(Press-News.org) Charles Darwin, the British naturalist who championed the theory of evolution, noted that corals form far-reaching structures, largely made of limestone, that surround tropical islands. He didn't know how they performed this feat.
Now, Rutgers scientists have shown that coral structures consist of a biomineral containing a highly organized organic mix of proteins that resembles what is in our bones. Their study, published in the END
Corals carefully organize proteins to form rock-hard skeletons
Scientists' findings suggest corals will withstand climate change
2021-04-08
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Solar and wind power could mitigate conflict in northeast Africa
2021-04-08
A new study shows that several disagreements between Ethiopia, Sudan and Egypt around Africa's largest hydropower plant, the new Grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam (GERD), could be alleviated by massively expanding solar and wind power across the region. Adapting GERD operation to support grid integration of solar and wind power would provide tangible energy and water benefits to all involved countries, creating regional win-win situations. "Our results call for integrated hydro-solar-wind planning to be taken up in the GERD negotiations," says Sebastian Sterl, energy ...
Regional habitat differences identified for threatened piping plovers on Atlantic coast
2021-04-08
Piping plovers, charismatic shorebirds that nest and feed on many Atlantic Coast beaches, rely on different kinds of coastal habitats in different regions along the Atlantic Coast, according to a new study by the U.S. Geological Survey and U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service.
The Atlantic Coast and Northern Great Plains populations of the piping plover were listed as federally threatened in 1985. The Atlantic coast population is managed in three regional recovery units, or regions: New England, which includes Massachusetts and Rhode Island; Mid-Atlantic, which includes New ...
NIH experts call for accelerated research to address concurrent HIV and COVID-19 pandemics
2021-04-08
WHAT:
The COVID-19 pandemic is affecting people with or at risk for HIV both indirectly, by interfering with HIV treatment and prevention services, and directly, by threatening individual health. An effective response to these dual pandemics requires unprecedented collaboration to accelerate basic and clinical research, as well as implementation science to expeditiously introduce evidence-based strategies into real-world settings. This message comes from a review article co-authored by Anthony S. Fauci, M.D., director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), part of the National Institutes of Health, and colleagues published in the Journal of Infectious Diseases.
By disrupting critical health care services, the COVID-19 pandemic threatens ...
Hospital rankings for complications after spinal fusion are 'unreliable'
2021-04-08
April 8, 2021 - Routinely collected data on patients undergoing spinal fusion surgery do not provide a valid basis for assessing and comparing hospital performance on patient safety outcomes, reports a study in Spine. The journal is published in the Lippincott portfolio by Wolters Kluwer.
At a time when hospitals are increasingly subject to online rankings or "pay-for-performance" reimbursement programs, metrics based on hospital administrative data are "unreliable for profiling hospital performance," concludes the new research by Jacob K. Greenberg, MD, MSCI, of Washington University in St Louis and colleagues. ...
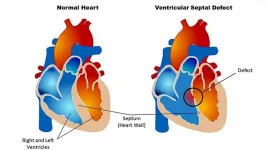
Lifetime monitoring after infant cardiac surgery may reduce adult hypertension risk
2021-04-08
In a medical records study covering thousands of children, a U.S.-Canadian team led by researchers at Johns Hopkins Medicine concludes that while surgery to correct congenital heart disease (CHD) within 10 years after birth may restore young hearts to healthy function, it also may be associated with an increased risk of hypertension -- high blood pressure -- within a few months or years after surgery. ...
UBCO researchers find a new use for waste
2021-04-08
Waste materials from the pulp and paper industry have long been seen as possible fillers for building products like cement, but for years these materials have ended up in the landfill. Now, researchers at UBC Okanagan are developing guidelines to use this waste for road construction in an environmentally friendly manner.
The researchers were particularly interested in wood-based pulp mill fly ash (PFA), which is a non-hazardous commercial waste product. The North American pulp and paper industry generates more than one million tons of ash annually by burning wood in ...
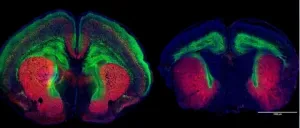
Autism gene study finds widespread impact to brain's growth signaling network
2021-04-08
JUPITER, FL -- Damage to the autism-associated gene Dyrk1a, sets off a cascade of problems in developing mouse brains, resulting in abnormal growth-factor signaling, undergrowth of neurons, smaller-than-average brain size, and, eventually, autism-like behaviors, a new study from Scripps Research, Florida, finds.
The study from neuroscientist Damon Page, PhD, describes a new mechanism underlying the brain undergrowth seen in individuals with Dyrk1a mutations. Page's team used those insights to target the affected pathway with an existing medicine, a growth hormone. It restored normal brain growth in the Dyrk1a mutant mice, Page says.
"As of now, there's simply no targeted treatments available for individuals with autism spectrum ...
'Pain is always a perception': Physical therapy can help prevent, treat opioid use disorder
2021-04-08
When you think of ways to treat opioid use disorder, you might think methadone clinics and Narcotics Anonymous meetings. You probably don't imagine stretches and strengthening exercises.
But Anne Swisher--professor at the West Virginia University School of Medicine--is working to address opioid misuse in an unconventional way: through physical therapy. She and her colleagues have enhanced physical therapy instruction at WVU to emphasize the profession's role in preventing and treating opioid use disorder.
"Students have different interests and passions within the profession, and they find their niche," said Swisher, a researcher and director of scholarship in the Division of Physical Therapy. "No matter what their passion is, there ...
'Emotional' reviews predict business success, new study shows
2021-04-08
EVANSTON, Ill. -- Five-star ratings are no guarantee to lead you to the perfect barber who truly understands your hair or to the espresso machine that brews a perfect cup of coffee.
That's because most products online are now rated positively, making it harder than ever to truly discern whether they will succeed in the marketplace.
A new study from Northwestern University Kellogg School of Management and the University of Massachusetts Boston was able to predict the success of movies, commercials, books and restaurants by relying on the "emotionality" of reviews instead of the star rating.
The researchers explored box office revenue of 2,400 movies, sales of 1.6 million books and real-world reservations at ...
Caught speeding: Clocking the fastest-spinning brown dwarfs
2021-04-08
Astronomers at Western University have discovered the most rapidly rotating brown dwarfs known. They found three brown dwarfs that each complete a full rotation roughly once every hour. That rate is so extreme that if these "failed stars" rotated any faster, they could come close to tearing themselves apart. Identified by NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope, the brown dwarfs were then studied by ground-based telescopes including Gemini North, which confirmed their surprisingly speedy rotation.
Three brown dwarfs have been discovered spinning faster than any other found before. Astronomers at Western University in Canada first measured the rotation speeds of these brown dwarfs using NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope and confirmed them with follow-up ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
New book captures hidden toll of immigration enforcement on families
New record: Laser cuts bone deeper than before
Heart attack deaths rose between 2011 and 2022 among adults younger than age 55
Will melting glaciers slow climate change? A prevailing theory is on shaky ground
New treatment may dramatically improve survival for those with deadly brain cancer
Here we grow: chondrocytes’ behavior reveals novel targets for bone growth disorders
Leaping puddles create new rules for water physics
Scientists identify key protein that stops malaria parasite growth
Wildfire smoke linked to rise in violent assaults, new 11-year study finds
New technology could use sunlight to break down ‘forever chemicals’
Green hydrogen without forever chemicals and iridium
Billion-DKK grant for research in green transformation of the built environment
For solar power to truly provide affordable energy access, we need to deploy it better
Middle-aged men are most vulnerable to faster aging due to ‘forever chemicals’
Starving cancer: Nutrient deprivation effects on synovial sarcoma
Speaking from the heart: Study identifies key concerns of parenting with an early-onset cardiovascular condition
From the Late Bronze Age to today - Old Irish Goat carries 3,000 years of Irish history
Emerging class of antibiotics to tackle global tuberculosis crisis
Researchers create distortion-resistant energy materials to improve lithium-ion batteries
Scientists create the most detailed molecular map to date of the developing Down syndrome brain
Nutrient uptake gets to the root of roots
Aspirin not a quick fix for preventing bowel cancer
HPV vaccination provides “sustained protection” against cervical cancer
Many post-authorization studies fail to comply with public disclosure rules
GLP-1 drugs combined with healthy lifestyle habits linked with reduced cardiovascular risk among diabetes patients
Solved: New analysis of Apollo Moon samples finally settles debate about lunar magnetic field
University of Birmingham to host national computing center
Play nicely: Children who are not friends connect better through play when given a goal
Surviving the extreme temperatures of the climate crisis calls for a revolution in home and building design
The wild can be ‘death trap’ for rescued animals
[Press-News.org] Corals carefully organize proteins to form rock-hard skeletonsScientists' findings suggest corals will withstand climate change