(Press-News.org) About two decades after first devising a new kind of vaccine, Oregon Health & Science University researchers are unlocking why it stops and ultimately clears the monkey form of HIV, called SIV, in about half of nonhuman primates - and why it's a promising candidate to stop HIV in people.
In scientific papers that were simultaneously published today in the journals Science and Science Immunology, creators of the cytomegalovirus, or CMV, vaccine platform describe the unusual biological mechanisms through which it works.
The findings also helped fine-tune VIR-1111, the CMV-based experimental vaccine against HIV that was developed at OHSU and is now being evaluated in a Phase 1 clinical trial. The trial is being conducted by Vir Biotechnology, which licensed the CMV vaccine platform technology from OHSU.
"Knowing the mechanism that the CMV-based SIV vaccine uses to work in rhesus macaques gives us a way to judge the potential of a human vaccine very quickly," said Louis Picker, M.D., the associate director of the OHSU Vaccine and Gene Therapy Institute and a professor of pathology/molecular microbiology and immunology in the OHSU School of Medicine. "If you have the wrong genes in the CMV vaccine, the critical immune response needed for efficacy won't develop. You have to thread the CMV vaccine's needle exactly if you want a high degree of protection, and you have to know what you're looking for."
Two of the papers describe that the cytomegalovirus vaccine needs to generate an unusual type of CD8-positive T cell response called MHC-E-restricted T cells to effectively fight off SIV in monkeys.
"We knew for a while that we have unusual T cell responses in monkeys that receive our CMV vaccine against SIV," said Klaus Frueh, Ph.D., a professor of molecular microbiology and immunology in the OHSU School of Medicine and OHSU Vaccine and Gene Therapy Institute. "But we didn't know if they were important for protection against SIV. This research shows clearly that, without this special MHC-E-restricted T cell response, we don't have protection."
The study published in Science Immunology shows that the vaccine was only able to generate these special T cells to fight off SIV if eight specific genes were missing or inactivated from the natural form of monkey CMV. And a corresponding paper published via Science's First Release describes how a specific cytomegalovirus protein known as Rh67 is required to generate MHC-E-restricted T cells to protect against SIV. Together, these papers suggest how a CMV-based vaccine needs to be designed to create these unconventional T cell responses.
And, in a separate Science Immunology paper that was also published today, a research team led by Andrew J. McMichael, Ph.D., of Oxford University looked into whether what has been learned from nonhuman primate experiments could be transferrable to humans. These researchers showed that MHC-E-restricted CD8-positive T cells could be increased and suppress HIV in laboratory cell cultures.
This new research is being published as the OHSU Vaccine and Gene Therapy Institute celebrates the 20th anniversary of its first building opening for research in April 2001. Picker and Frueh moved to Oregon to help start the institute: Picker has led its vaccine program since its founding, and Frueh joined forces with Picker in 2006. Picker first received a $3.5 million grant from the National Institutes of Health in 2004 to develop a CMV-based HIV vaccine. Picker says the following in a May 25, 2004, OHSU announcement about the grant: "We believe a persistent viral vector could produce a superior and more durable anti-HIV immune response that would, in effect, hold the line against HIV."
INFORMATION:
The following funding was awarded to OHSU in support of the research described in these three studies: the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (grants P01 AI094417, U19 AI128741, UM1 AI124377, R37 AI054292, R01AI140888, R01 AI059457), National Institutes of Health Office of the Director (grant P51 OD011092); National Cancer Institute (contract HHSN261200800001E), and the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation-supported Collaboration for AIDS Vaccine Discovery (OPP1033121).
In the interest of ensuring the integrity of our research and as part of our commitment to public transparency, OHSU actively regulates, tracks and manages relationships that our researchers may hold with entities outside of OHSU. In regards to this research, OHSU and several individuals have a significant financial interest in Vir Biotechnology Inc., a company that may have a commercial interest in the results of this research and technology. These individuals include Picker, Frueh, Sacha, Malouli, Hansen and Hancock.
The three studies are:
* Cytomegaloviral determinants of CD8+ T cell programming and RhCMV/SIV vaccine efficacy, Science, via First Release, March 25, 2021,
* Modulation of MHC-E transport by viral decoy ligands is required for RhCMV-SIV vaccine efficacy, Science Immunology, , March 25, 2021,
* HLA-E restricted Gag specific CD8+ T cells can suppress HIV-1 infection, offering vaccine opportunities, Science Immunology, March 25, 2021,
Related OHSU News stories:
* Jan. 6, 2021, OHSU-developed HIV vaccine tech tested in humans for first time, https://news.ohsu.edu/2021/01/06/ohsu-developed-hiv-vaccine-tech-tested-in-humans-for-first-time
* July 17, 2019, HIV vaccine nears clinical trial following new findings, https://news.ohsu.edu/2019/07/17/hiv-vaccine-nears-clinical-trial-following-new-findings
* Jan. 25, 2017, Vaccine technology developed by OHSU scientists acquired by industry leaders, https://news.ohsu.edu/2017/01/25/vaccine-technology-developed-by-ohsu-scientists-acquired-by-industry-leaders
* Sept. 11, 2013, OHSU AIDS vaccine candidate appears to completely clear virus from the body, https://news.ohsu.edu/2013/09/11/ohsu-aids-vaccine-candidate-appears-to-completely-clear-virus-from-the-body
SILVER SPRING, Md. - As concern has grown over COVID-19 variants and their implications for how well COVID-19 vaccines will protect against the virus, researchers have proposed a method to examine instances of SARS-COV-2 infections in people who have received a COVID-19 vaccine.
Genomic sieve analysis of these so-called "breakthrough" SARS-CoV-2 infections in COVID vaccine trials is a critical tool to identify viral mutations associated with vaccine failure and to predict how vaccination impacts the virus' evolution.
Dr. Morgane Rolland, Chief of Viral Genetics ...
Scientists at Sinai Health say they have discovered a new pathway that controls dangerous overreactions in a body's immune system, including deadly forms of hyper-inflammation.
In new findings out today in the journal Science, researchers at the Lunenfeld-Tanenbaum Research Institute (LTRI) detail how a protein known as WAVE2, a protein expressed in all immune cells, plays a critical role in maintaining immune system balance.
As part of the research, scientists knocked out, or turned off, WAVE2 in a subset of immune cells in mice, which led to severe autoimmunity and inflammation, ...
Despite having remarkable utility in treating movement disorders such as Parkinson's disease, deep brain stimulation (DBS) has confounded researchers, with a general lack of understanding of why it works at some frequencies and does not at others. Now a University of Houston biomedical engineer is presenting evidence in Nature Communications Biology that electrical stimulation of the brain at higher frequencies (>100Hz) induces resonating waveforms which can successfully recalibrate dysfunctional circuits causing movement symptoms.
"We investigated the modulations in local ?eld potentials induced by electrical stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus (STN) at therapeutic ...
Tel-Aviv, ISRAEL - March 25, 2021 - Wild Biotech, a preclinical stage drug discovery & development company emerging out of stealth mode, today announces the publication of its first major paper, which appears in the journal Science. The study mapped the gut microbiota of animals in the wild on an unprecedented scale, adding millions of potentially novel microbiome-based therapeutics for human diseases to the company's already massive database. Wild will use these findings to first tap its database for targets in inflammatory, immune and gastrointestinal diseases.
"For the study, we collected gut microbiota from almost 200 species of animals in the wild, covering diverse classes, feeding behaviors, geographies, and ...
Water scarcity in rural Alaska is not a new problem, but the situation is getting worse with climate change. Lasting solutions must encourage the use of alternative water supplies like rainwater catchment and grey water recycling. They must also address the affordability of water related to household income, say researchers from McGill University.
Washing hands with clean water is something most people take for granted, yet for Alaska's rural residents, this is often not the case. When people pay for water by the gallon, serious thought is given to how much is used - even during the COVID-19 pandemic.
In many rural Alaskan communities, where jobs are scarce and household income is low, the cost of water is a high burden, according to the study published in Environmental ...
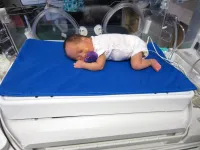
A medical device that has been shown to manage pain among babies born preterm can also help keep their brain oxygen levels steady during medical procedures, finds new analysis by researchers at UBC.
The device, called Calmer, is a pillow-sized therapeutic bed covered in soft fabric and inserted into the incubator. It can be programmed to mimic a parent's heartbeat and breathing rate-- providing a soothing presence by moving up and down gently to simulate a breathing motion and heartbeat sound for the baby when their parent cannot be present.
"For newborns and particularly for preterm babies, it's critical to keep overall blood oxygen levels steady, especially in the brain. The more stable their brain oxygenation is, the better for their brain development," ...
Researchers at the Georgia Institute of Technology have uncovered an innovative way to tap into the over-capacity of 5G networks, turning them into "a wireless power grid" for powering Internet of Things (IoT) devices that today need batteries to operate.
The Georgia Tech inventors have developed a flexible Rotman lens-based rectifying antenna (rectenna) system capable, for the first time, of millimeter-wave harvesting in the 28-GHz band. (The Rotman lens is key for beamforming networks and is frequently used in radar surveillance systems to see targets in multiple directions without physically moving the antenna system.)
But to harvest enough power to supply low-power devices at long ranges, large aperture antennas are required. The problem with ...
Researchers at Baylor College of Medicine, Shandong University in China and other institutions may have found an explanation for dawn phenomenon, an abnormal increase of blood sugar only in the morning, observed in many patients with type 2 diabetes. They report in the journal Nature that mice lacking the circadian clock gene called Rev-erb in the brain show characteristics similar to those of dawn phenomenon.
The researchers then looked at Rev-erb gene expression in patients with type 2 diabetes comparing a group with dawn phenomenon to a group without it and found that the gene's expression followed a different temporal pattern between these two groups. The findings support the idea that an altered daily rhythm of expression of the Rev-erb gene may underlie dawn phenomenon. Future ...
WASHINGTON (March 25, 2021)--Although demand for COVID-19 vaccines currently seems high, vaccine hesitancy could pose a major threat to public health efforts to end the pandemic, according to an editorial published today in the journal Science.
The authors, including David A. Broniatowski, associate director of the George Washington University Institute for Data, Democracy & Politics, point out that public sentiment towards vaccines are volatile in the face of events such as the recent controversy surrounding the AstraZeneca vaccine clinical trial data. For example, some people could develop safety concerns due to the news reporting about the AstraZeneca vaccine and then turn down the chance to ...
Narcissism is driven by insecurity, and not an inflated sense of self, finds a new study by a team of psychology researchers. Its research, which offers a more detailed understanding of this long-examined phenomenon, may also explain what motivates the self-focused nature of social media activity.
"For a long time, it was unclear why narcissists engage in unpleasant behaviors, such as self-congratulation, as it actually makes others think less of them," explains Pascal Wallisch, a clinical associate professor in New York University's Department of Psychology and the senior author of the paper, which appears in the journal Personality and Individual Differences. "This has become quite prevalent in the age of social media--a behavior that's been coined 'flexing'.
"Our ...