A simple laser for quantum-like classical light
2021-03-23
(Press-News.org) Tailoring light is much like tailoring cloth, cutting and snipping to turn a bland fabric into one with some desired pattern. In the case of light, the tailoring is usually done in the spatial degrees of freedom, such as its amplitude and phase (the "pattern" of light), and its polarization, while the cutting and snipping might be control with spatial light modulators and the like. This burgeoning field is known as structured light, and is pushing the limits in what we can do with light, enabling us to see smaller, focus tighter, image with wider fields of view, probe with fewer photons, and to pack information into light for new high-bandwidth communications. Structured light has also been used to test the classical-quantum boundary, pushing the limits with what classical light can do for quantum processes, and vice versa. This has opened the intriguing possibility to create classical light that has quantum-like properties, as if it is "classically entangled". But how to create and control such states of light, and how far can one "push the limits"?
The prevailing tools for structuring light from lasers is hindered by the complexity of the specialized lasers needed, often requiring customized geometries and/or elements, while the prevailing two-dimensional paradigm of using only "pattern" and "polarization", means accessing two-dimensional classically entangled light, mimicking quantum qubits, 1s and 0s. An example of this would be the well-known quantum Bell states, shown in Figure 1 (left), which as classical light appear as vectorial structured light, combining the two degrees of freedom of "pattern" and "polarization". These two degrees of freedom mimic the two dimensions of the qubit quantum state. To create higher dimensions requires finding more degrees of freedom in a system seeming constrained to just two.
In their paper "Creation and control of high-dimensional multi-partite classically entangled light", Chinese and South African scientists report on how to create arbitrary dimensional quantum-like classical light directly from a laser. They use a very simple laser available in most university teaching laboratories to show eight dimensional classically entangled light, a new world record. They then go on to manipulate and control this quantum-like light, creating the first classically entangled Greenberger-Horne-Zeilinger (GHZ) states, a rather famous set of high-dimensional quantum states, shown in Figure 1.
"Theorists have long suggested all the applications that would be possible with such quantum-like light, but the lack of any creation and control steps has prohibited any progress. Now we have shown how to overcome this hurdle," says Dr. Shen from Tsinghua University (present senior research fellow in University of Southampton), the lead author of the paper.
Traditionally, exotic structured light from lasers requires equally exotic laser systems, either with custom elements (metasurfaces for example) or custom geometries (topological photonic based for example). The laser built by the authors contained only a gain crystal and followed textbook design with just two off-the-shelf mirrors. Their elegant solution is itself build on a principle embedded in quantum mechanics: ray-wave duality. The authors could control both path and polarization inside the laser by a simple length adjustment, exploiting what is called ray-wave duality lasers. According to Prof. Forbes, the project supervisor, "what is remarkable is not only that we could create such exotic states of light, but that their source is as simple a laser as you could possibly imagine, with nothing more than a couple of standard mirrors." The authors realized that the crucial "extra" degrees of freedom were right in front of theirs eyes, needing only a new mathematical framework to recognize them. The approach allows in-principle any quantum state to be created by simply marking the wave-like rays that are produced by the laser and then externally controlling them with a spatial light modulator, molding them to shape. In a sense, the laser produces the dimensions needed, while later modulation and control molds the outcome to some desired state. To demonstrate this, the authors produced all the GHZ states, which span an eight dimensional space.
Because no-one had ever created such high-dimensional classically entangled light, the authors had to invent a new measurement approach, translating tomography of high-dimensional quantum states into a language and technique suitable for its classical light analogue. The result is a new tomography for classically entangled light, revealing its quantum-like correlations beyond the standard two dimensions.
This work provides a powerful approach to creating and controlling high-dimensional classical light with quantum-like properties, paving the way for exciting applications in quantum metrology, quantum error correction and optical communication, as well as in stimulating fundamental studies of quantum mechanics with much more versatile bright classical light.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-23
Distributed optical fiber sensing (DOFS) is currently a mature technology that allows "transforming" a conventional fiber optic into a continuous array of individual sensors, which are distributed along its length. Between the panoply of techniques developed in the field of DOFS, those based on phase-sensitive optical time-domain reflectometry (ΦOTDR) have gained a great deal of attention, mainly due to their ability to measure strain and temperature perturbations in real time. These unique features, along with other advantages of distributed sensors (reduced weight, electromagnetic immunity ...
2021-03-23
Light-emitting diodes (LEDs) are changing the lighting and display industry and have obtained significant advances than traditional lighting sources. The traditional materials LEDs, e.g., III-V semiconductor LEDs, organic LEDs (OLEDs) and quantum-dot LEDs (QLEDs), have achieved great success and gradually realized commercialization, but still face some challenges. The OLEDs have the low carrier transport capability and exciton recombination, which would hinder the improvement of brightness. Besides, QLEDs show challenges for the tedious manufacturing process and the reliance on hydrophobic insulating long ligands also hinders their stability and electrical conductivity.
Compared with these traditional materials, quasi-2D ...
2021-03-23
A large proportion of dementia deaths in England and Wales may be due to socioeconomic deprivation, according to new research led by Queen Mary University of London.
The team also found that socioeconomic deprivation was associated with younger age at death with dementia, and poorer access to accurate diagnosis.
Dementia is the leading cause of death in England and Wales, even during the COVID pandemic, and is the only disease in the top ten causes of death without effective treatment.
The research, published in the Journal of Alzheimer's Disease, examines Office for National Statistics mortality data for England and Wales, and finds that in 2017, 14,837 excess dementia deaths were attributable to deprivation, equating to 21.5 per cent of all dementia deaths ...
2021-03-23
Uncovering detailed travel patterns and habitat use of sharks along and across shelf territories has been historically challenging - especially for most pelagic shark species - which remain offshore for most of their lives. Their vertical diving behavior has been a subject of inquiry for a long time, and for young sharks in particular, has remained elusive.
Using cutting-edge 3D satellite technology, a study led by Florida Atlantic University's Harbor Branch Oceanographic Institute, in collaboration with NOAA's National Marine Fisheries Service; OCEARCH; The South Fork Natural History Museum and Nature Center; and the Wildlife Conservation Society, is ...
2021-03-23
Of the many perplexing questions surrounding SARS CoV-2, a mysterious new pathogen that has killed an estimated 2.6 million people worldwide, perhaps the most insistent is this: why does the illness seem to strike in such a haphazard way, sometimes sparing the 100 year old grandmother, while killing healthy young men and women in the prime of life?
A new study by Karen Anderson, Abhishek Singharoy and their colleagues at the Biodesign Institute at Arizona State University, may offer some tentative clues. Their research explores MHC-I, a critical protein component of the human adaptive immune system.
The research suggests that certain variant ...
2021-03-23
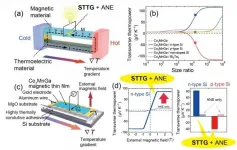
A NIMS research team devised a new thermoelectric generation mechanism with a hybrid structure composed of thermoelectric and magnetic materials. The team then actually fabricated this structure and observed the record-high thermopower appearing in the direction perpendicular to a temperature gradient (i.e., transverse thermoelectric generation). These results may offer insights into new mechanisms and structural designs applicable to the development of versatile energy harvesting technologies and highly sensitive heat flux sensors.
The Seebeck effect is a phenomenon in which a temperature gradient across a metal or semiconductor is converted into a thermoelectric voltage. Because this effect can be used to convert waste heat into electrical energy, its potential applications (e.g., ...
2021-03-23
Through an analysis of cellular components (cell fractions) from malignant ascites (fluid buildup in the abdomen caused by gastric cancer), a research collaboration based in Kumamoto University (Japan) has demonstrated that cellular senescence of cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) play an important role in the peritoneal dissemination of gastric cancer foci (cells different from surrounding cells). This understanding should enable the development of new treatments for cancer dissemination in the peritoneum by targeting cancer cells at focal sites and CAFs in patients with gastric cancer.
Peritoneal dissemination ...
2021-03-23
Plant species with short generation times are more sensitive to climate change than those with long generation times. This is one of the findings of a synthesis study by researchers from the German Centre for Integrative Biodiversity Research (iDiv), the Martin Luther University Halle-Wittenberg (MLU) and the Helmholtz-Centre for Environmental Research (UFZ). The international team comprehensively compiled worldwide available data, mostly from Europe and North America, to address the question of how plant populations react to climate change. The study, published in Nature Communications, shows that plant characteristics such as generation ...
2021-03-23
Consumption of ultra-processed foods and drink could increase the risk of developing colorectal cancer. This was the conclusion of a large study undertaken by the Barcelona Institute for Global Health (ISGlobal), a centre supported by the "la Caixa" Foundation, based on questionnaires about food behaviours completed by around 8,000 people in Spain. The study, the first of its kind in the country, also analysed the relationship between ultra-processed food and drink products and two other cancers; while no association was observed with prostate cancer, in the case of breast cancer a higher risk was observed in the sub-group of former and current smokers who reported a ...
2021-03-23
More extroverted people suffered mood declines while more introverted people saw mood improvements during the early COVID-19 pandemic, in survey of students at a U.S. university.
INFORMATION:
Publicly available article: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0248895
Article Title: "Personality trait predictors of adjustment during the COVID pandemic among college students"
Funding: This work was supported by a grant to Dr. Jim Hudziak from the Conrad Hilton Foundation (https://www.hiltonfoundation.org/). The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] A simple laser for quantum-like classical light