(Press-News.org) A sustainable, powerful micro-supercapacitor may be on the horizon, thanks to an international collaboration of researchers from Penn State and the University of Electronic Science and Technology of China. Until now, the high-capacity, fast-charging energy storage devices have been limited by the composition of their electrodes -- the connections responsible for managing the flow of electrons during charging and dispensing energy. Now, researchers have developed a better material to improve connectivity while maintaining recyclability and low cost.
They published their results on Feb. 8 in the Journal of Materials Chemistry A.
"The supercapacitor is a very powerful, energy-dense device with a fast-charging rate, in contrast to the typical battery -- but can we make it more powerful, faster and with a really high retention cycle?" asked Jia Zhu, corresponding author and doctoral student conducting research in the laboratory of Huanyu "Larry" Cheng, Dorothy Quiggle Career Development Professor in Penn State's Department of Engineering Science and Mechanics.
Zhu worked under Cheng's mentorship to explore the connections in a micro-supercapacitor, which they use in their research on small, wearable sensors to monitor vital signs and more. Cobalt oxide, an abundant, inexpensive material that has a theoretically high capacity to quickly transfer energy charges, typically makes up the electrodes. However, the materials that mix with cobalt oxide to make an electrode can react poorly, resulting in a much lower energy capacity than theoretically possible.
The researchers ran simulations of materials from an atomic library to see if adding another material -- also called doping -- could amplify the desired characteristics of cobalt oxide as an electrode by providing extra electrons while minimizing, or entirely removing, the negative effects. They modeled various material species and levels to see how they would interact with cobalt oxide.
"We screened possible materials but found many that might work were too expensive or toxic, so we selected tin," Zhu said. "Tin is widely available at a low cost, and it's not harmful to the environment."
In the simulations, the researchers found that by partially substituting some of the cobalt for tin and binding the material to a commercially available graphene film -- a single-atom thick material that supports electronic materials without changing their properties -- they could fabricate what they called a low-cost, easy-to-develop electrode.
Once the simulations were completed, the team in China conducted experiments to see if the simulation could be actualized.
"The experimental results verified a significantly increased conductivity of the cobalt oxide structure after partial substitution by tin," Zhu said. "The developed device is expected to have promising practical applications as the next-generation energy storage device."
Next, Zhu and Cheng plan to use their own version of graphene film -- a porous foam created by partially cutting and then breaking the material with lasers -- to fabricate a flexible capacitor to allow for easy and fast conductivity.
"The supercapacitor is one key component, but we're also interested in combining with other mechanisms to serve as both an energy harvester and a sensor," Cheng said. "Our goal is to put a lot of functions into a simple, self-powered device."
INFORMATION:
Co-authors on this paper include Yunjian Chen, Ni Wang, Xianzhong Tang and Wencheng Hu, all affiliated with the School of Materials and Energy, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China; and Sridhar Komarneni, Materials Research Institute (MRI) and Department of Ecosystem Science and Management, Penn State. Wang is also affiliated with MRI.
The National Natural Science Foundation of China supported this work.
An international collaboration between Great Ormond Street Hospital, the UCL GOS Institute for Child Health and Harvard Medical School has shown that the beneficial effects of gene therapy can be seen decades after the transplanted blood stem cells has been cleared by the body.
The research team monitored five patients who were successfully cured of SCID-X1 using gene therapy at GOSH. For 3-18 years patients' blood was regularly analysed to detect which cell types and biomarker chemicals were present in their blood. The results showed that even though the stem cells transplanted as part of gene therapy had been cleared by the patients, the all-important corrected immune cells, called T-cells, were still forming.
Gene therapy works by first removing ...
In researching the causes and potential treatments for degenerative conditions such as Alzheimer's or Parkinson's disease, neuroscientists frequently struggle to accurately identify cells needed to understand brain activity that gives rise to behavior changes such as declining memory or impaired balance and tremors.
A multidisciplinary team of Georgia Institute of Technology neuroscience researchers, borrowing from existing tools such as graphical models, have uncovered a better way to identify cells and understand the mechanisms of the diseases, potentially leading to better understanding, diagnosis, and treatment.
Their research findings were reported Feb. 24 in the journal eLife. The research was supported by the National Institutes of ...
Hydrogen is a pollution-free energy source when it's extracted from water using sunlight instead of fossil fuels. But current strategies for "splitting" or breaking apart water molecules with catalysts and light require the introduction of chemical additives to expedite the process. Now, researchers reporting in ACS ES&T Engineering have developed a catalyst that destroys medications and other compounds already present in wastewater to generate hydrogen fuel, getting rid of a contaminant while producing something useful.
Harnessing the sun's energy to split water to make hydrogen fuel is a promising renewable resource, but it is a slow process even when catalysts are used to speed it along. In some cases, alcohols or sugars are added to boost the rate of hydrogen production, ...
NEW YORK (March 17, 2021) -- High speed air dryers not only leave more contamination on poorly washed hands compared to paper towels, but during hand drying, they can also spread germs onto clothing, ultimately transferring more bacteria to other surfaces, according to a study published today in Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology, the journal of the Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America.
Past research has shown recommended handwashing practices for healthcare workers are often not followed with average adherence of 40%. To better understand the impact of hand drying in hand hygiene, researchers conducted an experiment to learn the role of different hand drying methods in spreading germs from poorly washed hands beyond the restroom.
For ...
Scientists in Japan have observed, and interfered with, the ultrafast motion of electron movement inside of a Xenon atom using the coherent pairs of short light waves in synchrotron radiation. Xenon, consisting of a nucleus surrounded by five nested shells containing a total of 54 electrons, is used in flash lamps, and it burns bright and fast. The luminescent electrons move there on a time scale of one billionth of a second. The fast electron movement is however six orders of magnitude slower than that the scientists observed. Using the synchrotron facility at Institute for Molecular Science, they tracked the electron movement in relaxation to shed energy by dropping from an outer shell to an inner shell. The process happens at a timescale of femtoseconds, ...
Researchers at Lund University in Sweden have designed a new bioink which allows small human-sized airways to be 3D-bioprinted with the help of patient cells for the first time. The 3D-printed constructs are biocompatible and support new blood vessel growth into the transplanted material. This is an important first step towards 3D-printing organs. The new study has been published in Advanced Materials.
Chronic lung diseases are the third leading cause of death worldwide with an EU cost of more than €380 billion annually. For many chronic diseases ...
The promotion of psychosocial health among individuals, groups, and society is an increasingly important subject in the field of public health. Psychosocial health is a complex interaction between the psyche of an individual and the social environment in which that individual lives. Promoting psychosocial health is often challenging and complex for health care professionals. Therefore, an important question of public health significance is: "how can we address and improve the psychosocial health of individuals, groups, as well as society in general?"
An interdisciplinary team of specialists ...
The use of artificial light at night around the world has increased enormously in recent years, causing adverse effects on the survival and reproduction of nocturnal organisms. Artificial light at night interferes with vital ecological processes such as the nighttime pollination of plants by nocturnal insects, which could have consequences for agricultural crop yields and reproduction of wild plants.
Scientists from the University of Zurich and Agroscope have now demonstrated for the first time that artificial light at night also adversely affects insects' pollination behavior during the daytime. In an experiment, they used commercial ...
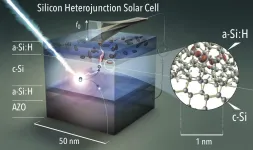
Silicon solar cells are now so cheap and efficient that they can generate electricity at prices of less than 2 cent/kWh. The most efficient silicon solar cells today are made with less than 10 nanometres thin selective amorphous silicon (a-Si:H) contact layers, which are responsible for separating the light-generated charges . Efficiencies of over 24% are achieved at HZB with such silicon heterojunction solar cells and are also part of a tandem solar cell that lead to a recently reported efficiency record of 29.15 % (A. Al-Ashouri, et al. Science 370, (2020)). The current world record from Japan for a ...
Tropical Cyclone (TC) is an intense atmospheric vortex with a warm core and low pressure structure, and generates over the tropical or subtropical warm ocean. The problem of TC genesis has been paid great attention by scientists since the 1950s, but due to the lack of the observation data over sea, this problem has become the most difficult and challenging topic in the researches of TC.
Cumulus convections are considered to be the most basic element in the TC generation process. The formation of TC in the Northwest Pacific is often associated with the mesoscale convective system (MCS) or mesoscale convective complex (MCC). Meanwhile, in the stratiform ...