunted by a Pandemic.'
Lead author Dr Jamie K. Reaser - along with a team of researchers from institutions including the African Wildlife Foundation, the University ...
Does your child have MIS-C, COVID-19 or Kawasaki disease?
2021-03-11
Exposure to SARS-Co-V2, the virus that causes COVID-19, can put otherwise healthy children and adolescents at risk for Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children (MIS-C), a rare but possibly life-threatening pediatric condition that can cause severe inflammation in organs like the heart, brain, lungs, kidneys and gastrointestinal system.
Diagnosing and treating MIS-C -- which has affected 2,600 children since May 2020 and is known to occur in children who have tested positive for SARS-Co-V2 or been exposed to someone with COVID-19 -- is difficult because respiratory and gastrointestinal symptoms can be similar to severe COVID-19. Other features of MIS-C are very similar to Kawasaki disease, which causes inflammation ...
Rare earths outside China: FAU researchers identify new deposits
2021-03-11
Rare earth elements are the gold of the 21st century: rare and highly prized all over the world. Most known and economically viable sources of rare earths are located in China, where more than 80 percent of them are refined. This has resulted in a near monopoly situation, with China dominating international trade, particularly in heavy rare earths. Geologists and materials scientists at FAU have now discovered a new way of finding new and previously unknown deposits of rare earths, or rare earth metals, worldwide. They have published the findings of their study in the journal Geology.
Rare earth metals are irreplaceable for manufacturing advanced high-tech industrial products due to their luminescent and ...
Wing tags severely impair flight in African Cape Vultures
2021-03-11
Conservationists who apply wing tags for identifying Cape Vultures--a species of African vulture that is vulnerable to extinction--are putting the birds' lives further at risk, a new movement ecology study has shown. Researchers from the Max Planck Institute of Animal Behavior in Germany and VulPro NPC in South Africa have demonstrated that Cape Vultures fitted with tags on their wings travelled shorter distances and flew slower than those fitted with bands around their legs. The research emphasises the importance of investigating the effects that tagging methods can have on the behaviour and conservation of species, prompting a shift towards the ...
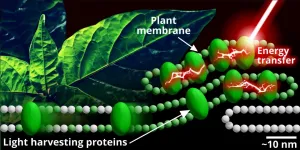
Starting small to answer the big questions about photosynthesis
2021-03-11
New scientific techniques are revealing the intricate role that proteins play in photosynthesis.
Despite being discovered almost 300 years ago, photosynthesis still holds many unanswered questions for science, particularly the way that proteins organise themselves to convert sunlight into chemical energy and at the same time, protect plants from too much sunlight.
Now a collaboration between researchers at the University of Leeds and Kobe University in Japan is developing a novel approach to the investigation of photosynthesis.
Using hybrid membranes that mimic natural plant membranes and advanced microscopes, they are opening photosynthesis to nanoscale investigation - the study of life at less than one billionth ...
Female snowy plovers are no bad mothers
2021-03-11
In snowy plovers, females have overcome traditional family stereotypes. They often abandon the family to begin a clutch with a new partner whereas the males continue to care for their young until they are independent. An international team led by scientists from the Max Planck Institute for Ornithology in Seewiesen, Germany, has now investigated the decision-making process that determines the duration of parental care by females. They found that offspring desertion often occurs either under poor environmental conditions, when chicks die despite being cared for by both parents, ...