'Germ Hunters' discover rare disease in rural Alberta
Fungal infection linked to bats has made the province home, according to researchers with Alberta Precision Labs and U of A.
2021-03-18
(Press-News.org) A rare pulmonary disease that is linked to bats has made Alberta home, according to new research led by provincial lab scientists.
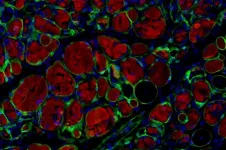
Infectious disease experts at Alberta Precision Laboratories (APL) and the University of Alberta have confirmed that histoplasmosis - a fungal infection transmitted through bat and bird droppings - is now found in Alberta. Their study extends the known range of the disease much further northwest from its traditional home in the central United States and parts of southern Ontario and Quebec.
"We were surprised at how many cases were locally acquired, as histoplasmosis has always been considered a travel-related infection," said Dr. Tanis Dingle, APL's lead clinical microbiologist for fungal diseases and an assistant professor in the U of A's Faculty of Medicine & Dentistry. "We now know that it is definitely living in Alberta and has the potential to infect people who come in contact with it."
The fungus can be present in contaminated dust particles, and when inhaled, patients experience respiratory infections with flu-like symptoms, including cough, fever, chills and headache. Cases are typically related to individuals who have come in contact with bat or bird droppings in old homes, churches, construction sites and parks.
Among 45 confirmed cases of histoplasmosis in Alberta between 2011 and 2018, the researchers used epidemiologic data and genetic analysis to determine that 15 of the cases were locally-acquired. The cases were primarily found in rural areas in central Alberta including Sundre, Stettler and county, Stony Plain and Spruce Grove. Previously, the geographic range of the fungus was not thought to expand further northwest than Minnesota, some 2000 km away. The results of the study were published this month in the medical journal The Lancet Microbe. In addition, early looks at the study led scientists at the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention to include the region in newly drawn maps of areas where the disease is known to occur.
"Knowing that histoplasmosis is here can help improve the diagnosis and treatment of patients who have no history of travel to the traditional risk areas," said Dr. Ilan Schwartz, assistant professor, division of infectious diseases, U of A. "Histoplasmosis can be a challenging disease to diagnosis and to treat, and patients often spend months before the correct diagnosis is made. Awareness that the disease is here is an essential first step for doctors to be able to consider the diagnosis and order the appropriate tests."
The researchers are also exploring whether climate change could be a factor in the spread of histoplasmosis to new geographies. In Alberta, increasing temperatures and decreasing precipitation have been documented over the past several decades, which might have resulted in more favorable conditions for Histoplasma to live in Alberta soils. The disease can survive in soil temperatures ranging from ?18°C to 37°C, the lower end of this range being common in Alberta winters.
The research team hopes to continue their work by further investigating soil samples to determine other areas in Alberta where the disease may be present.
INFORMATION:
The study, "Histoplasmosis acquired in Alberta, Canada: an epidemiological and genomic study," was published in the medical journal The Lancet Microbe.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-18
An international, open-label Phase 3 study, co-led by Susanna McColley, MD, from Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children's Hospital of Chicago, found that a regimen of three drugs (elexacaftor/tezacaftor/ivacaftor) that targets the genetic cause of cystic fibrosis was safe and effective in 6-11-year-olds with at least one copy of F508del mutation in the CFTR gene, which is estimated to represent almost 90 percent of the cystic fibrosis population in the United States.
For children in this age group who have only one copy of F508del mutation - or about 40 percent of patients with cystic fibrosis ...
2021-03-18
A UCLA-led research team has identified a chemical cocktail that enables the production of large numbers of muscle stem cells, which can self-renew and give rise to all types of skeletal muscle cells.
The advance could lead to the development of stem cell-based therapies for muscle loss or damage due to injury, age or disease. The research was published in Nature Biomedical Engineering.
Muscle stem cells are responsible for muscle growth, repair and regeneration following injury throughout a person's life. In fully grown adults, muscle stem cells are quiescent -- they remain inactive until they are called to respond to injury by self-replicating and creating all of the cell types necessary to repair damaged tissue.
But that regenerative capacity decreases as people ...
2021-03-18
Researchers from Skoltech were part of a research consortium studying a case of vertical COVID-19 transmission from mother to her unborn child that resulted in major complications in the pregnancy, premature birth and death of the child. The consortium used a Skoltech-developed proteomics method to verify the diagnosis. The paper was published in the journal Viruses.
The effects of SARS-CoV-2, the novel coronavirus, on maternal and perinatal outcomes are poorly understood due to limited data and research in pregnant women with COVID-19. There is some evidence suggesting vertical transmission from mother to fetus during pregnancy is possible, as, for instance, in China, immunoglobulin ...
2021-03-18
Dogs infected with the Leishmania parasite smell more attractive to female sand flies than males, say researchers.
The study published in PLOS Pathogens is led by Professor Gordon Hamilton of Lancaster University.
In Brazil, the parasite Leishmania infantum is transmitted by the bite of infected female Lutzomyia longipalpis sand flies.
Globally over 350 million people are at risk of leishmaniasis, with up to 300,000 new cases annually. In Brazil alone there are approximately 4,500 deaths each year from the visceral form of the disease and children under 15 years old are more likely to be affected.
Leishmania parasites ...
2021-03-18
WASHINGTON -- Even as vaccines are becoming more readily available in the U.S., protecting against the asymptomatic and pre-symptomatic spread of the virus (SARS-CoV-2) that causes COVID-19 is key to ending the pandemic, say two Georgetown infectious disease experts.
In their Perspective, " END ...
2021-03-18
CAMBRIDGE, MA -- Much of the carbon in space is believed to exist in the form of large molecules called polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs). Since the 1980s, circumstantial evidence has indicated that these molecules are abundant in space, but they have not been directly observed.
Now, a team of researchers led by MIT Assistant Professor Brett McGuire has identified two distinctive PAHs in a patch of space called the Taurus Molecular Cloud (TMC-1). PAHs were believed to form efficiently only at high temperatures -- on Earth, they occur as byproducts of burning fossil fuels, and they're also found in char marks on grilled ...
2021-03-18
One of great mysteries of human biology is how a single cell can give rise to the 37 trillion cells contained in the average body, each with its own specialized role. Researchers at Yale University and the Mayo Clinic have devised a way to recreate the earliest stages of cellular development that gives rise to such an amazing diversity of cell types.
Using skin cells harvested from two living humans, researchers in the lab of Yale's Flora Vaccarino were able to track their cellular lineage by identifying tiny variations or mutations contained within the genomes of those cells.
These "somatic" or non-inherited mutations are generated at each cell division during a human's development. The percentage of cells bearing the traces of any ...
2021-03-18
The small intestine is ground zero for survival of animals. It is responsible for absorbing the nutrients crucial to life and it wards off toxic chemicals and life-threatening bacteria.
In a new study published March 18 in the journal Science, Yale researchers report the critical role played by the gut's immune system in these key processes. The immune system, they found, not only defends against pathogens but regulates which nutrients are taken in.
The findings may provide insights into origins of metabolic disease and malnutrition that is common in ...
2021-03-18
93 million years ago, bizarre, winged sharks swam in the waters of the Gulf of Mexico. This newly described fossil species, called Aquilolamna milarcae, has allowed its discoverers to erect a new family. Like manta rays, these 'eagle sharks' are characterised by extremely long and thin pectoral fins reminiscent of wings. The specimen studied was 1.65 metres long and had a span of 1.90 metres.
Aquilolamna milarcae had a caudal fin with a well-developed superior lobe, typical of most pelagic sharks, such as whale sharks and tiger sharks. Thus, its anatomical features thus ...
2021-03-18
It's not just how hot the fires burn - it's also where they burn that matters. During the recent extreme fire season in Australia, which began in 2019 and burned into 2020, millions of tons of smoke particles were released into the atmosphere. Most of those particles followed a typical pattern, settling to the ground after a day or week; yet the ones created in fires burning in one corner of the country managed to blanket the entire Southern hemisphere for months. A pair of Israeli scientists managed to track puzzling January and February 2020 spikes in a measure of particle-laden haze to those fires, and then, in a paper recently published in Science, they ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] 'Germ Hunters' discover rare disease in rural Alberta
Fungal infection linked to bats has made the province home, according to researchers with Alberta Precision Labs and U of A.