No evidence that people alter daily travel after having symptoms that could be COVID-19
New George Mason University College of Health and Human Services study is one of first individual-level studies to track movements and symptoms during the COVID-19 pandemic
2021-03-26
(Press-News.org) How can we better understand how people move during the pandemic and how they spread COVID-19? New END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Researchers harvest energy from radio waves to power wearable devices
2021-03-25
From microwave ovens to Wi-Fi connections, the radio waves that permeate the environment are not just signals of energy consumed but are also sources of energy themselves. An international team of researchers, led by Huanyu "Larry" Cheng, Dorothy Quiggle Career Development Professor in the Penn State Department of Engineering Science and Mechanics, has developed a way to harvest energy from radio waves to power wearable devices.
The researchers recently published their method inMaterials Today Physics.
According to Cheng, current energy sources for wearable health-monitoring devices have their place in powering sensor devices, but each has its setbacks. Solar power, for example, can only harvest energy when exposed to the sun. A self-powered triboelectric device can only ...
A T-cell stimulatory protein and interleukin-10 synergize to prevent gut inflammation
2021-03-25
BIRMINGHAM, Ala. - Researchers have found an unexpected synergy between a T-cell stimulatory protein -- the ICOS ligand -- and interleukin-10, an immunoregulatory cytokine, to prevent inflammatory bowel disease in mice. The study will aid the understanding of, and future research into, this immune disorder, which includes Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis. About 1.6 million Americans have inflammatory bowel disease.
Interleukin-10, or IL-10, was already known as a major player to prevent gut inflammation by establishing and maintaining immune homeostasis in the gut, where it is vital for the host to have a peaceful coexistence with normal intestinal microbes, while the immune system still stands ...
Turning wood into plastic
2021-03-25
Efforts to shift from petrochemical plastics to renewable and biodegradable plastics have proven tricky -- the production process can require toxic chemicals and is expensive, and the mechanical strength and water stability is often insufficient. But researchers have made a breakthrough, using wood byproducts, that shows promise for producing more durable and sustainable bioplastics.
A study published in Nature Sustainability, co-authored by Yuan Yao, assistant professor of industrial ecology and sustainable systems at Yale School of the Environment (YSE), outlines the process of deconstructing the porous matrix of natural wood into a slurry. The researchers say the resulting material shows ...
Bringing Total Worker Health® to a multinational agribusiness in Latin America
2021-03-25
Researchers from the Center for Health, Work & Environment (CHWE) at the Colorado School of Public Health have published a paper in the International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health studying the effectiveness of applying Total Worker Health (TWH) in an international context. The study, led by a team at CHWE, is the first to examine how a TWH framework operates outside of a western context in Latin America workforces.
"Although recent reviews show that TWH intervention studies have had some global reach, the vast majority have been conducted in Western countries," says lead researcher Diana Jaramillo. "While global organizations, as well as governmental entities in Latin America, acknowledge the importance ...
When synthetic evolution rhymes with natural diversity
2021-03-25
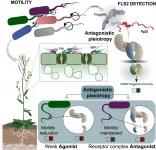
Researchers at GMI - Gregor Mendel Institute of Molecular Plant Biology of the Austrian Academy of Sciences, the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill and The Howard Hughes Medical Institute (HHMI) use two complementary approaches to unveil a co-evolutionary mechanism between bacteria and plants and also explain complex immune response patterns observed in the wild. Together the papers change the way scientists have been thinking about the relationship of a bacterial antigenic component with its plant immune receptor. The two papers are published back to back in the journal Cell Host & Microbe.
Immune responses have developed in virtually all organisms over evolutionary time scales to protect them from foreign ...
New class of versatile, high-performance quantum dots primed for medical imaging, quantum computing
2021-03-25
LOS ALAMOS, N.M., March 25, 2021--A new class of quantum dots deliver a stable stream of single, spectrally tunable infrared photons under ambient conditions and at room temperature, unlike other single photon emitters. This breakthrough opens a range of practical applications, including quantum communication, quantum metrology, medical imaging and diagnostics, and clandestine labeling.
"The demonstration of high single-photon purity in the infrared has immediate utility in areas such as quantum key distribution for secure communication," said Victor Klimov, lead author of a paper published ...
Carrying naloxone can save lives but newly abstinent opioid users resist
2021-03-25
Opioids are the main driver of fatal drug overdoses in the United States, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, resulting in 46,802 deaths in 2018, usually because the person stops breathing.
Naloxone -- a Food and Drug Administration-approved medication used to reverse overdoses from opioids, such as heroin, morphine and oxycodone -- works by restoring normal respiration to a person whose breathing has slowed or stopped.
"Opioid overdoses cause the largest number of accidental and avoidable deaths," said Peter Davidson, PhD, associate professor in the Department of Medicine at University of California San Diego School of Medicine. "The human toll of drug addiction is devastating. Using naloxone to prevent opiate overdoses can and has saved many lives."
In ...
Chemists achieve breakthrough in the production of three-dimensional molecular structures
2021-03-25
A major goal of organic and medicinal chemistry in recent decades has been the rapid synthesis of three-dimensional molecules for the development of new drugs. These drug candidates exhibit a variety of improved properties compared to predominantly flat molecular structures, which are reflected in clinical trials by higher efficacy and success rates. However, they could only be produced at great expense or not at all using previous methods. Chemists led by Prof. Frank Glorius (University of Münster, Germany) and his colleagues Prof. M. Kevin Brown (Indiana University Bloomington) and Prof. Kendall N. Houk (University of California, Los Angeles) have now succeeded in converting several classes of flat ...
Skoltech researchers create a new human height inheritance model
2021-03-25
Skoltech scientists and their colleagues have proposed a new human height inheritance model that accounts for the interaction between various factors that influence adult human height. The research was published in the European Journal of Human Genetics.
Human height is a classical quantitative trait that depends on sex, genetics, and the environment.
Scientists from Skoltech, Novosibirsk State University, the Institute of Cytology and Genetics of the Siberian Branch of RAS, and the Institute of Science and Technology in Vienna analyzed the human height distribution ...
Ocean currents predicted on enceladus
2021-03-25
Buried beneath 20 kilometers of ice, the subsurface ocean of Enceladus--one of Saturn's moons--appears to be churning with currents akin to those on Earth.
The theory, derived from the shape of Enceladus's ice shell, challenges the current thinking that the moon's global ocean is homogenous, apart from some vertical mixing driven by the warmth of the moon's core.
Enceladus, a tiny frozen ball about 500 kilometers in diameter (about 1/7th the diameter of Earth's moon), is the sixth largest moon of Saturn. Despite its small size, Enceladus attracted the ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Why does chronic back pain make everyday sounds feel harsher? Brain imaging study points to a treatable cause
Video messaging effectiveness depends on quality of streaming experience, research shows
Introducing the “bloom” cycle, or why plants are not stupid
The Lancet Oncology: Breast cancer remains the most common cancer among women worldwide, with annual cases expected to reach over 3.5 million by 2050
Improve education and transitional support for autistic people to prevent death by suicide, say experts
GLP-1 drugs like Ozempic could cut risk of major heart complications after heart attack, study finds
Study finds Earth may have twice as many vertebrate species as previously thought
NYU Langone orthopedic surgeons present latest clinical findings and research at AAOS 2026
New journal highlights how artificial intelligence can help solve global environmental crises
Study identifies three diverging global AI pathways shaping the future of technology and governance
Machine learning advances non targeted detection of environmental pollutants
ACP advises all adults 75 or older get a protein subunit RSV vaccine
New study finds earliest evidence of big land predators hunting plant-eaters
Newer groundwater associated with higher risk of Parkinson’s disease
New study identifies growth hormone receptor as possible target to improve lung cancer treatment
Routine helps children adjust to school, but harsh parenting may undo benefits
IEEE honors Pitt’s Fang Peng with medal in power engineering
SwRI and the NPSS Consortium release new version of NPSS® software with improved functionality
Study identifies molecular cause of taste loss after COVID
Accounting for soil saturation enhances atmospheric river flood warnings
The research that got sick veterans treatment
Study finds that on-demand wage access boosts savings and financial engagement for low-wage workers
Antarctica has lost 10 times the size of Greater Los Angeles in ice over 30 years
Scared of spiders? The real horror story is a world without them
New study moves nanomedicine one step closer to better and safer drug delivery
Illinois team tests the costs, benefits of agrivoltaics across the Midwest
Highly stable self-rectifying memristor arrays: Enabling reliable neuromorphic computing via multi-state regulation
Composite superionic electrolytes for pressure-less solid-state batteries achieved by continuously perpendicularly aligned 2D pathways
Exploring why some people may prefer alcohol over other rewards
How expectations about artificial sweeteners may affect their taste
[Press-News.org] No evidence that people alter daily travel after having symptoms that could be COVID-19New George Mason University College of Health and Human Services study is one of first individual-level studies to track movements and symptoms during the COVID-19 pandemic