Fungi could manipulate bacteria to enrich soil with nutrients
Researchers have discovered a group of soil bacteria that could yield alternatives to conventional fertilizers for enriching soil and improving crop yields
2021-04-02
(Press-News.org) ITHACA, NY, April 2, 2021 - A team of researchers from the Boyce Thompson Institute (BTI) has discovered a distinct group of bacteria that may help fungi and plants acquire soil nutrients. The findings could point the way to cost-effective and eco-friendly methods of enriching soil and improving crop yields, reducing farmers' reliance on conventional fertilizers.
Researchers know that arbuscular mycorrhizal (AM) fungi establish symbiotic relationships with the roots of 70% of all land plants. In this relationship, plants trade fatty acids for the fungi's nitrogen and phosphorus. However, AM fungi lack the enzymes needed to free nitrogen and phosphorus from complex organic molecules.
A trio of BTI scientists led by END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
How pathogenic bacteria weather the slings and arrows of infection
2021-04-02
Infectious diseases are a leading cause of global mortality. During an infection, bacteria experience many different stresses -- some from the host itself, some from co-colonizing microbes and others from therapies employed to treat the infection. In this arms race to outwit their competition, bacteria have evolved mechanisms to stay alive in the face of adversities. One such mechanism is the stringent response pathway. Understanding how the activation of the stringent response pathway is controlled can provide clues to treat infection.
In new research published this week online in the journal END ...
Lanternfly's attraction to vertical silhouettes could help monitor, trap it
2021-04-02
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. -- Like moths to a flame, spotted lanternflies are visually drawn toward and seemingly captivated by vertical objects such as utility poles, a behavior that could be valuable in predicting where the pests might be heading, according to entomologists in Penn State's College of Agricultural Sciences.
Research from the laboratory of Tom Baker, recently published in the Journal of Insect Behavior, is laying the foundation for future strategies to monitor and possibly trap the invasive insect from Asia, which first was found in North America in Berks County, Pennsylvania, in 2014. The planthopper now is confirmed in 34 Pennsylvania counties and several surrounding states.
These findings show that telephone poles attract flight-dispersing ...
Toddler TV time not to blame for attention problems
2021-04-02
Acomprehensive review published in the journal Psychological Science re-examines previous work that claimed to show a direct link between early screen time and attention problems in children. Although other studies do not reflect these findings, the earlier research continues to be widely reported by the media.
"The findings from the original study, upon further scrutiny, are not borne out. We found that there is still no evidence that TV, by itself, causes ADHD or any kind of attention problems in young children," said Wallace E. Dixon, Jr., a professor of psychology ...
Baby aspirin linked to lower risk of colorectal cancer death
2021-04-02
Long-term, regular use of baby aspirin--at least 15 times per month--prior to a diagnosis of colorectal cancer (CRC) may reduce the risk of death from the disease by limiting the spread of cancerous tumors pre-diagnosis, according to a study led by Cedars-Sinai Cancer researchers.
While previous research has offered consistent evidence that low-dose aspirin use reduces colorectal cancer risk, key findings from the study, published in the peer-reviewed Journal of the National Cancer Institute, revealed that the use of baby aspirin prior to the diagnosis of non-metastatic CRC was associated with a lower rate of metastasis, or tumor spread. Starting ...
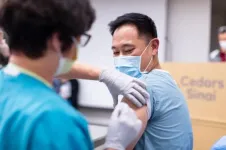
COVID-19 survivors might need just one dose of two-part vaccine
2021-04-02
LOS ANGELES (April 1, 2021) -- A single dose of the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine for individuals who previously had COVID-19 generates an immunologic response similar to that of individuals receiving the two-dose recommended sequence, according to a Cedars-Sinai study published today by the journal Nature Medicine.
"Our findings extend those from smaller studies reported elsewhere and support a potential strategy of providing a single dose of vaccine to persons with a confirmed prior history of coronavirus infection, along with two doses for people not previously infected," said Susan Cheng, MD, MPH, MMSc, associate professor of Cardiology and director of Public Health Research at ...
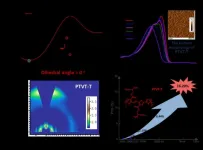
A PTV-based polymer enabled organic solar cells with over 16% efficiency
2021-04-02
Organic solar cell (OSC) is one of the most important green energy technologies. The photovoltaic efficiencies of OSCs are closely related to the photoactive layers, which are prepared by blending electron donor and acceptor materials. With the emergence of a large number of new organic photovoltaic materials and effective molecular modification methods, the photovoltaic efficiency of OSCs has been greatly improved. Accordingly, the molecular structure of the materials is becoming much more complex with high costs, which is difficult to meet the requirements of the industrialization of OSCs. Thus, it is of great importance to develop novel photovoltaic ...
Probiotics keep calves healthy, too!
2021-04-02
Scientists in Japan have developed and tested a novel probiotic formulation to control severe diarrhea in calves, ensuring their health and reducing mortality, and in turn reducing economic loss.
The health of calves is a crucial component in animal husbandry; diseases that affect calves cause economic losses to livestock farms either directly, due to death of the calves, or indirectly, due to weight loss that reduces productivity over the animals' lifespans. In Japan, bovine rotavirus (BRV) and bovine cryptosporidiosis infections are major diseases that cause severe diarrhea in calves.
A team of scientists from Hokkaido, including Associate Professor Satoru Konnai of the Faculty of Veterinary Medicine at Hokkaido University, have ...
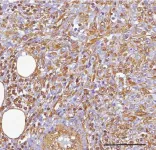
Targeting microRNAs could unmask hidden vulnerability in breast cancer stem cells
2021-04-02
Researchers in Italy have identified a pair of microRNA molecules that help maintain a population of cancerous stem cells that drive the growth of breast cancers and initiate tumor relapse after treatment. The study, which will be published April 2 in the Journal of Cell Biology (JCB), reveals that targeting these microRNAs makes cancer stem cells more susceptible to some chemotherapies and could potentially improve the prognosis of patients with aggressive forms of breast cancer.
Many tumors contain a small population of cancer stem cells that initiate tumor growth and give rise to the various cell types found in tumors. Moreover, because cancer stem cells are often resistant to radio- and chemotherapies, they can survive and promote tumor ...
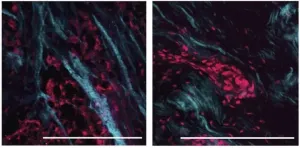
Therapeutic resistance linked to softer tissue environment in breast cancer
2021-04-02
Researchers at the University of California, San Francisco, have discovered that aggressive, triple-negative breast cancers (TNBCs) can evade treatment by reorganizing and softening the collagen matrix that surrounds the cancer cells. The study, which will be published April 2 in the Journal of Experimental Medicine (JEM), shows that the softer matrix activates a signaling pathway that promotes the cancer cells' survival, and suggests that targeting this pathway could enhance the effectiveness of chemo- and radiotherapy in TNBC patients.
TNBC is an aggressive type of breast cancer with worse survival rates than other forms of the disease. Because TNBC cells lack the HER2 signaling ...
Massive X-ray screening identifies promising candidates for COVID drugs
2021-04-02
A team of researchers has identified several candidates for drugs against the coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 at DESY´s high-brilliance X-ray lightsource PETRA III. They bind to an important protein of the virus and could thus be the basis for a drug against Covid-19. In a so-called X-ray screening, the researchers, under the leadership of DESY, tested almost 6000 known active substances that already exist for the treatment of other diseases in a short amount of time. After measuring about 7000 samples, the team was able to identify a total of 37 substances that bind to the main protease (Mpro) of the SARS-CoV-2 virus, as the scientists report online today in the journal ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
New knowledge on heritability paves the way for better treatment of people with chronic inflammatory bowel disease
Under the Lens: Microbiologists Nicola Holden and Gil Domingue weigh in on the raw milk debate
Science reveals why you can’t resist a snack – even when you’re full
Kidney cancer study finds belzutifan plus pembrolizumab post-surgery helps patients at high risk for relapse stay cancer-free longer
Alkali cation effects in electrochemical carbon dioxide reduction
Test platforms for charging wireless cars now fit on a bench
$3 million NIH grant funds national study of Medicare Advantage’s benefit expansion into social supports
Amplified Sciences achieves CAP accreditation for cutting-edge diagnostic lab
Fred Hutch announces 12 recipients of the annual Harold M. Weintraub Graduate Student Award
Native forest litter helps rebuild soil life in post-mining landscapes
Mountain soils in arid regions may emit more greenhouse gas as climate shifts, new study finds
Pairing biochar with other soil amendments could unlock stronger gains in soil health
Why do we get a skip in our step when we’re happy? Thank dopamine
UC Irvine scientists uncover cellular mechanism behind muscle repair
Platform to map living brain noninvasively takes next big step
Stress-testing the Cascadia Subduction Zone reveals variability that could impact how earthquakes spread
We may be underestimating the true carbon cost of northern wildfires
Blood test predicts which bladder cancer patients may safely skip surgery
Kennesaw State's Vijay Anand honored as National Academy of Inventors Senior Member
Recovery from whaling reveals the role of age in Humpback reproduction
Can the canny tick help prevent disease like MS and cancer?
Newcomer children show lower rates of emergency department use for non‑urgent conditions, study finds
Cognitive and neuropsychiatric function in former American football players
From trash to climate tech: rubber gloves find new life as carbon capturers materials
A step towards needed treatments for hantaviruses in new molecular map
Boys are more motivated, while girls are more compassionate?
Study identifies opposing roles for IL6 and IL6R in long-term mortality
AI accurately spots medical disorder from privacy-conscious hand images
Transient Pauli blocking for broadband ultrafast optical switching
Political polarization can spur CO2 emissions, stymie climate action
[Press-News.org] Fungi could manipulate bacteria to enrich soil with nutrientsResearchers have discovered a group of soil bacteria that could yield alternatives to conventional fertilizers for enriching soil and improving crop yields