INFORMATION:
Reprogramming fibroblasts could result in scar-free wound healing, suggests study in mice
2021-04-22
(Press-News.org) Researchers have determined a way to potentially minimize or eliminate scarring in wounded skin, by further decoding the scar-promoting role of a specific class of dermal fibroblast cells in mice. By preventing these cells from expressing the transcription factor Engrailed-1 (En-1), Shamik Mascharak and colleagues reprogrammed these cells to take on a different identity, capable of regenerating wounded skin - including the restoration of structures such as hair follicles and sweat glands that are absent in scarred skin tissue. With further development and testing, their discovery could lead to therapies to reduce or completely avoid scarring in human patients. Fibroblast cells that express En-1 - called Engrailed-1 lineage-positive fibroblasts (EPFs) - have been implicated in scar formation, but the precise underlying mechanisms have remained unknown. Mascharak et al. noted that, while the progenitor cells of EPFs do not express En-1 in newborn and infant mice, fully functional EPFs are a known feature of skin wounds in adult mammals. Accordingly, they set out to determine whether EPFs proliferate in mammals as they age, or whether they expand locally at wound sites in response to new damage. Through a series of cell transplantation and genetic tracing experiments to explore the expression of En-1 in wounded mouse skin, Mascharak et al. found evidence for a closely related type of cells, called Engrailed-1 lineage-negative fibroblasts (ENFs), that do not express En-1. Mechanical signals activate the canonical Yes-associated protein (YAP) pathway in ENF cells, which in turn prompts the cells to begin expressing En-1, completing their transformation to scar-promoting EPF cells. By blocking the YAP pathway by either administering the inhibitor compound verteporfin or knocking out the YAP gene, Mascharak et al. encouraged these cells to retain their identity as ENFs, enabling the cells to rebuild the wounded skin, complete with regenerated sweat glands and hair follicles. "Tissue scarring is a leading cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide," note Piotr Konieczny and Shruti Naik in a related Focus. "The findings by Mascharak et al. thus hold great promise not only for [anti-scarring] therapies but also for the simultaneous activation of the skin's regenerative properties."
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
China requires switch to zero-carbon energy to achieve more ambitious Paris Agreement goal, models S
2021-04-22
A new multi-model analysis suggests that China will need to reduce its carbon emissions by over 90% and its energy consumption by almost 40%, in order to meet the more ambitious target set by the 2016 Paris Agreement. The Agreement called for no more than a 1.5°Celsius (C) global temperature rise by 2050. These results provide a clear directive for China to deploy multiple strategies at once for long-term emission mitigation, the authors say. The findings also highlight the need for more research on the economic consequences of working toward a 1.5°C warming limit, arguing that current studies are far from adequate to inform the sixth assessment report (AR 6) on climate change planned for release by the United Nations' Intergovernmental ...
Medical record analysis links cannabis use disorder in pregnancy to infant health problems
2021-04-22
A new study of nearly five million live births recorded in California from 2001 to 2012 found that babies born to mothers diagnosed with cannabis use disorders at delivery were more likely to experience negative health outcomes, including preterm birth and low birth weight, compared to babies born to mothers without a cannabis use disorder diagnosis. The analysis, published today in Addiction and funded by the National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA), part of the National Institutes of Health, adds to a growing body of evidence that prenatal exposure to cannabis (marijuana) may be associated with poor birth outcomes, and sheds light on infant health one year after birth.
Recent studies have shown the ...
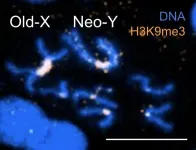
Toxic masculinity: Y chromosome contributes to a shorter lifespan in male flies
2021-04-22
Males may have shorter lifespans than females due to repetitive sections of the Y chromosome that create toxic effects as males get older. These new findings appear in a study by Doris Bachtrog of the University of California, Berkeley published April 22 in PLOS Genetics.
In humans and other species with XY sex chromosomes, females often live longer than males. One possible explanation for this disparity may be repetitive sequences within the genome. While both males and females carry these repeat sequences, scientists have suspected that the large number of repeats ...
Cannabis use disorder rate rose among pregnant women between 2001-2012
2021-04-22
A study of almost 5 million live births in California by researchers at the Herbert Wertheim School of Public Health and Human Longevity Science at University of California San Diego reports that babies born to mothers diagnosed with cannabis use disorder were more likely to experience negative health outcomes, such as preterm birth and low birth weight, than babies born to mothers without a cannabis use disorder diagnosis.
The findings are published online in the April 22, 2021 issue of the journal Addiction. The National Institute on Drug Abuse, part of the National Institutes of Health, funded the study.
Cannabis use disorder is a diagnostic term with specific criteria that defines continued cannabis use despite ...
Anti-aging compound improves muscle glucose metabolism in people
2021-04-22
A natural compound previously demonstrated to counteract aspects of aging and improve metabolic health in mice has clinically relevant effects in people, according to new research at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis.
A small clinical trial of postmenopausal women with prediabetes shows that the compound NMN (nicotinamide mononucleotide) improved the ability of insulin to increase glucose uptake in skeletal muscle, which often is abnormal in people with obesity, prediabetes or Type 2 diabetes. NMN also improved expression of genes that are involved in muscle structure and remodeling. However, the treatment did not lower blood glucose or blood pressure, improve blood lipid profile, increase insulin sensitivity in the liver, reduce fat ...
What does 1.5 °C warming limit mean for China?
2021-04-22
As part of the Paris Agreement, nearly all countries agreed to take steps to limit the average increase in global surface temperature to less than 2 °C, or preferably 1.5 °C, compared with preindustrial levels. Since the Agreement was adopted, however, concerns about global warming suggest that countries should aim for the "preferable" warming limit of 1.5 °C.
What are the implications for China of trying to achieve this lower limit?
Prof. DUAN Hongbo from the University of Chinese Academy of Sciences and Prof. WANG Shouyang from the Academy of Mathematics and Systems Science of the Chinese Academy ...
Researchers trace spinal neuron family tree
2021-04-22
LA JOLLA--(April 22, 2021) Spinal cord nerve cells branching through the body resemble trees with limbs fanning out in every direction. But this image can also be used to tell the story of how these neurons, their jobs becoming more specialized over time, arose through developmental and evolutionary history. Salk researchers have, for the first time, traced the development of spinal cord neurons using genetic signatures and revealed how different subtypes of the cells may have evolved and ultimately function to regulate our body movements.
The findings, published in ...
International research teams explore genetic effects of Chernobyl radiation
2021-04-22
In two landmark studies, researchers have used cutting-edge genomic tools to investigate the potential health effects of exposure to ionizing radiation, a known carcinogen, from the 1986 accident at the Chernobyl nuclear power plant in northern Ukraine. One study found no evidence that radiation exposure to parents resulted in new genetic changes being passed from parent to child. The second study documented the genetic changes in the tumors of people who developed thyroid cancer after being exposed as children or fetuses to the radiation released by the accident.
The findings, published around the ...
Scientists uncover a molecule that can help coronavirus escape antibodies
2021-04-22
Researchers have found that a natural molecule can effectively block the binding of a subset of human antibodies to SARS-CoV-2. The discovery may help explain why some COVID-19 patients can become severely ill despite having high levels of antibodies against the virus.
In their research, published in Science Advances today (22 April 2021), teams from the Francis Crick Institute, in collaboration with researchers at Imperial College London, Kings College London and UCL (University College London), found that biliverdin and bilirubin, natural molecules present in the body, can suppress the ...
Scientists unmask new neutralizing antibody target on SARS-CoV-2 spike protein
2021-04-22
Researchers have identified another potential target for neutralizing antibodies on the SARS-CoV-2 Spike protein that is masked by metabolites in the blood. As a result of this masking, the target may be inaccessible to antibodies, because they must compete with metabolite molecules to bind to the otherwise open region, the study authors speculate. This competitive binding activity may represent another method of immune evasion by the SARS-CoV-2 virus. Although further validation work is needed, the findings suggest that strategies to unmask this region - thus making it more visible and accessible to antibodies - may help lead to new vaccine designs. ...