(Press-News.org) Chestnut Hill, MA (4/1/2021) - A gender gap in negotiation emerges as early as age eight, a finding that sheds new light on the wage gap women face in the workforce, according to new research from Boston College's Cooperation Lab, lead by Associate Professor of Psychology and Neuroscience Katherine McAuliffe.
The study of 240 boys and girls between ages four and nine, published recently in the journal Psychological Science, found the gap appears when girls who participated in the study were asked to negotiate with a male evaluator, a finding that mirrors the dynamics of the negotiation gap that persists between men and women in the workforce.
The researchers say this study is the first to identify a gender gap in negotiation among children.
"We found that--consistent with adult work--girls asked for less than boys when negotiating with a man," said McAuliffe. "We did not see this gender gap when children were negotiating with a woman. There is still much more work to be done, but one thing this tells us is that we should be teaching young girls to advocate for themselves in the context of negotiation from as early elementary school."
The results point to a disparity that takes root in childhood which may help explain the well-documented gender gap in pay that separates women and men, said McAuliffe, who co-authored the study with New York University graduate student Sophie Arnold, who spent two summers working in McAuliffe's Cooperation Lab, which studies how attributes like fairness develop in children.
McAuliffe and Arnold say the findings reveal a need to determine if cultural signals sent to girls are to blame and whether there should be interventions in childhood to ensure that both girls and boys feel comfortable advocating for themselves, regardless of the gender of the person they are talking with.
"Boys and girls performed equally between the ages of four and seven," said Arnold, whose work on the project became her undergraduate honors thesis at the University of Chicago. "But by age eight, we see girls are requesting less than boys when they are negotiating with a man. It's not that girls are negotiating less overall - it's only when children are negotiating with a man that we see these gender differences emerge."
Prior studies of adults have found gender differences in negotiation, but could not explain their origins, said the authors. The researchers tested 240 children between the ages of 4 and 9 to determine whether girls in the age range would negotiate differently than boys and whether girls, like women, would ask for less from a man than a woman.
"Although adult research supports the existence of gender differences in negotiation, it cannot reveal their origins. Learning when these gender differences emerge is imperative for understanding what individual and societal factors lead to these gender differences in adulthood," write Arnold and McAuliffe.
The experiments were modeled on real-world scenarios, the authors said. In phase one, children completed a task and then were allowed to ask for as many stickers as they liked as a reward. Unbeknownst to them, the evaluator would always accept requests for two stickers or less, and always reject requests above that threshold. If a request was rejected, negotiations would progress to the next phase.
In the second phase, the evaluator explained the rules of negotiation to the children and spelled out how their next sticker requests could be handled in a way that highlighted the risk and reward inherent to negotiations.
The results revealed a significant interaction between age, participant gender, and evaluator gender. For girls, the number of stickers initially requested decreased with age when the evaluator was a male. When the evaluator was female, girls requested more stickers with age.
Boys, on the other hand, made requests that did not change with age or the gender of the evaluator.
In measuring persistence, a proxy for negotiation length, the study found that girls' persistence decreased with age when the evaluator was male, but remained the same with age when the evaluator was female. For boys, persistence did not change with age or depending on the gender of the evaluator.
"Our study is the first to show that gender differences in negotiation emerge in childhood," the co-authors write. "Older girls in our paradigm differed from boys in how much they were willing to ask for from a male evaluator, showing a striking resemblance to findings in adults. Girls are not asking for less from both evaluators but instead are negotiating less only with the male evaluator."
"Our findings add negotiation to the list of early-developing gendered behaviors that may lead to and magnify the wage gap in adulthood," the researchers report.
McAuliffe said the next steps in this area of study include trying to determine why these differences emerge.
She and Arnold highlighted two potential avenues for future research: status and gender stereotypes. It could be the case that the gender differences observed in this study are not unique to gender but reflect a more general dynamic due to perceived status of social groups. Namely, that individuals perceived to be a part of a lower status group (in the US, with respect to gender, this would be girls or women) request less from individuals who are perceived to be part of a higher status group (men).
With respect to gender stereotypes, it could be the case that girls are adopting gender stereotypes about communality or modesty that in turn shape their behavior with men. More research is needed to understand how these avenues contribute to the development of gender differences in negotiation.
The challenge of the next steps in this research are clarifying exactly what explains the development of this behavior and trying to develop interventions that could help remedy the imbalance, said McAuliffe.
INFORMATION:
Statement Highlights:
Two-thirds of people with heart disease are ages 60 and older.
People who have had a heart attack or stroke are 20 times more likely to have additional cardiac events compared to people without heart disease.
Lifestyle modifications and medication adherence are key strategies to address heart disease.
Mobile health technology, which incorporates apps, devices, texting and phone calls, can inform and monitor older adults to support lifestyle modifications.
DALLAS, April 1, 2021 -- Mobile health technology can be beneficial in encouraging lifestyle behavior changes and medication adherence among adults ages 60 and older with existing heart disease, yet more research is needed to determine what methods are the most effective, according to a new scientific statement ...
New research, led by scientists at the University of Nottingham, suggests that the environment in which men live may affect their reproductive health.
The research, published in Scientific Reports, looked at the effects of geographical location on polluting chemicals found in dog testes, some of which are known to affect reproductive health. The unique research focused on dogs because, as a popular pet, they share the same environment as people and are effectively exposed to the same household chemicals as their owners.
The team also looked for signs of abnormalities ...
It is well known that climate-induced sea level rise is a major threat. New research has found that previous ice loss events could have caused sea-level rise at rates of around 3.6 metres per century, offering vital clues as to what lies ahead should climate change continue unabated.
A team of scientists, led by researchers from Durham University, used geological records of past sea levels to shed light on the ice sheets responsible for a rapid pulse of sea-level rise in Earth's recent past.
Geological records tell us that, at the end of the last ice age around 14,600 years ago, sea levels rose at ten times the current rate due to Meltwater Pulse 1A (MWP-1A); a 500 year, ~18 metre sea-level rise event.
Until now, the scientific community has not ...
Genome sequencing of thousands of SARS-CoV-2 samples shows that surges of COVID-19 cases are driven by the appearance of new coronavirus variants, according to new research from the School of Veterinary Medicine at the University of California, Davis published April 1 in Scientific Reports.
"As variants emerge, you're going to get new outbreaks," said Bart Weimer, professor of population health and reproduction at the UC Davis School of Veterinary Medicine. The merger of classical epidemiology with genomics provides a tool public health authorities could use to predict the course of pandemics, whether of coronavirus, influenza or some new pathogen.
Although it has just 15 genes, SARS-CoV-2 is constantly mutating. Most of these changes make very little ...
Hamilton, ON (April 1, 2021) - People living with the often-debilitating effects of Crohn's disease may finally gain some relief, thanks to ground-breaking research led by McMaster University.
McMaster investigator Brian Coombes said his team identified a strain of adherent-invasive E-coli (AIEC) that is strongly implicated in the condition and is often found in the intestines of people with Crohn's disease.
"If you examine the gut lining of patients with Crohn's disease, you will find that around 70 to 80 per cent of them test positive for AIEC bacteria, but one of the things we don't understand is why," said Coombes, professor and chair of the Department of Biochemistry and ...
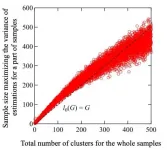
Ishikawa, Japan - Any high-performance computing should be able to handle a vast amount of data in a short amount of time -- an important aspect on which entire fields (data science, Big Data) are based. Usually, the first step to managing a large amount of data is to either classify it based on well-defined attributes or--as is typical in machine learning--"cluster" them into groups such that data points in the same group are more similar to one another than to those in another group. However, for an extremely large dataset, which can have trillions of sample points, it is tedious to even group data points into a single cluster without huge memory requirements.
"The problem can be formulated as follows: Suppose we have a clustering tool that ...
The kangaskhan, Australia's only species of endemic Pokemon in Pokemon Go, is commonly poached within its natural habitat by Pokemon trainers for use in fighting contests
Researchers used several species distribution modeling algorithms to predict how climate change, on top of the already existing human-induced pressures, would impact the distribution of the kangaskhan in the future
In addition to this, they found a way to measure how biased commonly used species distribution models are, and found that some models are so biased that their results weren't influenced by the data at all
The ...
Obesity rates have increased dramatically in developed countries over the past 40 years -- and many people have assumed that food marketing is at least in part to blame. But are people with obesity really more susceptible to food marketing? And if they are, is that a permanent predisposition, or can it change over time?
According to a new study by UBC Sauder School of Business Assistant Professor Dr. Yann Cornil (he/him/his) and French researchers, people with obesity do tend to be more responsive to food marketing -- but when their weight drops significantly, so does their responsiveness to marketing.
For the study, which was published in the Journal of Consumer Psychology, the researchers followed three groups: patients with severe ...
Oak Brook, IL - The April edition of SLAS Discovery is a special issue on advances in protein degradation curated by guest editors M. Paola Castaldi, Ph.D., and Stewart L. Fisher, Ph.D.
Targeted protein degradation has generated interest within the drug discovery arena due to the inhibition of one particular function of a protein not often delivering the successful results that comes from whole-protein depletion. The pharmacology of PROTACs present challenges, however, namely for the development of orally bioavailable drugs. In the article "Target Validation Using PROTACs: Applying the Four Pillars Framework" authors Rados?aw P. Nowak, Ph.D., and Lyn H. Jones, Ph.D., describe the application of a translational pharmacology framework (the four pillars) ...
Oak Brook, IL - The April edition of SLAS Technology features the cover article "Therapeutic Potential of Reactive Oxygen Species: State of the Art and Recent Advances" by Valeria Graceffa, Ph.D. (Institute of Technology Sligo, Sligo, Ireland).
The cover article explores the therapeutic potential of reactive oxygen species (ROS) including applications ranging from wound healing and hair growth enhancement, to cancer treatment, stem cell differentiation and tissue engineering. At low concentrations, ROS can be utilized as inexpensive and convenient inducers of tissue regeneration, triggering stem cell differentiation and enhancing collagen synthesis. Recent cancer studies have represented ROS as the 'Achilles Heels' of cancers given their high basal levels, leaving ...