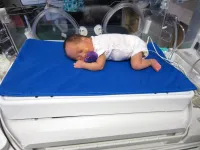
Therapeutic bed can help keep preterm newborns' brain oxygen levels stable
2021-03-25
(Press-News.org) A medical device that has been shown to manage pain among babies born preterm can also help keep their brain oxygen levels steady during medical procedures, finds new analysis by researchers at UBC.
The device, called Calmer, is a pillow-sized therapeutic bed covered in soft fabric and inserted into the incubator. It can be programmed to mimic a parent's heartbeat and breathing rate-- providing a soothing presence by moving up and down gently to simulate a breathing motion and heartbeat sound for the baby when their parent cannot be present.
"For newborns and particularly for preterm babies, it's critical to keep overall blood oxygen levels steady, especially in the brain. The more stable their brain oxygenation is, the better for their brain development," says researcher Dr. Manon Ranger, a UBC nursing professor who studies the health of vulnerable infants.
The team conducted a randomized clinical trial with 29 premature babies admitted to the neonatal intensive care unit, or NICU, at BC Women's Hospital + Health Centre. Half the participants received the usual care--facilitated tucking, where a caregiver holds the infant in a flexed position, plus a soother--during a painful procedure (a blood draw). The other half were placed on Calmer.
When their brain oxygen levels were measured, both groups showed similar results: their brain oxygen levels stayed largely steady during the procedure.
"A parent's touch, generally speaking, is ultimately the most soothing presence for an infant. It relieves pain, helps them gain weight and promotes brain growth while reducing stress," said Ranger, who is also an investigator at BC Children's Hospital and Women's Health Research Institute.
"However, this option is not always available in NICUs. Our research shows that when a parent or caregiver cannot be physically present, Calmer is an effective alternative. This is especially relevant in the current COVID-19 pandemic context, where many hospital settings must restrict contact with visitors."
Calmer was developed by Dr. Liisa Holsti, a professor in the department of occupational science and occupational therapy at UBC, and an investigator at BC Children's Hospital and Women's Health Research Institute; and Dr. Karon Maclean, a UBC professor of computer science. Other researchers from BC Children's Hospital, the British Columbia Institute of Technology and the BC Women's Hospital and Health Centre also contributed to its development.
"We were very pleased that our preliminary trial results showed that Calmer has the potential to benefit these infants whose brains are particularly vulnerable to pain and stress," said Holsti. "We are expanding our evaluation of this device in more rigorous real-world conditions, and we're in the process of redesigning it to be used in low- and middle-income countries, so that infants worldwide who need it can have the benefit of Calmer treatment."
For their next step, the team is planning to test longer-term use of Calmer on preterm infants' physical growth and brain development in the NICU. This project recently received funding from UBC's Health Innovation Funding Investment (HIFI) awards.
INFORMATION:
"Cerebral hemodynamic response to a therapeutic bed for procedural pain management in preterm infants in the NICU: a randomized controlled trial" was published January 2021 in Pain Reports
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-25
Researchers at the Georgia Institute of Technology have uncovered an innovative way to tap into the over-capacity of 5G networks, turning them into "a wireless power grid" for powering Internet of Things (IoT) devices that today need batteries to operate.
The Georgia Tech inventors have developed a flexible Rotman lens-based rectifying antenna (rectenna) system capable, for the first time, of millimeter-wave harvesting in the 28-GHz band. (The Rotman lens is key for beamforming networks and is frequently used in radar surveillance systems to see targets in multiple directions without physically moving the antenna system.)
But to harvest enough power to supply low-power devices at long ranges, large aperture antennas are required. The problem with ...
2021-03-25
Researchers at Baylor College of Medicine, Shandong University in China and other institutions may have found an explanation for dawn phenomenon, an abnormal increase of blood sugar only in the morning, observed in many patients with type 2 diabetes. They report in the journal Nature that mice lacking the circadian clock gene called Rev-erb in the brain show characteristics similar to those of dawn phenomenon.
The researchers then looked at Rev-erb gene expression in patients with type 2 diabetes comparing a group with dawn phenomenon to a group without it and found that the gene's expression followed a different temporal pattern between these two groups. The findings support the idea that an altered daily rhythm of expression of the Rev-erb gene may underlie dawn phenomenon. Future ...
2021-03-25
WASHINGTON (March 25, 2021)--Although demand for COVID-19 vaccines currently seems high, vaccine hesitancy could pose a major threat to public health efforts to end the pandemic, according to an editorial published today in the journal Science.
The authors, including David A. Broniatowski, associate director of the George Washington University Institute for Data, Democracy & Politics, point out that public sentiment towards vaccines are volatile in the face of events such as the recent controversy surrounding the AstraZeneca vaccine clinical trial data. For example, some people could develop safety concerns due to the news reporting about the AstraZeneca vaccine and then turn down the chance to ...
2021-03-25
Narcissism is driven by insecurity, and not an inflated sense of self, finds a new study by a team of psychology researchers. Its research, which offers a more detailed understanding of this long-examined phenomenon, may also explain what motivates the self-focused nature of social media activity.
"For a long time, it was unclear why narcissists engage in unpleasant behaviors, such as self-congratulation, as it actually makes others think less of them," explains Pascal Wallisch, a clinical associate professor in New York University's Department of Psychology and the senior author of the paper, which appears in the journal Personality and Individual Differences. "This has become quite prevalent in the age of social media--a behavior that's been coined 'flexing'.
"Our ...
2021-03-25
A study by prof. Bas van Bavel and prof. Marten Scheffer shows that throughout history, most disasters and pandemics have boosted inequality instead of levelling it. Whether such disastrous events function as levellers or not, depends on the distribution of economic wealth and political leverage within a society at the moment of crisis. Their findings on the historical effects of crises on equality in societies are now published open access in Nature HSS Communications.
It is often thought that the main levellers of inequality in societies were natural disasters such as epidemics or earthquakes, and social turmoil such as wars and ...
2021-03-25
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. -- Materials that contain special polymer molecules may someday be able to warn us when they are about to fail, researchers said. Engineers at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign have improved their previously developed force-sensitive molecules, called mechanophores, to produce reversible, rapid and vibrant color change when a force is applied.
The new study led by postdoctoral researcher Hai Qian, materials science and engineering professor and head Nancy Sottos, and Beckman Institute of Advanced Science and Technology director Jeffrey Moore is published in the journal Chem.
Moore's team has been working with mechanophores for more than a decade, but past efforts have produced molecules that were slow to react and return to their original state, if at all. ...
2021-03-25
Bright semiconductor nanocrystals known as quantum dots give QLED TV screens their vibrant colors. But attempts to increase the intensity of that light generate heat instead, reducing the dots' light-producing efficiency.
A new study explains why, and the results have broad implications for developing future quantum and photonics technologies where light replaces electrons in computers and fluids in refrigerators, for example.
In a QLED TV screen, dots absorb blue light and turn it into green or red. At the low energies where TV screens operate, this conversion of light from one color to another is virtually 100% efficient. But at the higher excitation energies required for brighter screens and other ...
2021-03-25
In the year since the coronavirus pandemic upended how just about every person on the planet interacts with one another, video conferencing has become the de facto tool for group collaboration within many organizations. The prevalent assumption is that technology that helps to mimic face-to-face interactions via a video camera will be most effective in achieving the same results, yet there's little data to actually back up this presumption. Now, a new study challenges this assumption and suggests that non-visual communication methods that better synchronize and boost audio cues are in fact more effective.
Synchrony Promotes Collective Intelligence
Researchers from Carnegie Mellon's Tepper School of Business and the Department of Communication at the University of California, Santa ...
2021-03-25
Despite having remarkable utility in treating movement disorders such as Parkinson's disease, deep brain stimulation (DBS) has confounded researchers, with a general lack of understanding of why it works at some frequencies and does not at others. Now a University of Houston biomedical engineer is presenting evidence in Nature Communications Biology that electrical stimulation of the brain at higher frequencies (>100Hz) induces resonating waveforms which can successfully recalibrate dysfunctional circuits causing movement symptoms.
"We investigated the modulations in local ?eld potentials induced by electrical stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus (STN) at therapeutic and non-therapeutic frequencies in Parkinson's disease patients ...
2021-03-25
LA JOLLA--The glow of a panther's eyes in the darkness. The zig-zagging of a shark's dorsal fin above the water.
Humans are always scanning the world for threats. We want the chance to react, to move, to call for help, before danger strikes. Our cells do the same thing.
The innate immune system is the body's early alert system. It scans cells constantly for signs that a pathogen or dangerous mutation could cause disease. And what does it like to look for? Misplaced genetic material.
The building blocks of DNA, called nucleic acids, are supposed to be hidden away in the cell nucleus. Diseases can change that. Viruses churn out genetic material in parts of the cell where it's not supposed to be. Cancer cells do too.
"Cancer cells harbor damaged DNA," says ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Therapeutic bed can help keep preterm newborns' brain oxygen levels stable