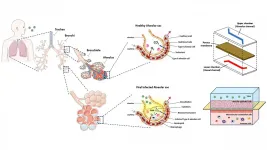
(Press-News.org) WASHINGTON, March 23, 2021 -- Scientists have been working for the past year to find ways to curb the effects of the COVID-19 pandemic. Though it is outside their typical realm of study, physicists have been playing an important role in many aspects of research about the pandemic and its impact on people.
Particle physicists' keen understanding of gas handling systems positioned them at the forefront for pioneering low-cost, mass-producible ventilators to help address the worldwide shortage. Led by Cristian Galbiati, professor of physics at Princeton University and the Gran Sasso Science Institute, an international, interdisciplinary team called the Mechanical Ventilator Milano (MVM) collaboration spearheaded one effort and presents the design in the journal Physics of Fluids, from AIP Publishing.
The project began in March 2020, shortly after Italy went into lockdown. Only one week later, the MVM collaboration had a working prototype.
The ventilator consists of a gas inlet valve and a gas outlet valve, along with a series of controls and alarms to ensure proper monitoring and customizability from patient to patient. The design is built from readily available parts and is presented under an open license, allowing developing countries to quickly and easily manufacture their own units.
"The idea behind the design was to have a system as simple as possible -- delivery of air through a single valve, exhaust of air through a single valve," said Galbiati.
Because the MVM is developed specifically for COVID-19 patients, it has reduced functionality compared to typical ventilators. This simpler design cuts the cost of production up to fivefold to under $10,000 per unit.
"This pandemic comes upon us, and you feel somewhat helpless as someone who isn't a medical physicist," said physics Nobel laureate Arthur McDonald, at Queen's University and a co-author on the paper. "Our collaboration of particle physicists, engineers, and software specialists from national labs, academia, and industry have applied their existing talents to create a new, accessible design and to provide a new manufacturing capability internationally to address the most serious cases during the pandemic."
"For a scientist committed to fundamental research, such as the search for the dark matter of the universe, it is extremely important to devote time and experience to build devices that can help to improve people's health," said Walter Bonivento, a senior scientist at INFN Cagliari and co-author on the paper.
The MVM has already received emergency use authorization from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration and received Health Canada Medical Device Directorate authorization. About 6,000 units have been delivered to date under a contract from the Canadian government for its stockpile, with the potential for more, if requested. Donations from Canada to developing countries in need have also been considered from the beginning of the contract award.
INFORMATION:
More information about the project can be found on the MVM Collaboration website.
The article "The novel Mechanical Ventilator Milano for the COVID-19 pandemic" is authored by A. Abba, C. Accorsi, P. Agnes, E. Alessi, P. Amaudruz, A. Annovi, F. Ardellier Desages, S. Back, C. Badia, J. Bagger, V. Basile, G. Batignani, A. Bayo, B. Bell, M. Beschi, D. Biagini, G. Bianchi, S. Bicelli, D. Bishop, T. Boccali, A. Bombarda, S. Bonfanti, W.M. Bonivento, M. Bouchard, M. Breviario, S. Brice, R. Brown, J.M. Calvo-Mozota, L. Camozzi, M. Camozzi, A. Capra, M. Caravati, M. Carlini, A. Ceccanti, B. Celano, J.M. Cela Ruiz, C. Charette, G. Cogliati, M. Constable, C. Crippa, G. Croci, S. Cudmore, C.E. Dahl, A. Dal Molin, M. Daley, C. Di Guardo, G. D'Avenio, O. Davignon, M. Del Tutto, J. De Ruiter, A. Devoto, P. Diaz Gomez Maqueo, F. Di Francesco, M. Dossi, E. Druszkiewicz, C. Duma, E. Elliott, D. Farina, C. Fernandes, F. Ferroni, G. Finocchiaro, G. Fiorillo, R. Ford, G. Foti, R.D. Fournier, D. Franco, K. Frickbergs, F. Gabriele, C. Galbiati, P. Garcia Abia, A. Gargantini, L. Giacomelli, F. Giacomini, F. Giacomini, L.S. Giarratana, S. Gillespie, D. Giorgi, T. Girma, R. Gobui, D. Goeldi, F. Golf, P. Gorel, G. Gorini, E. Gramellini, G. Grosso, F. Guescini, E. Guetre, G. Hackman, T. Hadden, W. Hawkins, K. Hayashi, A. Heavey, G. Hersak, N. Hessey, G. Hockin, K. Hudson, A. Ianni, C. Ienzi, V. Ippolito, C.C. James, C. Jillings, C. Kendziora, S. Khan, E. Kim, M. King, S. King, A. Kittmer, I. Kochanek, J. Kowalkowski, R. Krücken, M. Kushoro, S. Kuula, M. Laclaustra, G. Leblond, L. Lee, A. Lennarz, M. Leyton, X. Li, P. Liimatainen, C. Lim, T. Lindner, T. Lomonaco, P. Lu, R. Lubna, G.A. Lukhanin, G. Luzón, M. MacDonald, G. Magni, R. Maharaj, S. Manni, C. Mapelli, P. Margetak, L. Martin, S. Martin, M. Martínez, N. Massacret, P. McClurg, A.B. McDonald, E. Meazzi, R. Migalla, T. Mohayai, L. Molinari Tosatti, G. Monzani, C. Moretti, B. Morrison, M. Mountaniol, A. Muraro, P. Napoli, F. Nati, C. Natzke, A.J. Noble, A. Norrick, K. Olchanski, A. Ortiz de Solorzano, F. Padula, M. Pallavicini, I. Palumbo, E. Panontin, N. Papini, L. Parmeggiano, S. Parmeggiano, K. Patel, A. Patel, M. Paterno, C. Pellegrino, P. Pelliccione, V. Pesudo, A. Pocar, A. Pope, S. Pordes, F. Prelz, O. Putignano, J.L. Raaf, C. Ratti, M. Razeti, A. Razeto, D. Reed, J. Refsgaard, T. Reilly, A. Renshaw, F. Retriere, E. Riccobene, D. Rigamonti, A. Rizz, J. Rode, J. Romualdez, L. Russel, D. Sablone, S. Sala, D. Salomoni, P. Salvo, A. Sandoval, E. Sansoucy, R. Santorelli, C. Savarese, E. Scapparone, T. Schaubel, S. Scorza, M. Settimo, B. Shaw, S. Shawyer, A. Sher, A. Shi, P. Skensved, A. Slutsky, B. Smith, N.J.T. Smith, A. Stenzler, C. Straubel, P. Stringari, M. Suchenek, B. Sur, S. Tacchino, L. Takeuchi, M. Tardocchi, R. Tartaglia, E. Thomas, D. Trask, J. Tseng, L. Tseng, L. VanPagee, V. Vedia, B. Velghe, S. Viel, A. Visioli, L. Viviani, D. Vonica, M. Wada, D. Walter, H. Wang, M.H.L.S. Wang, S. Westerdale, D. Wood, D. Yates, S. Yue, and V. Zambrano. The article will appear in Physics of Fluids on March 23, 2021 (DOI: 10.1063/5.0044445).
After that date, it can be accessed at https://aip.scitation.org/doi/10.1063/5.0044445.
ABOUT THE JOURNAL
Physics of Fluids is devoted to the publication of original theoretical, computational, and experimental contributions to the dynamics of gases, liquids, and complex fluids. See https://aip.scitation.org/journal/phf.
Bottom Line: The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) concludes that current evidence is insufficient to make a recommendation about screening for hearing loss in asymptomatic adults 50 and older. Nearly 16% of U.S. adults 18 and over report difficulty hearing. Hearing loss has been associated with an increased risk of falls, hospitalizations, social isolation and cognitive decline. The USPSTF routinely makes recommendations about the effectiveness of preventive care services and this recommendation is similar to its 2012 statement.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2021.2566)
Editor's Note: Please see the article for additional information, including ...
WASHINGTON, March 23, 2021 -- According to the National Institutes of Health, respiratory viruses are the most frequent cause of disease and death in humans, a fact highlighted by the COVID-19 pandemic. Despite the potential to cause severe disease, over 70% of viral infections remain asymptomatic.
Animal models have been used widely to understand how these viruses infect the host and how the host responds to prevent infection and onset of diseases. Data based on animal models, however, does not always apply well to humans, given the variability ...
What The Study Did: Employees of a health care system were surveyed on the eve of vaccine distribution to encourage them to receive a COVID-19 vaccine, assess their intentions to do so and understand reasons for hesitancy.
Authors: Michelle N. Meyer, Ph.D., J.D., Center for Translational Bioethics and Health Care Policy at the Geisinger Health System in Danville, Pennsylvania, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.5344)
Editor's Note: Please see the article for additional information, including ...
What The Study Did: This study of working-age people enrolled in private health plans from March 2019 through June 2020 documented patterns of care at the onset of COVID-19.
Authors: Jonathan P. Weiner, Dr.P.H., Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health in Baltimore, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.2618)
Editor's Note: The article includes funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, ...
What The Study Did: Researchers investigated representation of Black Americans in clinical trials of cardiovascular drugs approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration between 2006 and 2020.
Authors: Jiarui Li, M.D., of the Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College in Beijing, China, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.2640)
Editor's Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
INFORMATION:
Media ...
CABI-led Plantwise plant clinics can help promote more sustainable ways to fight crop pests and diseases in Rwanda and Zambia - such as the fall armyworm - with the judicial use of pesticides within Integrated Pest Management (IPM) plans.
Dr Justice Tambo, lead author of the study published in the journal Food Policy, surveyed 1,474 farm households in Rwanda and Zambia and found that although farmers who visit plant clinics show a higher probability of opting for pesticides for pest control, they do not use them intensively and are more likely to adopt safer and more sustainable alternatives.
The scientists, which include researchers ...
Denver--March 26, 2021---A lymph node collection kit can help surgeons attain compete resection and improve long-term survival after curative-intent lung cancer surgery, according to a study published in the Journal of Thoracic Oncology Clinical and Research Reports. The journal is published by the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer.
Surgical resection is the most important curative treatment for non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). With successful implementation of lung cancer screening programs, the proportion of patients with NSCLC who undergo surgery is likely to increase significantly.
"However, poor surgical quality reduces the survival benefit of curative-intent surgery and suboptimal ...
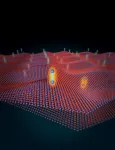
The discovery of the material graphene, which consists of only one layer of carbon atoms, was the starting signal for a global race: Today, so-called "2D materials" are produced, made of different types of atoms. Atomically thin layers that often have very special material properties not found in conventional, thicker materials.
Now another chapter is being added to this field of research: If two such 2D layers are stacked at the right angle, even more new possibilities arise. The way in which the atoms of the two layers interact creates intricate geometric patterns, and these patterns have a decisive impact on the material properties, as a research team from TU Wien and the University of Texas ...
The possibly oldest cephalopods in the earth's history stem from the Avalon Peninsula in Newfoundland (Canada). They were discovered by earth scientists from Heidelberg University. The 522 million-year-old fossils could turn out to be the first known form of these highly evolved invertebrate organisms, whose living descendants today include species such as the cuttlefish, octopus and nautilus. In that case, the find would indicate that the cephalopods evolved about 30 million years earlier than has been assumed.
"If they should actually be cephalopods, we would have to backdate the origin of cephalopods into the early Cambrian period," says Dr Anne Hildenbrand ...
Russian scientists have proposed a new algorithm for automatic decoding and interpreting the decoder weights, which can be used both in brain-computer interfaces and in fundamental research. The results of the study were published in the Journal of Neural Engineering.
Brain-computer interfaces are needed to create robotic prostheses and neuroimplants, rehabilitation simulators, and devices that can be controlled by the power of thought. These devices help people who have suffered a stroke or physical injury to move (in the case of a robotic chair or prostheses), communicate, use a computer, and operate household appliances. In addition, in combination with machine learning methods, neural interfaces ...