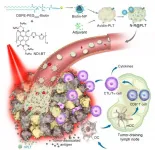
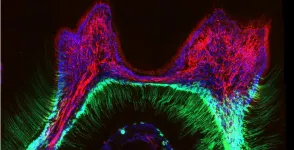
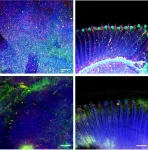
Signals from muscle protect from dementia
Scientists at St. Jude are studying how signals sent from skeletal muscle affect the brain
2021-03-26
(Press-News.org) How do different parts of the body communicate? Scientists at St. Jude are studying how signals sent from skeletal muscle affect the brain.
The team studied fruit flies and cutting-edge brain cell models called organoids. They focused on the signals muscles send when stressed. The researchers found that stress signals rely on an enzyme called Amyrel amylase and its product, the disaccharide maltose.
The scientists showed that mimicking the stress signals can protect the brain and retina from aging. The signals work by preventing the buildup of misfolded protein aggregates. Findings suggest that tailoring this signaling may potentially help combat neurodegenerative conditions like age-related dementia and Alzheimer's disease.
"We found that a stress response induced in muscle could impact not only the muscle but also promote protein quality control in distant tissues like the brain and retina," said Fabio Demontis, PhD, of St. Jude Developmental Neurobiology. "This stress response was actually protecting those tissues during aging."
INFORMATION:
Cell Metabolism published a report on this work.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-26
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) is underestimating methane emissions from oil and gas production in its annual Inventory of U.S. Greenhouse Gas Emissions and Sinks, according to new research from the Harvard John A. Paulson School of Engineering and Applied Sciences (SEAS). The research team found 90 percent higher emissions from oil production and 50 percent higher emissions for natural gas production than EPA estimated in its latest inventory.
The paper is published in the journal Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics.
The research team, led by Joannes Maasakkers, a former graduate student at SEAS, developed a method to trace and map ...
2021-03-26
Australian researchers have discovered a new way to target an aggressive childhood cancer, neuroblastoma, one of the most common and dangerous cancers in young children.
The discovery may also have important implications for some other aggressive cancers in children, including certain brain tumours, as well as some adult cancers, including ovarian and prostate cancer.
The new research, led by scientists at Children's Cancer Institute and published in Nature Communications, has discovered that a cellular protein called ALYREF plays a crucial role in accelerating the effects of the cancer driver gene, MYCN, in neuroblastoma.
Scientists have known for some time that the one third of children with neuroblastoma who have ...
2021-03-26
Tumor targeting and intratumoral penetration are long-standing issues for cancer therapeutics.
Researchers from the Institute of Process Engineering (IPE) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences and the University of Chinese Academy of Sciences (UCAS) have developed a new platelet-based formulation which demonstrated potent therapeutic effects against cancer in murine models.
The scientists utilized the aggregation and activation features of the platelets to address issues of tumor targeting and intratumoral penetration. Upon carrying photothermal nanoparticles and immunostimulators, this biomimetic formulation also achieves an efficient combination therapy against multiple types of cancer.
This study was published in Science Advances on March 26.
Recently, photothermal ...
2021-03-26
One million species are under threat of extinction worldwide, primarily due to adverse human impact. The loss of a species is an ethical tragedy, but additionally, it can have dramatic effects on the functioning of ecosystems on Earth. In each ecosystem, species have their roles, just like actors do in a play. These roles depend on the characteristics of the species, like their size, weight, shape, reproductive capacity, or the food resources they use. If some species are similar, they can sometimes substitute each other and keep the ecosystem going even if one of them is lost. However, the accumulated ...
2021-03-26
For people with tooth decay, drinking a cold beverage can be agony.
"It's a unique kind of pain," says David Clapham, vice president and chief scientific officer of the Howard Hughes Medical Institute (HHMI). "It's just excruciating."
Now, he and an international team of scientists have figured out how teeth sense the cold and pinpointed the molecular and cellular players involved. In both mice and humans, tooth cells called odontoblasts contain cold-sensitive proteins that detect temperature drops, the team reports March 26, 2021, in the journal Science Advances. Signals from these cells can ultimately trigger a jolt of pain to the brain.
The work offers an explanation for how one ...
2021-03-26
Because of their interactions and conflicts with the major contemporaneous civilizations of Eurasia, the Scythians enjoy a legendary status in historiography and popular culture. The Scythians had major influences on the cultures of their powerful neighbors, spreading new technologies such as saddles and other improvements for horse riding. The ancient Greek, Roman, Persian and Chinese empires all left a multitude of sources describing, from their perspectives, the customs and practices of the feared horse warriors that came from the interior lands of Eurasia.
Still, despite evidence from external sources, little is known about Scythian history. Without a written ...
2021-03-26
'A persistent and troubling rural disadvantage'
Strategies needed to support rural Americans
CHICAGO ---Heart failure deaths are persistently higher in rural areas of the United States compared with urban areas, reports a new Northwestern Medicine study. The research also showed race disparities in heart failure are prevalent in rural and urban areas with greatest increases among Black adults under 65 years old.
Heart failure deaths have been increasing nationally since 2011, but there is significant geographic variation in these patterns based on race.
"This work demonstrates a persistent and troubling rural disadvantage with significantly higher rates of death in rural areas compared with urban areas," said lead study author Dr. Sadiya ...
2021-03-26
University of Maryland School of Medicine (UMSOM) researchers have identified the most toxic proteins made by SARS-COV-2--the virus that causes COVID-19 - and then used an FDA-approved cancer drug to blunt the viral protein's detrimental effects. In their experiments in fruit flies and human cell lines, the team discovered the cell process that the virus hijacks, illuminating new potential candidate drugs that could be tested for treating severe COVID-19 disease patients. Their findings were published in two studies simultaneously on March XX in Cell & Bioscience, a Springer Nature journal.
"Our work suggests there is a way to prevent SARS-COV-2 from injuring the body's tissues and doing extensive damage," says senior author of ...
2021-03-26
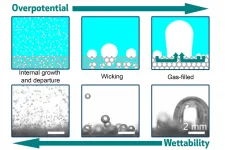
Using electricity to split water into hydrogen and oxygen can be an effective way to produce clean-burning hydrogen fuel, with further benefits if that electricity is generated from renewable energy sources. But as water-splitting technologies improve, often using porous electrode materials to provide greater surface areas for electrochemical reactions, their efficiency is often limited by the formation of bubbles that can block or clog the reactive surfaces.
Now, a study at MIT has for the first time analyzed and quantified how bubbles form on these porous electrodes. The researchers have found that there are three different ways bubbles can form on and depart from the surface, and that these can be precisely controlled ...
2021-03-26
Limerick, Ireland, 26 March 2020: Researchers at Lero, the Science Foundation Ireland Research Centre for Software and University of Limerick (UL), have found video gamers can significantly improve their esport skills by training for just 10 minutes a day.
The research team at Lero's Esports Science Research Lab (ESRL) at UL also found novice gamers benefited most when they wore a custom headset delivering transcranial Direct Current Stimulation (tDCS) for 20 minutes before training sessions.
Dr Mark Campbell, director of Lero's Esports Science Research Lab (ESRL) and senior lecturer in sports psychology at UL, said their work showed that neurostimulation could accelerate motor performance improvements specifically in novice esports ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Signals from muscle protect from dementia
Scientists at St. Jude are studying how signals sent from skeletal muscle affect the brain