Cool and COVID-safe: How radiant cooling could keep our cities comfortable and healthy
Combination of special cooling panels and natural ventilation can minimize disease transmission while saving energy
2021-04-20
(Press-News.org) A novel system of chilled panels that can replace air conditioning can also help reduce the risk of indoor disease transmission, suggests new analysis from the University of British Columbia, University of Pennsylvania and Princeton University.
The researchers computed air conditioning requirements in 60 of the world's most populous cities--with the additional ventilation required due to COVID-19. Then, they compared the energy costs with their cooling method, using the chilled panels and natural ventilation.
The results, published in the COVID-19 edition of Applied Energy, showed that the alternative solution can save up to 45 per cent of the required energy, while ensuring building occupants are comfortable and rooms are adequately refreshed.
Dr. Adam Rysanek, a professor in the school of architecture and landscape architecture at UBC and co-author of the paper, notes that many public health guidelines, as well as building industry bodies, recommend increasing the flow of fresh, outdoor air into buildings in order to reduce the risk of spreading COVID-19 and other diseases.
"However, if we continue to rely on conventional HVAC systems to increase indoor fresh air rates, we may actually double energy consumption. That's the nature of conventional HVAC."
"Alternatively, we can encourage people to install new types of radiant cooling systems, which allow them to keep their windows open even when it's hot outside. These alternative systems can provide a sufficient level of thermal comfort, increase protection against disease while lessening the impact on the environment," noted Rysanek, director of the Building Decisions Research Group at UBC's faculty of applied science.
Rysanek and his colleagues earlier demonstrated their cooling system in the hot and humid climate of Singapore. They built a public pavilion featuring a system of chilled tubes enclosed within a condensation-preventing membrane. This allowed occupants to feel comfortable, and even cold, without changing the air temperature surrounding the human body.
"You can think of it as lean A/C--or, even better, as a green alternative to energy-guzzling air conditioning," said Rysanek.
Toronto is one of the cities included in the latest analysis, as are Beijing, Miami, Mumbai, New York and Paris. In all these regions, peak summer temperatures can soar past 35 degrees Celsius (95 degrees Fahrenheit).
"A key impact of climate change is the accelerating rise in average and peak temperatures, particularly in urban areas. We are expecting the appetite for indoor cooling will ramp up in the years ahead. Yet, if we want to mitigate urban heat and ensure people are healthy and comfortable while reducing our energy use, we need to seriously consider revolutionising our historical approach to air-conditioning," adds Rysanek.
Rysanek notes that, though chilled panel systems have been around for decades, adding the special membrane devised by the research team could be the key to making it a commercially viable alternative to traditional HVAC systems in all climates.
Interview languages: English
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-04-20
Nearly three-quarters of Earth's land had been transformed by humans by 10,000BC, but new research shows it largely wasn't at the expense of the natural world.
A study involving University of Queensland researchers combined global maps of population and land use over the past 12,000 years with current biodiversity data, demonstrating the effective environmental stewardship of Indigenous and traditional peoples.
UQ's Professor James Watson said the findings challenged the modern assumption that human 'development' inevitably led to environmental destruction.
"There's a paradigm among natural scientists, conservationists and policymakers that ...
2021-04-20
Unless you've studied chemistry in college, it's unlikely you've come across the name aziridine. An organic compound with the molecular formula, C2H4NH, aziridines are well-known among medicinal chemists, who make use of the compound to prepare pharmaceutical drugs such as Mitomycin C, a chemotherapeutic agent known for its anti-tumor activity. Specifically, aziridines are what chemists call "enantiomers"--molecules that are mirror images of each other and cannot be superposed on one another. A peculiarity with enantiomers is that the biological activity ...
2021-04-20
A team headed by Dr. Phillip M. Maffettone (currently at National Synchrotron Light Source II in Upton, USA) and Professor Andrew Cooper from the Department of Chemistry and Materials Innovation Factory at the University of Liverpool joined forces with the Bochum-based group headed by Lars Banko and Professor Alfred Ludwig from the Chair of Materials Discovery and Interfaces and Yury Lysogorskiy from the Interdisciplinary Centre for Advanced Materials Simulation. The international team published their report in the journal Nature Computational Science from 19 April 2021.
Previously manual, time-consuming, error-prone
Efficient analysis of X-ray diffraction data (XRD) plays a crucial role in the discovery of new materials, for example for the energy ...
2021-04-20
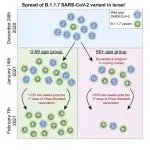
A new study at Tel Aviv University found that the British variant (termed: B.1.1.7) of Covid-19 is 45% more contagious than the original virus. The researchers relied on data from about 300,000 PCR tests for Covid-19 obtained from the COVID-19 testing lab, which was established in collaboration with the Electra Group.
The new study was conducted by Prof. Ariel Munitz and Prof. Moti Gerlitz of the Department of Clinical Microbiology and Immunology at the Sackler Faculty of Medicine, together with Dr. Dan Yamin and PhD student Matan Yechezkel from the Laboratory for Epidemic Modeling and Analysis (LEMA) at the Department of Industrial Engineering, all at Tel Aviv University. The study's results were published in the prominent scientific ...
2021-04-20
Musty, moldy, smoky or horse dung-like smelling cocoa is not suitable for chocolate production. As part of a larger research project, a team of scientists led by Martin Steinhaus from the Leibniz Institute for Food Systems Biology at the Technical University of Munich has identified the odorants responsible for such off-flavors. The food industry can now use these results to objectively assess the sensory quality of fermented cocoa based on odorant concentrations. The research team published the data in the Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry.
Who likes chocolate ...
2021-04-20
An international group of scientific experts co-directed by CNRS oceanographer Jean-Pierre Gattuso* has stated the requirements for coral reef survival in an article published in Biological Conservation. Over 500 million people rely on coral reefs for the protection they confer against submersion, the fishing resources they offer, and the tourism they help attract. Yet these ecosystems are among the most threatened by global warming: since the 1980s, there has been a rise in the number of bleaching episodes, during which corals expel the microscopic algae that keep them alive. While these events are reversible if the temperature change is only ...
2021-04-20
The largest study of its type in the UK has identified differences in the immune response to COVID-19, between people with no symptoms, compared to those suffering a more serious reaction to the virus.
Researchers from the Wellcome Sanger Institute, Newcastle University, University College London, University of Cambridge, EMBL's European Bioinformatics Institute (EMBL-EBI) and their collaborators within the Human Cell Atlas initiative, found raised levels of specific immune cells in asymptomatic people. They also showed people with more serious symptoms had lost these protective cell types, but gained inflammatory cells. These differences in the immune response could help explain serious lung inflammation and blood clotting symptoms, and could be used to identify potential ...
2021-04-20
Scientists have developed a new biomaterial that regrows blood vessels and bone, potentially providing a single-stage approach when repairing large bone defects.
The study, led by researchers from RCSI University of Medicine and Health Sciences and SFI AMBER Centre, is published in the Journal of Controlled Release.
Previous RCSI-led research had found that activating a mechanosensitive gene, called placental growth factor (PGF), at different doses promoted bone regeneration and grew new blood vessels. Using this knowledge, the researchers developed a biomaterial that delivers PGF at different concentrations.
Inspired by the natural way in ...
2021-04-20
ROCHESTER, Minn. -- A new Mayo Clinic study bolsters evidence that colorectal cancer is often imprinted in family genes and passed on from one generation to the next.
In the study, published in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology, researchers within the Mayo Clinic Center for Individualized Medicine found 1 in 6 patients with colorectal cancer had an inherited cancer-related gene mutation, which likely predisposed them to the disease. In addition, the researchers discovered that 60% of these cases would not have been detected if relying on a standard guideline-based approach.
"We found that 15.5% of the 361 patients with colorectal cancer had an inherited mutation in a gene associated with the development of their cancer," says Niloy Jewel Samadder, M.D., a Mayo ...
2021-04-20
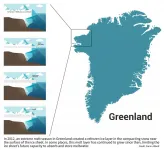
Nearly a decade ago, global news outlets reported vast ice melt in the Arctic as sapphire lakes glimmered across the previously frozen Greenland Ice Sheet, one of the most important contributors to sea-level rise. Now researchers have revealed the long-term impact of that extreme melt.
Using a new approach to ice-penetrating radar data, Stanford University scientists show that this melting left behind a contiguous layer of refrozen ice inside the snowpack, including near the middle of the ice sheet where surface melting is usually minimal. Most importantly, the formation of the melt layer changed the ice sheet's behavior by reducing its ability to store future meltwater. The research appears in Nature Communications ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Cool and COVID-safe: How radiant cooling could keep our cities comfortable and healthy
Combination of special cooling panels and natural ventilation can minimize disease transmission while saving energy