Can a 3D printed beetle model simulate the real thing?
Researchers assess the feasibility of using 3D printed insects in mating studies
2021-04-08
(Press-News.org) When it comes to choosing a partner, humans tend to be attracted by characteristics like personality and common interests. In contrast, insects tend to be a bit shallow, as they choose a mate based on appearance, and in some cases, smells. One example is the leaf beetle, which produces chemical pheromones that are on their cuticles, or the exterior surface of the beetle. They use these 'scents' to assess beetle sex and mating status (whether beetles are sexually mature or not).
Kari Segraves, professor of biology in the College of Arts and Sciences, is interested in researching the chemical and visual signals that contribute to mate selection by these beetles. This work is part of a larger project focused on understanding how new species are formed. By definition, species are related organisms that share common characteristics and are capable of interbreeding. Mating studies are essential in determining the mechanisms that might lead to reproductive barriers between newly formed species.
In the past, she and her colleagues have used a variety of models during these studies, including dead females and even round glass beads. To find a new and improved way of studying these insects, Segraves recently collaborated with Huai-Jun Xue and Si-Qin Ge from the Institute of Zoology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, to design, produce and test 3D printed beetle models to find out if they would be a feasible option when testing mate choice in these and possibly other insects. They believe this novel research to be the first time that 3D printed beetles have been used in mating tests.
According to Segraves, they designed this study after receiving some unusual results in a mating experiment that focused on the chemical signals used by leaf beetles. In that study, they used dead beetles as mating models and swapped the chemical signals between the sexes so that the male model smelled like a female and the female model smelled like a male. Contrary to what they expected, they found that males did not have a preference for female over male chemical signals. This suggested that the trial itself may have been flawed because they had shown that the beetles always preferred females in another experiment that used chemically unaltered dead beetle models. They were concerned that more chemicals were being released after they had washed the dead models and that this was altering the results.
"We thought it would be a good idea to try using 3D printed models instead of dead females because the plastic used in 3D printing doesn't have chemicals that would be confused as mating signals by the beetles," Segraves says. She and fellow researchers from the Chinese Academy of Sciences conducted the planning and design of the work, and the 3D beetles were produced and tested in Huai-Jun Xue's lab in China.
"In the study, we learned that the 3D models worked and were more effective than models that weren't shaped like the beetles such as glass beads," Segraves notes. Another interesting result revealed that males use color in mate selection as males tested on black versus white 3D models all chose the black models.
In the end, the researchers determined that when given an option, the beetles opt for the real thing over the 3D counterpart. When males were offered dead females with the reapplied chemical signals, males preferred dead females over black 3D models coated with the female scent. But Segraves says that's to be expected given that there are probably other types of signals that can't be replicated by 3D printing such as tactile signals.
Their results indicate that in the absence of a dead female beetle, 3D-printed models can provide a feasible and cost-effective method for mating studies of insects. Segraves believes that going forward, researchers studying beetles and other similar insects should use a combination of models. While dead females are most realistic, the 3D printed models allows scientists to more tightly control the chemicals that are present in a given experiment.
INFORMATION:
Their full study, 3D-printed insect models offer a feasible method for mating studies of chrysomelid beetles, appeared in the journal Chemoecology.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-04-08
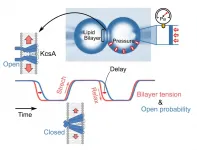
Ion channels play an indispensable role in cellular physiology, and understanding the physical features that affect ion channel functions is a matter of considerable interest to biologists. Given that mechanosensitivity is an intrinsic feature of cells, the complex set of mechanical stresses acting on a cell at any time represents an important consideration in the field of cellular physiology. In fact, stretching forces created by mechanical stress are sometimes necessary to activate ion channels. As Professor Masayuki Iwamoto and Professor Shigetoshi Oiki of the University of Fukui ...
2021-04-08
BIRMINGHAM, Ala. - Six years ago, Michael Niederweis, Ph.D., described the first toxin ever found for the deadly pathogen Mycobacterium tuberculosis. This toxin, tuberculosis necrotizing toxin, or TNT, became the founding member of a novel class of previously unrecognized toxins present in more than 600 bacterial and fungal species, as determined by protein sequence similarity. The toxin is released as M. tuberculosis bacteria survive and grow inside their human macrophage host, killing the macrophage and allowing the escape and spread of the bacteria.
For 132 years, ...
2021-04-08
With the help of machine-learning techniques, a team of astronomers has discovered a dozen quasars that have been warped by a naturally occurring cosmic "lens" and split into four similar images. Quasars are extremely luminous cores of distant galaxies that are powered by supermassive black holes.
Over the past four decades, astronomers had found about 50 of these "quadruply imaged quasars," or quads for short, which occur when the gravity of a massive galaxy that happens to sit in front of a quasar splits its single image into four. The latest study, which spanned only a year and a half, increases the number of known quads by about 25 percent and demonstrates the power of machine learning to assist ...
2021-04-08
Past surveys have shown that more than 80% of dog owners report observing jealous behaviors from their dogs--vocalizations, agitated behavior, pulling on a leash--when they give attention to other dogs. New research published in the journal Psychological Science supports these observations and finds that dogs also exhibit jealous behaviors when they merely imagine that their owner is interacting with a potential rival, in this case, a highly realistic artificial dog.
"Research has supported what many dog owners firmly believe--dogs exhibit jealous behavior when their human companion interacts with a potential rival," said Amalia Bastos with ...
2021-04-08
Charles Darwin, the British naturalist who championed the theory of evolution, noted that corals form far-reaching structures, largely made of limestone, that surround tropical islands. He didn't know how they performed this feat.
Now, Rutgers scientists have shown that coral structures consist of a biomineral containing a highly organized organic mix of proteins that resembles what is in our bones. Their study, published in the END ...
2021-04-08
A new study shows that several disagreements between Ethiopia, Sudan and Egypt around Africa's largest hydropower plant, the new Grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam (GERD), could be alleviated by massively expanding solar and wind power across the region. Adapting GERD operation to support grid integration of solar and wind power would provide tangible energy and water benefits to all involved countries, creating regional win-win situations. "Our results call for integrated hydro-solar-wind planning to be taken up in the GERD negotiations," says Sebastian Sterl, energy ...
2021-04-08
Piping plovers, charismatic shorebirds that nest and feed on many Atlantic Coast beaches, rely on different kinds of coastal habitats in different regions along the Atlantic Coast, according to a new study by the U.S. Geological Survey and U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service.
The Atlantic Coast and Northern Great Plains populations of the piping plover were listed as federally threatened in 1985. The Atlantic coast population is managed in three regional recovery units, or regions: New England, which includes Massachusetts and Rhode Island; Mid-Atlantic, which includes New ...
2021-04-08
WHAT:
The COVID-19 pandemic is affecting people with or at risk for HIV both indirectly, by interfering with HIV treatment and prevention services, and directly, by threatening individual health. An effective response to these dual pandemics requires unprecedented collaboration to accelerate basic and clinical research, as well as implementation science to expeditiously introduce evidence-based strategies into real-world settings. This message comes from a review article co-authored by Anthony S. Fauci, M.D., director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), part of the National Institutes of Health, and colleagues published in the Journal of Infectious Diseases.
By disrupting critical health care services, the COVID-19 pandemic threatens ...
2021-04-08
April 8, 2021 - Routinely collected data on patients undergoing spinal fusion surgery do not provide a valid basis for assessing and comparing hospital performance on patient safety outcomes, reports a study in Spine. The journal is published in the Lippincott portfolio by Wolters Kluwer.
At a time when hospitals are increasingly subject to online rankings or "pay-for-performance" reimbursement programs, metrics based on hospital administrative data are "unreliable for profiling hospital performance," concludes the new research by Jacob K. Greenberg, MD, MSCI, of Washington University in St Louis and colleagues. ...
2021-04-08
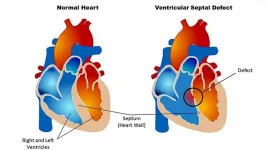
In a medical records study covering thousands of children, a U.S.-Canadian team led by researchers at Johns Hopkins Medicine concludes that while surgery to correct congenital heart disease (CHD) within 10 years after birth may restore young hearts to healthy function, it also may be associated with an increased risk of hypertension -- high blood pressure -- within a few months or years after surgery. ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Can a 3D printed beetle model simulate the real thing?
Researchers assess the feasibility of using 3D printed insects in mating studies