Double-duty catalyst generates hydrogen fuel while cleaning up wastewater
2021-03-17
(Press-News.org) Hydrogen is a pollution-free energy source when it's extracted from water using sunlight instead of fossil fuels. But current strategies for "splitting" or breaking apart water molecules with catalysts and light require the introduction of chemical additives to expedite the process. Now, researchers reporting in ACS ES&T Engineering have developed a catalyst that destroys medications and other compounds already present in wastewater to generate hydrogen fuel, getting rid of a contaminant while producing something useful.
Harnessing the sun's energy to split water to make hydrogen fuel is a promising renewable resource, but it is a slow process even when catalysts are used to speed it along. In some cases, alcohols or sugars are added to boost the rate of hydrogen production, but these chemicals are destroyed as hydrogen is generated, meaning the approach is not renewable. In a separate strategy, researchers have tried using contaminants in wastewater to enhance hydrogen fuel generation. While titanium-based catalysts worked for both removing contaminants and generating hydrogen, the efficiencies were lower than expected for both steps because of their overlapping reaction sites. One way to reduce such interferences is to make catalysts by fusing together different conductive metals, thus creating separate places for reactions to occur. So, Chuanhao Li and colleagues wanted to combine cobalt oxide and titanium dioxide to create a dual-functioning catalyst that would break down common drugs in wastewater while also efficiently converting water into hydrogen for fuel.
To make the catalyst, the researchers coated nanoscale titanium dioxide crystals with a thin layer of cobalt oxide. Initial tests showed that this material didn't produce much hydrogen, so as a next step, the team spiked this dual catalyst with 1% by weight of platinum nanoparticles -- an efficient though expensive catalyst for generating hydrogen. In the presence of simulated sunlight, the platinum-impregnated catalyst degraded two antibiotics and produced substantial amounts of hydrogen. Finally, the team tested their product on real wastewater, water from a river in China and deionized water samples. Under simulated sunlight, the catalyst stimulated hydrogen production in all three samples. The greatest amount of hydrogen was obtained from the wastewater sample. The researchers say their catalyst could be a sustainable wastewater treatment option by generating hydrogen fuel at the same time.
INFORMATION:
The authors acknowledge funding from National Natural Science Foundation of China, Science and Technology Planning Project of Guangdong Province, Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities from Sun Yat-sen University and the Research Fund Program of Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Environmental Pollution Control and Remediation Technology.
The abstract that accompanies this paper is available here.
For more of the latest research news, register for our upcoming meeting, ACS Spring 2021. Journalists and public information officers are encouraged to apply for complimentary press registration by emailing us at newsroom@acs.org.
The American Chemical Society (ACS) is a nonprofit organization chartered by the U.S. Congress. ACS' mission is to advance the broader chemistry enterprise and its practitioners for the benefit of Earth and its people. The Society is a global leader in providing access to chemistry-related information and research through its multiple research solutions, peer-reviewed journals, scientific conferences, eBooks and weekly news periodical Chemical & Engineering News. ACS journals are among the most cited, most trusted and most read within the scientific literature; however, ACS itself does not conduct chemical research. As a specialist in scientific information solutions (including SciFinder® and STN®), its CAS division powers global research, discovery and innovation. ACS' main offices are in Washington, D.C., and Columbus, Ohio.
To automatically receive news releases from the American Chemical Society, contact newsroom@acs.org.
Follow us: Twitter | Facebook
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-17
NEW YORK (March 17, 2021) -- High speed air dryers not only leave more contamination on poorly washed hands compared to paper towels, but during hand drying, they can also spread germs onto clothing, ultimately transferring more bacteria to other surfaces, according to a study published today in Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology, the journal of the Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America.
Past research has shown recommended handwashing practices for healthcare workers are often not followed with average adherence of 40%. To better understand the impact of hand drying in hand hygiene, researchers conducted an experiment to learn the role of different hand drying methods in spreading germs from poorly washed hands beyond the restroom.
For ...
2021-03-17
Scientists in Japan have observed, and interfered with, the ultrafast motion of electron movement inside of a Xenon atom using the coherent pairs of short light waves in synchrotron radiation. Xenon, consisting of a nucleus surrounded by five nested shells containing a total of 54 electrons, is used in flash lamps, and it burns bright and fast. The luminescent electrons move there on a time scale of one billionth of a second. The fast electron movement is however six orders of magnitude slower than that the scientists observed. Using the synchrotron facility at Institute for Molecular Science, they tracked the electron movement in relaxation to shed energy by dropping from an outer shell to an inner shell. The process happens at a timescale of femtoseconds, ...
2021-03-17
Researchers at Lund University in Sweden have designed a new bioink which allows small human-sized airways to be 3D-bioprinted with the help of patient cells for the first time. The 3D-printed constructs are biocompatible and support new blood vessel growth into the transplanted material. This is an important first step towards 3D-printing organs. The new study has been published in Advanced Materials.
Chronic lung diseases are the third leading cause of death worldwide with an EU cost of more than €380 billion annually. For many chronic diseases ...
2021-03-17
The promotion of psychosocial health among individuals, groups, and society is an increasingly important subject in the field of public health. Psychosocial health is a complex interaction between the psyche of an individual and the social environment in which that individual lives. Promoting psychosocial health is often challenging and complex for health care professionals. Therefore, an important question of public health significance is: "how can we address and improve the psychosocial health of individuals, groups, as well as society in general?"
An interdisciplinary team of specialists ...
2021-03-17
The use of artificial light at night around the world has increased enormously in recent years, causing adverse effects on the survival and reproduction of nocturnal organisms. Artificial light at night interferes with vital ecological processes such as the nighttime pollination of plants by nocturnal insects, which could have consequences for agricultural crop yields and reproduction of wild plants.
Scientists from the University of Zurich and Agroscope have now demonstrated for the first time that artificial light at night also adversely affects insects' pollination behavior during the daytime. In an experiment, they used commercial ...
2021-03-17
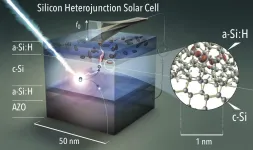
Silicon solar cells are now so cheap and efficient that they can generate electricity at prices of less than 2 cent/kWh. The most efficient silicon solar cells today are made with less than 10 nanometres thin selective amorphous silicon (a-Si:H) contact layers, which are responsible for separating the light-generated charges . Efficiencies of over 24% are achieved at HZB with such silicon heterojunction solar cells and are also part of a tandem solar cell that lead to a recently reported efficiency record of 29.15 % (A. Al-Ashouri, et al. Science 370, (2020)). The current world record from Japan for a ...
2021-03-17
Tropical Cyclone (TC) is an intense atmospheric vortex with a warm core and low pressure structure, and generates over the tropical or subtropical warm ocean. The problem of TC genesis has been paid great attention by scientists since the 1950s, but due to the lack of the observation data over sea, this problem has become the most difficult and challenging topic in the researches of TC.
Cumulus convections are considered to be the most basic element in the TC generation process. The formation of TC in the Northwest Pacific is often associated with the mesoscale convective system (MCS) or mesoscale convective complex (MCC). Meanwhile, in the stratiform ...
2021-03-17
Not least because of the COVID-19 pandemic, conspiracy theories are more topical than ever. They are reported and discussed in almost all media and communication channels. But what influence do they have on our behavior? Scientists led by behavioral economist Loukas Balafoutas investigated this question in a recently published study. The result: We don't need to believe in conspiracy theories for them to have an impact on us. Merely being confronted with them suffices.
Previous studies have shown that beliefs in conspiracy theories have an influence on the behavior of their adherents. For example, they lead to lower voter turnout or a lower willingness to get vaccinated. For years now, conspiracy theories have been ...
2021-03-17
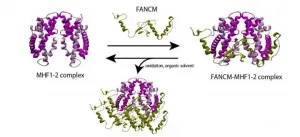
One of the most vital functions performed by the cells in our body is DNA repair, a task so crucial to our well-being that failing to execute it can lead to consequences as dreadful as cancer. The process of DNA repair involves a complex interplay between several gene pathways and proteins. One such pathway is the "Fanconi anemia (FA) pathway," whose genes participate in DNA repair. FANCM, a component of this pathway, is tasked with the elimination of harmful DNA "inter-strand cross-links," and interacts with another component called MHF in order to function. The importance of the FANCM-MHF complex is well-documented: its loss can result in chromosomal ...
2021-03-17
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) infections are among the major global health problems. Particularly problematic is the high number of chronic courses of the disease, causing the deaths of more than 800.000 people globally every year. So far, there is no therapy to cure the condition. "With the discovery of a new hepatitis B virus in donkeys and zebras capable of causing prolonged infections, we now have the opportunity for a better understanding of the chronic course of the disease and thus also for mitigation or prevention of severe clinical consequences," explains Prof. Dr. Jan Felix Drexler, DZIF ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Double-duty catalyst generates hydrogen fuel while cleaning up wastewater