Plants remember drought
2021-03-29
(Press-News.org) "I've been studying how plants regulate their water balance for over 35 years. To find a completely new and unexpected way for saving water has certainly been one of the most surprising discoveries in my life." So says Professor Rainer Hedrich, plant scientist and biophysicist from Julius-Maximilians-Universität (JMU) Würzburg in Bavaria, Germany.
Hedrich's group discovered this new strategy together with researchers from the University of Adelaide in Australia. The results have been published in the journal Nature Communications.
GABA quantity as stress memory
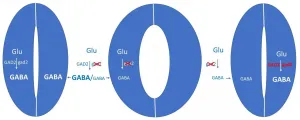
The publication shows: plants use the signalling molecule GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid) to remember the dryness of a day. The drier it is, the more GABA accumulates in the plant tissue during the day. And the next morning, the amount of GABA determines how wide the plant opens its leaf pores. The opening width of these pores can limit water loss.
GABA is a signalling molecule that also occurs in humans and animals: there it is a messenger substance of the nervous system. Plants have no nerve cells and no brain. And yet GABA is now also found in them in connection with memory-like processes.
Rainer Hedrich names another connection: Short-term memory, which the carnivorous Venus flytrap uses to count the number of times its prey touches it, depends on the calcium level in the cell. And it is the calcium level that regulates the enzymatic biosynthesis of GABA in plants.
Low water needs, high drought tolerance
The GABA effect has been demonstrated in various crops, as Professor Matthew Gilliham of the University of Adelaide explains: "Under the influence of GABA, barley, broad beans and soybeans, for example, close their leaf pores." Laboratory plants that produce more GABA due to mutations also react in this way. In experiments, these mutants need less water and survive drought longer.
Scientists know of other signalling substances in plants that cause the leaf pores to close. But GABA relies on a completely different mechanism of action, explains the lead author of the publication, Dr Bo Xu from the Australian Research Council Centre of Excellence in Plant Energy Biology.
Drought-tolerant plants for the future
Insights into the water-saving mechanisms and drought tolerance of plants are becoming increasingly important in times of climate change. For some years now, increasing heat and drought have been affecting many crops. The earth's water resources that can be used for agriculture are also threatened. Mankind is therefore likely to be increasingly dependent on new varieties that still produce good yields with as little water as possible.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-29
Applied physicists at the University of Sydney have proposed new standards to measure moisture leaks into bionic devices such as pacemakers, cochlear hearing implants and retinal replacements.
The researchers, who received an industry partnership funding through the Australian Research Council to undertake the study, say the new moisture standards could give the wearers of bionic implants extra confidence in the operation of the life-changing devices. They also say that the improved moisture-testing regime could be used in the emerging renewable energy industry where new-generation solar cells require high standards of humidity control.
Bionic implants must be able to operate successfully in moist environments ...
2021-03-29
Scientists reported new research results today suggesting that artificial objects in orbit around the Earth are brightening night skies on our planet significantly more than previously understood.
The research, accepted for publication in Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society: Letters, finds that the number of objects orbiting Earth could elevate the overall brightness of the night sky by more than 10 percent above natural light levels across a large part of the planet. This would exceed a threshold that astronomers set over 40 years ago for considering a location "light polluted".
"Our primary motivation was to estimate the potential contribution to night sky brightness from external sources, such ...
2021-03-29
A team of scientists led by Nanyang Technological University, Singapore (NTU Singapore) has developed a diagnostic test that can detect the virus that causes COVID-19 even after it has gone through mutations.
Called the VaNGuard (Variant Nucleotide Guard) test, it makes use of a gene-editing tool known as CRISPR, which is used widely in scientific research to alter DNA sequences and modify gene function in human cells under lab conditions, and more recently, in diagnostic applications.
Since viruses have the ability to evolve over time, a diagnostic test robust against potential mutations ...
2021-03-29
Scientists at MIPT have found a possible explanation for the anomalously fast release of gas from nuclear fuel. Supercomputer simulations have uncovered an unexpected mechanism for accelerating the escape of gas bubbles from the uranium dioxide crystal matrix to the surface. The result points the way to eliminate the paradoxical discrepancy of several orders of magnitude between existing theoretical models and experimental results. The paper was published in the Journal of Nuclear Materials.
The diffusion of gas bubbles during reactor operation is one of the important topics in nuclear power relating to radiation safety. Bubbles of gaseous fission products (mainly xenon), accumulating in the fuel, affect many of its properties. Therefore, it is important, ...
2021-03-29
Researchers at the University of Southampton have developed a new way of using nanomaterials to identify and enrich skeletal stem cells - a discovery which could eventually lead to new treatments for major bone fractures and the repair of lost or damaged bone.
Working together, a team of physicists, chemists and tissue engineering experts used specially designed gold nanoparticles to 'seek out' specific human bone stem cells - creating a fluorescent glow to reveal their presence among other types of cells and allow them to be isolated or 'enriched'.
The researchers concluded their new technique is simpler and quicker than other methods and up to 50-500 times more effective at enriching stem cells.
The study, led by Professor ...
2021-03-29
The vast majority of the world's largest meat and dairy companies have not made an explicit commitment to achieving net-zero emissions by 2050, finds a new analysis by researchers at New York University.
The study, which appears in the journal Climatic Change, examines the climate impacts of the biggest 35 largest meat and dairy companies around the globe as well as their influence in shaping political responses to climate change.
It is the first peer-reviewed study to assess climate responsibilities of the largest meat and dairy companies.
"Large meat and dairy companies are not doing enough to tackle climate change, and countries are not doing enough in terms of holding them accountable," says Jennifer ...
2021-03-29
Research into the flower preferences of pollinating moths may have delivered a vital clue to the simple factors needed for the emergence of new species.
Strong coevolutionary relationships between plants and animal pollinators have long been recognised as a potential driver of high rates of speciation in the 275,000 extant flowering plants.
Shifts between pollinators, such as bumblebees, hummingbirds, hawkmoths and bats, often coincide with plant speciation events.
Each of these pollinator "guilds" is attracted by a different set of floral traits such as colour, patterns, scent, shape, and nectar reward, collectively known as a pollination ...
2021-03-29
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. -- Why do some people with cold sores around their lips experience painful lesions, while others have no symptoms at all, yet still spread the virus? A new study conducted at Penn State finds that these differences could be due to variations in the way certain strains of herpes simplex (HSV-1) -- the virus that causes cold sores, as well as genital herpes -- activate gene expression in neurons.
"HSV-1 occurs in more than half the global population," said Moriah Szpara, associate professor of biology and biochemistry and molecular biology. "Not only does it cause recurrent problems, such as cold sores ...
2021-03-29
Transition metal perovskites oxides exhibit several desirable properties, including high-temperature superconductivity and electrocatalysis. Now, scientists at Tokyo Institute of Technology explore the structure and properties of a perovskite oxide, PbFeO3, in anticipation of the unusual charge distribution and exotic magnetic transitions displayed by such systems. They report two of the magnetic transitions, with a distinctive transition above room temperature and look into its causes, opening doors to potential applications in realizing new spintronic devices.
The advent of electronics has revolutionized our lives to an extent where it is impossible to imagine going about our day without relying on an electronic device in some form. What is even more remarkable, ...
2021-03-29
In a new publication from Cardiovascular Innovations and Applications; DOI https://doi.org/10.15212/CVIA.2021.0008, Zeyi Cheng, Miaomiao Qi, Chengyuan Zhang and Yanxia Mao from Sichuan University, Sichuan, China, Second Hospital of Lanzhou University, Lanzhou, China and The Second Medical School of Lanzhou University, Lanzhou, China consider myocardial fibrosis in the pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy.
The authors review the application of myocardial fibrosis in the diagnosis and treatment of HCM, focusing on research progress and the application ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Plants remember drought