Ancient genomes trace the origin and decline of the Scythians
2021-03-26
(Press-News.org) Because of their interactions and conflicts with the major contemporaneous civilizations of Eurasia, the Scythians enjoy a legendary status in historiography and popular culture. The Scythians had major influences on the cultures of their powerful neighbors, spreading new technologies such as saddles and other improvements for horse riding. The ancient Greek, Roman, Persian and Chinese empires all left a multitude of sources describing, from their perspectives, the customs and practices of the feared horse warriors that came from the interior lands of Eurasia.
Still, despite evidence from external sources, little is known about Scythian history. Without a written language or direct sources, the language or languages they spoke, where they came from and the extent to which the various cultures spread across such a huge area were in fact related to one another, remain unclear.
The Iron Age transition and the formation of the genetic profile of the Scythians
A new study published in Science Advances by an international team of geneticists, anthropologists and archeologists lead by scientists from the Archaeogenetics Department of the Max Planck Institute for the Science of Human History in Jena, Germany, helps illuminate the history of the Scythians with 111 ancient genomes from key Scythian and non-Scythian archaeological cultures of the Central Asian steppe. The results of this study reveal that substantial genetic turnovers were associated with the decline of the long-lasting Bronze Age sedentary groups and the rise of Scythian nomad cultures in the Iron Age. Their findings show that, following the relatively homogenous ancestry of the late Bronze Age herders, at the turn of the first millennium BCE, influxes from the east, west and south into the steppe formed new admixed gene pools.
The diverse peoples of the Central Asian Steppe
The study goes even further, identifying at least two main sources of origin for the nomadic Iron Age groups. An eastern source likely originated from populations in the Altai Mountains that, during the course of the Iron Age, spread west and south, admixing as they moved. These genetic results match with the timing and locations found in the archeological record and suggest an expansion of populations from the Altai area, where the earliest Scythian burials are found, connecting different renowned cultures such as the Saka, the Tasmola and the Pazyryk found in southern, central and eastern Kazakhstan respectively. Surprisingly, the groups located in the western Ural Mountains descend from a second separate, but simultaneous source. Contrary to the eastern case, this western gene pool, characteristic of the early Sauromatian-Sarmatian cultures, remained largely consistent through the westward spread of the Sarmatian cultures from the Urals into the Pontic-Caspian steppe.
The decline of the Scythian cultures associated with new genetic turnovers
The study also covers the transition period after the Iron Age, revealing new genetic turnovers and admixture events. These events intensified at the turn of the first millennium CE, concurrent with the decline and then disappearance of the Scythian cultures in the Central Steppe. In this case, the new far eastern Eurasian influx is plausibly associated with the spread of the nomad empires of the Eastern steppe in the first centuries CE, such as the Xiongnu and Xianbei confederations, as well as minor influxes from Iranian sources likely linked to the expansion of Persian-related civilization from the south.
Although many of the open questions on the history of the Scythians cannot be solved by ancient DNA alone, this study demonstrates how much the populations of Eurasia have changed and intermixed through time. Future studies should continue to explore the dynamics of these trans-Eurasian connections by covering different periods and geographic regions, revealing the history of connections between west, central and east Eurasia in the remote past and their genetic legacy in present day Eurasian populations.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-26
'A persistent and troubling rural disadvantage'
Strategies needed to support rural Americans
CHICAGO ---Heart failure deaths are persistently higher in rural areas of the United States compared with urban areas, reports a new Northwestern Medicine study. The research also showed race disparities in heart failure are prevalent in rural and urban areas with greatest increases among Black adults under 65 years old.
Heart failure deaths have been increasing nationally since 2011, but there is significant geographic variation in these patterns based on race.
"This work demonstrates a persistent and troubling rural disadvantage with significantly higher rates of death in rural areas compared with urban areas," said lead study author Dr. Sadiya ...
2021-03-26
University of Maryland School of Medicine (UMSOM) researchers have identified the most toxic proteins made by SARS-COV-2--the virus that causes COVID-19 - and then used an FDA-approved cancer drug to blunt the viral protein's detrimental effects. In their experiments in fruit flies and human cell lines, the team discovered the cell process that the virus hijacks, illuminating new potential candidate drugs that could be tested for treating severe COVID-19 disease patients. Their findings were published in two studies simultaneously on March XX in Cell & Bioscience, a Springer Nature journal.
"Our work suggests there is a way to prevent SARS-COV-2 from injuring the body's tissues and doing extensive damage," says senior author of ...
2021-03-26
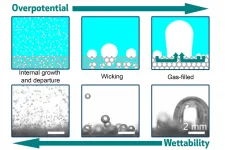
Using electricity to split water into hydrogen and oxygen can be an effective way to produce clean-burning hydrogen fuel, with further benefits if that electricity is generated from renewable energy sources. But as water-splitting technologies improve, often using porous electrode materials to provide greater surface areas for electrochemical reactions, their efficiency is often limited by the formation of bubbles that can block or clog the reactive surfaces.
Now, a study at MIT has for the first time analyzed and quantified how bubbles form on these porous electrodes. The researchers have found that there are three different ways bubbles can form on and depart from the surface, and that these can be precisely controlled ...
2021-03-26
Limerick, Ireland, 26 March 2020: Researchers at Lero, the Science Foundation Ireland Research Centre for Software and University of Limerick (UL), have found video gamers can significantly improve their esport skills by training for just 10 minutes a day.
The research team at Lero's Esports Science Research Lab (ESRL) at UL also found novice gamers benefited most when they wore a custom headset delivering transcranial Direct Current Stimulation (tDCS) for 20 minutes before training sessions.
Dr Mark Campbell, director of Lero's Esports Science Research Lab (ESRL) and senior lecturer in sports psychology at UL, said their work showed that neurostimulation could accelerate motor performance improvements specifically in novice esports ...
2021-03-26
Patients with lupus are more likely to have metabolic syndrome and insulin resistance - both factors linked to heart disease - if they have lower vitamin D levels, a new study reveals.
Researchers believe that boosting vitamin D levels may improve control of these cardiovascular risk factors, as well as improving long-term outcomes for patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE).
Given that photosensitivity is a key feature of SLE, the scientists say that a combination of avoiding the sun, using high-factor sunblock and living in more northerly ...
2021-03-26
What The Study Did: Insurance claims were used to assess patterns of telehealth use across surgical specialties before and during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Authors: Grace F.Chao, M.D., M.Sc., of the National Clinician Scholars Program at the University of Michigan and Veterans Affairs Ann Arbor in Michigan, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamasurg.2021.0979)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest and funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions ...
2021-03-26
What The Study Did: This article discusses possible pathogenic mechanisms of brain dysfunction in patients with COVID-19.
Authors: Maura Boldrini, M.D., Ph.D., of the New York State Psychiatric Institute, Columbia University Irving Medical Center in New York, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2021.0500)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial ...
2021-03-26
Bariatric surgery can significantly reduce the risk of cancer--and especially obesity-related cancers--by as much as half in certain individuals, according to a study by researchers at Rutgers Robert Wood Johnson Medical School's Center for Liver Diseases and Liver Masses.
The research, published in the journal Gastroenterology, is the first to show bariatric surgery significantly decreases the risk of cancer in individuals with severe obesity and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). The risk reduction is even more pronounced in individuals with NAFLD-cirrhosis, the researchers say.
"We knew that obesity leads to certain problems, including cancer, but no one ...
2021-03-26
The alarm bells began ringing when dozens of eagles were found dead near an Arkansas lake.
Their deaths--and, later, the deaths of other waterfowl, amphibians and fish--were the result of a neurological disease that caused holes to form in the white matter of their brains. Field and laboratory research over nearly three decades has established the primary clues needed to solve this wildlife mystery: Eagle and waterfowl deaths occur in late fall and winter within reservoirs with excess invasive aquatic weeds, and birds can die within five days after arrival.
But until recently, the toxin that caused the disease, vacuolar myelinopathy, was unknown.
Now, after years spent identifying a new toxic blue-green algal (cyanobacteria) species and isolating ...
2021-03-26
PITTSBURGH, March 26, 2021 - As evidence mounts supporting the use of monoclonal antibody treatment to reduce hospitalizations and deaths from COVID-19, UPMC and University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine physician-scientists are sharing the health system's experience administering the life-saving medication.
In a report published today in the scientific journal Open Forum Infectious Diseases, the UPMC/Pitt team shares how it quickly established the largest and most equitable distribution network for COVID-19 monoclonal antibody infusions across Pennsylvania. The team today also reported preliminary results confirming the treatment reduced likelihood of hospitalization ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Ancient genomes trace the origin and decline of the Scythians