Webcam designed like a human eye: researchers question ubiquitous technology
2021-04-13
(Press-News.org) With 'Eyecam' they now present the prototype of a webcam that not only looks like a human eye, but imitates its movements realistically. "The goal of our project is not to develop a 'better' design for cameras, but to spark a discussion. We want to draw attention to the fact that we are surrounded by sensing devices every day. That raises the question of how that affects us," says Marc Teyssier. In 2020, the French scientist completed his doctorate on the topic of anthropomorphic design in Paris. Now he is a postdoctoral researcher in the Human-Computer Interaction Lab at Saarland University in Germany.
The research team at Saarland Informatics Campus has developed a webcam that not only looks like a human eye, but also realistically imitates unconscious eye movements such as blinking or raising the eyebrow. "With 'Eyecam' we are exploring the question of whether a technical device should reflect its function in its design," adds computer scientist Marion Koelle, who did her doctorate on the social acceptance of body-worn cameras. "There are different ways of seeing, all of which have their own unique connotations, such as observing, recognizing, watching, or even spying. Also, a camera designed as an eye can send nonverbal signals through facial expressions. This opens up a whole new layer of interaction that hasn't existed in technical devices before," Koelle adds.
"The research is part of a whole series of work within a large EU-funded project, the ERC Starting Grant 'InteractiveSkin'. Here we are researching how interfaces that have properties of the human body can improve the interaction between humans and computers," says lab director Professor Jürgen Steimle.
The researchers use the unique capabilities and optics of their new development to explore different facets of ubiquitous sensing. Already today, webcams are a potential privacy risk. 'Eyecam' exaggerates this aspect, acting as an observer by opening its eye and tracking the user with its gaze. Alternatively, the anthropomorphic camera could be used for self-reflection, with the artificial eye getting ever more tired and repeatedly falling shut as the user sits in front of the computer late at night. Or it could take on the role of a pet that is simply there, looking around from time to time and reacting with delight when its owner enters the room.
"Our application scenarios are fictional and are intended to encourage people to think about how we interact with technical devices today, but also in the future. What is special is that we can experience and recreate our imagined scenarios with the help of a physically existing prototype," says Marc Teyssier. To reach as many people as possible with their thought-provoking development, the group has published the blueprints for their device.
INFORMATION:
Original Publication:
The original publication titled "Eyecam: Revealing Relations between Humans and Sensing Devices through an Anthropomorphic Webcam" was accepted by the world's largest conference in the field of human-machine interaction. In May, it will be published at the 32nd "ACM Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems (CHI)" in Yokohama (Japan). Besides Marc Teyssier and Marion Koelle, Paul Strohmeier, Bruno Fruchard and Professor Jürgen Steimle, all from Saarland University, were involved in the project.
A PDF preprint version of the paper can be found at: https://hci.cs.uni-saarland.de/wp-content/uploads/projects/critical_design/eyecam/teyssier_chi21_eyecam.pdf
Further Information:
https://hci.cs.uni-saarland.de/projects/eyecam/
https://marcteyssier.com/projects/eyecam/ (Video demonstration)
https://chi2021.acm.org/
https://erc.europa.eu/projects-figures/stories/tech-filled-tattoos-interact-surrounding-world
https://www.uni-saarland.de/universitaet/aktuell/artikel/nr/23327.html (Press pictures)
Questions can be directed at:
Prof. Dr. Jürgen Steimle
Email: steimle@cs.uni-saarland.de
Tel.: +49 681 302 71080
Dr. Marc Teyssier
Email: teyssier@cs.uni-saarland.de
Tel.: +49 681 302 71084
Dr. Marion Koelle
Email: koelle@cs.uni-saarland.de
Tel.: +49 681 302 71931
Background Saarland Informatics Campus:
800 scientists and about 2100 students from more than 80 nations make the Saarland Informatics Campus (SIC) one of the leading locations for computer science in Germany and Europe. Five world-renowned research institutes, namely the German Research Center for Artificial Intelligence (DFKI), the Max Planck Institute for Computer Science, the Max Planck Institute for Software Systems, the Center for Bioinformatics and the Cluster for "Multimodal Computing and Interaction" as well as Saarland University with three departments and 24 degree programs cover the entire spectrum of computer science.
Editor:
Philipp Zapf-Schramm
Competence Center Computer Science
Saarland Informatics Campus
Phone: +49 681 302-70741
E-Mail: pzapf@mmci.uni-saarland.de
Public relations work at the Saarland Informatics Campus is supported by the Competence Center Computer Science Saarland, funded by the European Regional Development Fund (ERDF) and the Saarland State Chancellery.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-04-13
Human non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is a little-understood condition that significantly increases the risk of inflammation, fibrosis and liver cancer and ultimately requires liver transplant.
"NAFLD has been difficult to study mainly because we had no good animal model," said corresponding author Dr. Karl-Dimiter Bissig, who was at Baylor during the development of this project and is now at Duke University.
The disease has both genetic and nutritional components, which have been hard to understand in human studies, and murine models ...
2021-04-13
A new study verifies the age and origin of one of the oldest specimens of Homo erectus--a very successful early human who roamed the world for nearly 2 million years. In doing so, the researchers also found two new specimens at the site--likely the earliest pieces of the Homo erectus skeleton yet discovered. Details are published today in the journal Nature Communications.
"Homo erectus is the first hominin that we know about that has a body plan more like our own and seemed to be on its way to being more human-like," said Ashley Hammond, an assistant curator in the American Museum of Natural History's Division of Anthropology and the lead author of the new study. "It had longer lower limbs than upper limbs, a torso ...
2021-04-13
ITHACA, N.Y. - The muon is a tiny particle, but it has the giant potential to upend our understanding of the subatomic world and reveal an undiscovered type of fundamental physics.
That possibility is looking more and more likely, according to the initial results of an international collaboration - hosted by the U.S. Department of Energy's Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory - that involved key contributions by a Cornell team led by Lawrence Gibbons, professor of physics in the College of Arts and Sciences.
The collaboration, which brought together 200 scientists from 35 institutions in seven countries, set out to confirm the findings of a 1998 experiment that startled physicists by indicating that muons' magnetic ...
2021-04-13
In the Cascadia subduction zone, medium and large-sized "intraslab" earthquakes, which take place at greater than crustal depths within the subducting plate, will likely produce only a few detectable aftershocks, according to a new study.
The findings could have implications for forecasting aftershock seismic hazard in the Pacific Northwest, say Joan Gomberg of the U.S. Geological Survey and Paul Bodin of the University of Washington in Seattle, in their paper published in the Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America.
Researchers now calculate aftershock forecasts in the region based in part on data from subduction zones around the world. ...
2021-04-13
In a series of experiments that began with amoebas -- single-celled organisms that extend podlike appendages to move around -- Johns Hopkins Medicine scientists say they have identified a genetic pathway that could be activated to help sweep out mucus from the lungs of people with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease a widespread lung ailment.
"Physician-scientists and fundamental biologists worked together to understand a problem at the root of a major human illness, and the problem, as often happens, relates to the core biology of cells," says Doug Robinson, Ph.D., professor of cell ...
2021-04-13
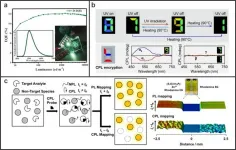
Circularly polarized light exhibits promising applications in future displays and photonic technologies. Traditionally, circularly polarized light is converted from unpolarized light by the linear polarizer and the quarter-wave plate. During this indirectly physical process, at least 50% of energy will be lost. Circularly polarized luminescence (CPL) from chiral luminophores provides an ideal approach to directly generate circularly polarized light, in which the energy loss induced by polarized filter can be reduced. Among various chiral luminophores, organic micro-/nano-structures have attracted increasing attention owing to the high quantum efficiency ...
2021-04-13
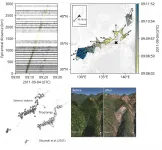
Tsukuba, Japan - Tropical cyclones like typhoons may invoke imagery of violent winds and storm surges flooding coastal areas, but with the heavy rainfall these storms may bring, another major hazard they can cause is landslides--sometimes a whole series of landslides across an affected area over a short time. Detecting these landslides is often difficult during the hazardous weather conditions that trigger them. New methods to rapidly detect and respond to these events can help mitigate their harm, as well as better understand the physical processes themselves.
In a new study published in Geophysical Journal International, a research team led ...
2021-04-13
Hokkaido University researchers have clarified different causes of past glacial river floods in the far north of Greenland, and what it means for the region's residents as the climate changes.
The river flowing from the Qaanaaq Glacier in northwest Greenland flooded in 2015 and 2016, washing out the only road connecting the small village of Qaanaaq and its 600 residents to the local airport. What caused the floods was unclear at the time. Now, by combining physical field measurements and meteorological data into a numerical model, researchers at Japan's Hokkaido ...
2021-04-13
The semiconductor industry and pretty much all of electronics today are dominated by silicon. In transistors, computer chips, and solar cells, silicon has been a standard component for decades. But all this may change soon, with gallium nitride (GaN) emerging as a powerful, even superior, alternative. While not very heard of, GaN semiconductors have been in the electronics market since 1990s and are often employed in power electronic devices due to their relatively larger bandgap than silicon--an aspect that makes it a better candidate for high-voltage and high-temperature applications. Moreover, current travels quicker through GaN, which ensures fewer switching losses during switching applications.
Not everything about GaN is perfect, however. While impurities are usually desirable ...
2021-04-13
People who have recovered from COVID-19, especially those with pre-existing cardiovascular conditions, may be at risk of developing blood clots due to a lingering and overactive immune response, according to a study led by Nanyang Technological University, Singapore (NTU) scientists.
The team of researchers, led by NTU Assistant Professor Christine Cheung, investigated the possible link between COVID-19 and an increased risk of blood clot formation, shedding new light on "long-haul COVID" - the name given to the medium- and long-term health consequences of COVID-19.
The findings may help to explain why some people who have recovered from COVID-19 exhibit symptoms of blood clotting complications after their initial recovery. In some cases, they are at increased risk of heart attack, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Webcam designed like a human eye: researchers question ubiquitous technology