(Press-News.org) Politicians and business leaders often make claims about why certain sectors in the economy are shrinking, such as the decline in U.S. manufacturing is due to robotics or trade with China. Such assessments are flawed, as the sectoral composition of the economy is mostly driven by preferences and not by productivity, according to a recent study that models this long-run structural change in the economy. As consumers become richer, they spend more on services such as health and education whose demand is much more income elastic, and less on agriculture and manufactured goods. Until now, productivity has often been considered at least as important, if not more, than preferences, in shaping the sectoral composition of the economy. The results are published in Econometrica.
"The reason why we spend a smaller share of our income in manufacturing goods and more in services is not because somebody outside the US is producing manufacturing for us, or because manufacturing goods are becoming cheaper, it's because we want to consume more services as we become richer," explains study co-author Diego Comin, a professor of economics at Dartmouth. "This is a sign of wealth, as opposed to a sign of a trade policy or trade competition, or productivity growth in a certain sector. It's easy to assume that changes in the economy are due to something external to us like trade or technology. Yet, people may not realize the consequences our consumption patterns have on the economy."
To examine the underlying factors that drive the composition of the economy, researchers from Dartmouth, Boston College and Northwestern University used household data from the U.S. and India, and country-level data for 39 countries from the post-war period, from 1970 to 2005. They grouped household data into three categories: agriculture (products from crops or animals), manufacturing (goods that you can touch) and services for which no products are transferred.
The findings revealed that as countries become richer, their expenditures moved towards services and move away from agriculture and manufacturing smoothly over very long periods of time, rather than shifting abruptly from one sector to the next once a certain income threshold is crossed, as other researchers have hypothesized. Because the impact of income on the sectoral composition of the economy does not wind down, income and preferences play a larger role than productivity in affecting the sectoral composition of the economy. As part of the analysis, the researchers created a mathematical model consistent with this observation.
Approximately 80% of the U.S. economy is comprised of services according to the U.S. Bureau of Economic Analysis. Services include: accommodation, arts, business, education, entertainment, financial, government, health, information, insurance, recreation, technology, telecommunication, transportation, and more. "When the economy experiences a decline in manufacturing, this is a reflection of consumers wanting to buy less manufactured goods and spend more on services," says Comin. "It's part of our preferences. As you make more money, do you want to buy a new refrigerator or help pay for your child's college education? A new fridge or other consumer product is likely to be a small share of expenditure."
The researchers found that the model applies to both data on a household level and country level. They tested their model against others and found that it fits the data better than others because it captured well the empirical observation that the impact of income on consumption of services vs. manufacturing is stable over very long periods of time.
"Our results demonstrate that once preferences are modelled correctly, they account for over 90% of the sectoral transformation of a broad set of economies, including the U.S.," explains Comin.
INFORMATION:
Comin is available for comment at: diego.comin@dartmouth.edu.
With the offshore wind industry expanding in the United States and elsewhere, a new study raises questions about how the noise from impact pile driving to install turbine supports can affect feeding behaviors of longfin squid, a commercially and ecologically important cephalopod.
The research, conducted by scientists from the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) and other institutions, is believed to be the first to demonstrate that anthropogenic noise prompts changes in cephalopod feeding behaviors.
"The whole reason we are doing this study is because we are concerned about how construction from offshore wind farms and the sounds associated with that are going to affect important fisheries species, one ...
A considerably higher dose of the anti-tuberculosis drug rifampicin is safe and can also lead to a shorter treatment for tuberculosis and less resistance. This is what researchers from Radboud university medical center in Nijmegen, the Netherlands, write in a recent publication. With this they complete a year-long search for the right dosing of an old drug against tuberculosis that appears to be the key drug.
Tuberculosis is a deadly, pertinacious bacterial infectious disease that affects nine million people worldwide each year, mainly in countries in low and middle income countries. For over a million, ...
Northwestern engineering researchers have demonstrated a new approach to chemical catalysis that results in high propylene yields using less energy. The findings could support more energy-efficient production processes for many plastics.
One of the highest volume chemical products, more than $100 billion worth of propylene is produced each year and used primarily to produce polypropylene for a variety of materials, from injection moldings in car parts to consumer products. Producing propylene is also energy intensive, requiring temperatures around 800 degrees Celsius to convert propane gas to propylene.
One technique, called oxidative dehydrogenation, ...
A researcher from Skoltech has filled in the gaps connecting quantum simulators with more traditional quantum computers, discovering a new computationally universal model of quantum computation, the variational model. The paper was published as a Letter in the journal Physical Review A. The work made the Editors' Suggestion list.
A quantum simulator is built to share properties with a target quantum system we wish to understand. Early quantum simulators were "dedicated" - that means they could not be programmed, tuned or adjusted and so could mimic one or very few target systems. Modern quantum simulators enable some control over their settings, offering more possibilities.
In contrast to quantum simulators, the long-promised quantum computer is a fully programmable quantum system. While ...
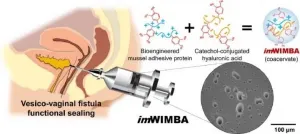
A Korean research team has recently developed an innovative vesico-vaginal fistula treatment method using the mussel adhesive protein (MAP) that can effectively seal fistulas in organs even when exposed to urine.
Professor Hyung Joon Cha, Dr. Hyo Jeong Kim (currently at Korea Research Institute of Chemical Technology), and Dr. Tae Yoon Park of POSTECH's Department of Chemical Engineering with Professor Seok Ho Kang of the Department of Urology at Korea University School of Medicine and Professor Jong Hyun Pyun of the Department of Urology at Kangbuk Samsung Hospital have together improved the underwater adhesive using mussel protein and applied it to a pig model that simulated a vesico-vaginal fistula. ...
Osaka, Japan - Scientists from the Graduate School of Science at Osaka University created superabsorbent polymer (SAP) microparticles that self-assemble into structures that can be modified by adjusting the proportion of particle type. This research may lead to new tunable biomimetic "smart materials" that can sense and respond to specific chemicals.
Biological molecules in living organisms have a remarkable ability to form self-assembled structures when triggered by an external molecule. This has led scientists to try to create other "smart materials" that respond to their environment. Now, a team of researchers at Osaka University has come up with a tunable system involving poly(sodium acrylate) microparticles that can have one of two types of chemical ...
The white paper, published today (March 22) by REPHRAIN, the National Research Centre on Privacy, Harm Reduction and Adversarial Influence Online in collaboration with the Dutch National Police, offers a solution to big data problems that tend to hamper police probes into this type of law-breaking.
The practice of attribution - who did what - is becoming increasingly complex as organised crimes incorporate deception, deletion and encryption in today's Information Age. Even when law enforcement are able to retrieve evidence via digital forensics, the complexities of the collected data mean it cannot be easily processed into factual police reports. ...
One prospective source of renewable energy is hydrogen gas produced from water with the aid of sunlight. Researchers at Linköping University, Sweden, have developed a material, nanoporous cubic silicon carbide, that exhibits promising properties to capture solar energy and split water for hydrogen gas production. The study has been published in the journal ACS Nano.
"New sustainable energy systems are needed to meet global energy and environmental challenges, such as increasing carbon dioxide emissions and climate change", says Jianwu Sun, senior lecturer in the ...
A lot of the attention around "pandemic pets" has focused on families with children getting a cat, dog or other pet in 2020, during a time when many people were learning or working from home.
But a new poll shows that older adults also got in on the trend.
According to the National Poll on Healthy Aging, 10% of all people between the ages of 50 and 80 got a new pet between March 2020 and January 2021.
The percentage was indeed higher - 16% -- among the people in this age range who have at least one child or teen living with them. But the vast majority of people between the ages of 50 and 80 don't live with someone under age 18 -- and nearly 9% of them also got a pet during the pandemic.
All told, 59% of people age 50 to 80 who completed the poll in January 2021 are pet owners. ...
The Covid-19 pandemic severely impacted the mental health of young people, with increased levels of clinical depression being identified, a new study published in the journal Psychiatry Research reports. A decrease in alcohol consumption was also identified amongst young people during the pandemic.
During this unique study researchers from the University of Surrey surveyed 259 young people pre- pandemic (autumn 2019) and in the midst of initial lockdown measures (May/June 2020) on their levels of depression, anxiety, wellbeing, alcohol use and sleep quality.
Researchers found evidence of a substantial impact on the mental health of these young adults due ...