New study reveals charge transfer at interface of spinel oxide and ceria during CO oxidation
2021-04-14
(Press-News.org) A recent study has unveiled the reason behind the exceptional catalytic performance of non-noble metal-base mixed catalysts. This is thanks to a new synthetic strategy for the production of cube-shaped catalysts that could further simplify the structure of complex catalysts.
This breakthrough has been led by Professor Kwangjin An and his research team in the School of Energy and Chemical Engineering at UNIST, in collaboration with Professor Taeghwan Hyeon and his research team from Seoul National University. In their study, the researchers found a new principle that active charge transfer, which appears at the interface created between the two types of non-noble metals, could enhance the catalytic performance of complex oxide catalysts. The research team expects that their findings could contribute to the development of catalysts that could convert methane efficiently to fuels and high value-added chemicals.
The interface created between an active metal and oxide support has been known to affect the catalytic performance due to the charge transfer process. However, owing to their complex interface structures and synthetic challenges, oxide-oxide interfaces produced by supported spinel oxide catalysts have been less studied.
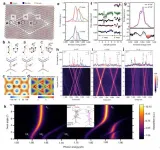
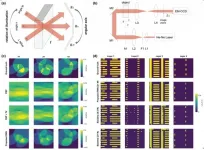
In this work, the research team proposed a synthetic strategy for heterostructured spinel oxide (Co3O4, Mn3O4, and Fe3O4) nanocubes (NCs) with a controlled CeO2 layer that enabled investigation of the role of the interface in catalytic oxidation of CO and H2. They developed a selective deposition process to produce CeO2-deposited spinel NCs with 1, 3, and 6 facets of CeO2 (MCe-1F, MCe-3F, and MCe-6F NCs for spinel oxide).
According to the research team, CeO2-deposited Co3O4 NCs exhibited a 12-times higher CO oxidation rate than the pristine Co3O4 NCs. Furthermore, various in situ characterization techniques, revealed that the deposited CeO2 prevents the reduction of Co3O4 by supplying oxygen. They also found that the maximized interface resulting from Co3O4 NCs with three facets covered by CeO2 layers exhibit the highest CO oxidation rate even under O2-deficient conditions, which resulted from the versatile variation in the oxidation state.
"This study provides a comprehensive understanding of the Mars-van Krevelen (MvK) mechanism, occurring on the nanoscale at the Co3O4-CeO2 interfaces," noted the research team. "The same activity trend and hot electron flow are observed for H2 oxidation reactions using catalytic nanodiodes, thereby demonstrating that the origin of the activity enhancement is charge transfer at the interface."
INFORMATION:
The findings of this research have been published in the February 2021 issue of ACS Catalysis and featured on the cover of the print edition. This study has been supported by various organizations, including the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) and the Ministry of Trade, Industry & Energy (MOTIE).
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-04-14
TMDs vdW heterostructures generally possess a type-II band alignment which facilitates the formation of interlayer excitons between the constituent monolayers. Manipulation of the interlayer excitons in TMDs vdW heterostructures hold great promise for developing excitonic integrated circuits that serve as the counterpart of electronic integrated circuits, which allows the photons and excitons transforming between each other and thus bridges the optical communication and signal processing at the integrated circuit. Consequently, numerous researches have been carried out in order to get a deep insight ...
2021-04-14
A wide range of objects, from biological cells to integrated circuits, are tomographically imaged to identify their interior structures. Volumetric reconstruction of the objects' interiors is of practical implications, for instance, quantitative phase imaging of the cells and failure analysis of the circuits to validate their designs. Limiting the tomographic angular range is often desirable to reduce the time of radiation exposure and avoid any devastating effects upon the samples, or even unavoidable due to the structure of objects like in the case of tomosynthesis for mammography. However, tomographic reconstruction from limited angular views is not always welcome in an algorithmic sense, ...
2021-04-14
Research by Australian scientists could pave the way to a new treatment for a currently incurable brain cancer in children called Diffuse Intrinsic Pontine Glioma, or DIPG. Affecting about 20 children in Australia each year, DIPG is a devastating disease with an average survival time of just nine months after diagnosis.
The research, led by scientists at Children's Cancer Institute and published this week in the international journal, Cell Reports, offers an exciting new therapeutic approach for the treatment of DIPG by using a new anti-cancer drug.
The new drug, CBL0137, is an anti-cancer compound developed from the antimalarial drug quinacrine. The researchers found that CBL0137 directly ...
2021-04-14
Intestinal worm infections can leave women in sub-Saharan Africa more vulnerable to sexually-transmitted viral infections, a new study reveals.
The rate and severity of sexually-transmitted viral infections (STI) in the region are very high, as are those of worm infections, which when caught in the intestine can change immunity in other parts of the body.
Researchers at the Universities of Birmingham and Cape Town led an international team which discovered that intestinal worm infection can change vaginal immunity and increase the likelihood of Herpes simplex virus type 2 (HSV-2) infection - the main cause of genital herpes. ...
2021-04-14
Non-alcoholic fatty liver, NAFLD, is associated with several health risks. According to a new registry study led by researchers at Karolinska Institutet in Sweden, NAFLD is linked to a 17-fold increased risk of liver cancer. The findings, published in Hepatology, underscore the need for improved follow-up of NAFLD patients with the goal of reducing the risk of cancer.
"In this study with detailed liver histology data, we were able to quantify the increased risk of cancer associated with NAFLD, particularly hepatocellular carcinoma," says first author, Tracey G. Simon, researcher at the Department of Medical Epidemiology and Biostatistics, Karolinska Institutet, and hepatologist at Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard ...
2021-04-14
An outbreak of vomiting among dogs has been traced back to a type of animal coronavirus by researchers.
Vets across the country began reporting cases of acute onset prolific vomiting in 2019/20.
The Small Animal Veterinary Surveillance Network (SAVSNet) at the University of Liverpool asked vets for help in collecting data, with 1,258 case questionnaires from vets and owners plus 95 clinical samples from 71 animals.
Based on this data, a team from the universities of Liverpool, Lancaster, Manchester and Bristol identified the outbreak as most likely to ...
2021-04-14
ITHACA, N.Y. - Women's increased agricultural labor during harvest season, in addition to domestic house care, often comes at the cost of their health, according to new research from the Tata-Cornell Institute for Agriculture and Nutrition (TCI).
Programs aimed at improving nutritional outcomes in rural India should account for the tradeoffs that women experience when their agricultural work increases, according to the study, "Seasonal time trade-offs and nutrition outcomes for women in agriculture: Evidence from rural India," which published in the journal Food Policy on March ...
2021-04-14
PHILADELPHIA-- Humans have a uniquely high density of sweat glands embedded in their skin--10 times the density of chimpanzees and macaques. Now, researchers at Penn Medicine have discovered how this distinctive, hyper-cooling trait evolved in the human genome. In a study published today in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the USA, researchers showed that the higher density of sweat glands in humans is due, to a great extent, to accumulated changes in a regulatory region of DNA--called an enhancer region--that drives the expression of a sweat gland-building gene, explaining why humans are the sweatiest ...
2021-04-14
PHOENIX, Ariz. -- April 13, 2021 -- Findings of a study by the Translational Genomics Research Institute (TGen), an affiliate of City of Hope, suggest that increasing expression of a gene known as ABCC1 could not only reduce the deposition of a hard plaque in the brain that leads to Alzheimer's disease, but might also prevent or delay this memory-robbing disease from developing.
ABCC1, also known as MRP1, has previously been shown in laboratory models to remove a plaque-forming protein known as amyloid beta (Abeta) from specialized endothelial cells that surround and protect ...
2021-04-14
Compared to newborns conceived traditionally, newborns conceived through in vitro fertilization (IVF) are more likely to have certain chemical modifications to their DNA, according to a study by researchers at the National Institutes of Health. The changes involve DNA methylation--the binding of compounds known as methyl groups to DNA--which can alter gene activity. Only one of the modifications was seen by the time the children were 9 years old.
The study was conducted by Edwina Yeung, Ph.D., and colleagues in NIH's Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] New study reveals charge transfer at interface of spinel oxide and ceria during CO oxidation