(Press-News.org) Gossip is often considered socially taboo and dismissed for its negative tone, but a Dartmouth study illustrates some of its merits. Gossip facilitates social connection and enables learning about the world indirectly through other people's experiences.
Gossip is not necessarily spreading rumors or saying bad things about other people but can include small talk in-person or online, such as having a private chat during a Zoom meeting. Prior research has found that approximately 14% of people's daily conversations are gossip, and primarily neutral in tone.
"Gossip is a complex form of communication that is often misunderstood," says Eshin Jolly, a post-doctoral researcher in the Computational Social Affective Neuroscience Laboratory (COSAN) who co-authored the study with Luke Chang, an assistant professor of psychological and brain sciences and director of the COSAN Lab at Dartmouth. "It can be a means of social and substantive connection beyond its typical negative connotation," adds Jolly.
Jolly and Chang were curious why people in their personal and professional lives spend so much time exchanging information about themselves and other people, and sought to determine why people gossip and what function it serves.
They created a game online to examine the role of gossip and how it manifests as information becomes more uncertain within the game. Participants played 10 rounds of the game together in six-person groups. In each round, players were given $10 and could choose to keep the money or invest any portion of it into a group fund that was multiplied by 1.5x and divided equally among the players. The game creates an inherent tension between selfish freeriding and cooperative behavior, and is considered what researchers refer to as a public goods game.
In some conditions, information was restricted so that participants could only observe the behavior of a few other players in their group. "Our inspiration was creating a life-like scenario, in which you're a member of a community and affected by the actions of all other community members, but most of whom you rarely observe and engage with directly," Jolly explained. In some games, players could privately chat with another player in the group. This allowed players to relay information about other players' behavior to their partner, such as whether another player was freeriding. Afterwards, players reported their willingness to play with each player again.
Published in Current Biology, their findings demonstrate how gossip is a "rich, multifaceted communication" with several social functions. Different types of gossip emerged depending on the amount of information available. Spontaneous conversations about others occurred more frequently during games when players could only observe the behavior of a few of their group members. When players could directly observe all of their group members, they tended to chit-chat and discuss a wider array of topics.
Participants relied on second-hand information from their partners to stay informed about other peoples' behavior that they could not see, illustrating how gossip enables individuals to learn from the experiences of others when direct observation is not feasible.
The findings also showed that participants who chatted with each other felt the most connected with each other at the end of the game and even shared similar impressions of the other players in their group.
Chang explains that, "By exchanging information with others, gossip is a way of forming relationships. It involves trust and facilitates a social bond that is reinforced as further communication takes place."
In a typical public goods game, players contribute less over time and an unraveling effect occurs that propagates through a network of people. However, in this study, cooperation declined less over time when players could privately communicate. Communication increased collective cooperation.
The researchers explain that gossip should not be relegated to just "baseless trash talk". According to the paper, the team's findings on the role of gossip are consistent with creating a "shared reality" in which friends and colleagues often find common bonds, establish alliances, exchange personal information, and discuss the behavior of others to establish a consensus of socially acceptable behavior.
"Gossip can be useful because it helps people learn through the experiences of others, while enabling them to become closer to each other in the process," says Jolly.
INFORMATION:
Jolly is available for comment at: eshin.jolly@dartmouth.edu Chang is available for comment at: luke.j.chang@dartmouth.edu.
Powered flight in animals -that uses flapping wings to generate thrust- is a very energetically demanding mode of locomotion that requires many anatomical and physiological adaptations. In fact, the capability to develop it has only appeared four times in the evolutionary history of animals: on insects, pterosaurs, birds and bats.
A research paper published in 2020 in the scientific journal Current Biology concluded that, apart from birds -the only living descendants of dinosaurs-, powered flight would have originated independently in other three groups of dinosaurs. A conclusion that makes a great impact, as it increases the number of vertebrates that would have developed this costly mode of locomotion, ...
A major hurdle to developing new and effective treatments for drug addiction is better understanding how exactly it manifests itself before, during and after chronic use. In a paper published online in the April 21, 2021 issue of the journal eNeuro, an international team of researchers led by scientists at University of California San Diego School of Medicine describe the creation of two unique collections of more than 20,000 biological samples collected from laboratory rats before, during and after chronic use of cocaine and oxycodone.
Developed by the Preclinical Addiction Research Consortium, located in the Department of Psychiatry at UC San Diego School of Medicine and at Skaggs School of Pharmacy ...
Corn is America's top agricultural crop, and also one of its most wasteful. About half the harvest--stalks, leaves, husks, and cobs-- remains as waste after the kernels have been stripped from the cobs. These leftovers, known as corn stover, have few commercial or industrial uses aside from burning. A new paper by engineers at UC Riverside describes an energy-efficient way to put corn stover back into the economy by transforming it into activated carbon for use in water treatment.
Activated carbon, also called activated charcoal, is charred biological material that has been treated to create millions of microscopic pores that increase how much the material can absorb. It has many industrial ...
How often have you laid in bed scrolling through news stories, social media or responding to a text? After staring at the screen, have you ever found that it is harder to fall asleep?
It's widely believed that the emitted blue light from phones disrupts melatonin secretion and sleep cycles. To reduce this blue light emission and the strain on eyes, Apple introduced an iOS feature called Night Shift in 2016; a feature that adjusts the screen's colors to warmer hues after sunset. Android phones soon followed with a similar option, and now most smartphones have some sort of night mode function that claims ...
The process designed to harvest on Earth the fusion energy that powers the sun and stars can sometimes be tricked. Researchers at the U.S. Department of Energy's (DOE) Princeton Plasma Physics laboratory have derived and demonstrated a bit of slight-of-hand called "quasi-symmetry" that could accelerate the development of fusion energy as a safe, clean and virtually limitless source of power for generating electricity.
Fusion reactions combine light elements in the form of plasma -- the hot, charged state of matter composed of free electrons and atomic nuclei that makes up 99 percent of the visible universe ...
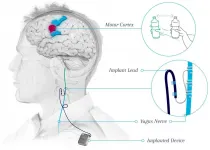
LOS ANGELES -- Every year, more than 795,000 people in the United States have a stroke. Of these, approximately 80% lose arm function and as many as 50-60% of this population still experience problems six months later.
Traditionally, stroke patients try to regain motor function through physical rehabilitation, where patients re-learn pre-stroke skills, such as eating motions and grasping. However, most patients eventually plateau and stop improving over time.
Now, results of a clinical trial published in The Lancet gives patients new hope in their recovery.
Patients who received a novel treatment that combines vagus nerve stimulation (VNS) and rehabilitation showed ...
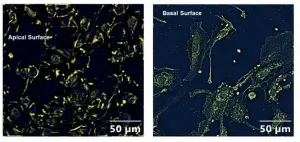
A new study performed in human lung airway cells is one of the first to show a potential link between exposure to organophosphate pesticides and increased susceptibility to COVID-19 infection. The findings could have implications for veterans, many of whom were exposed to organophosphate pesticides during wartime.
Exposure to organophosphate pesticides is thought to be one of the possible causes of Gulf War Illness, a cluster of medically unexplained chronic symptoms that can include fatigue, headaches, joint pain, indigestion, insomnia, dizziness, respiratory disorders and memory problems. More than 25% of Gulf War veterans are estimated to experience this condition.
"We have identified a basic mechanism linked with inflammation that could increase susceptibility to COVID-19 infection ...
During infection, SARS-CoV-2 binds to a cellular receptor known as angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) before entering a cell and replicating. Because it is not well established whether common blood pressure medications can increase the levels of ACE2, there has been some concern that patients taking these medications might be more susceptible to COVID-19.
In a new study, researchers led by Hans Ackerman, MD, DPhil, in the Laboratory of Malaria and Vector Research (LMVR) at the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, found that mice treated with an ACE inhibitor blood pressure medication showed increased levels of ACE2. However, mice that received both an ACE inhibitor and a different blood pressure medicine known as an angiotensin ...
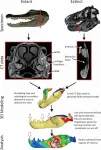
Tyrannosaurus rex dinosaurs chomped through bone by keeping a joint in their lower jaw steady like an alligator, rather than flexible like a snake, according to a study being presented at the END ...
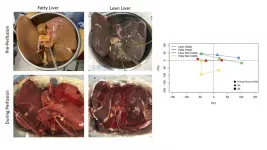
Thousands of livers donated for transplantation are discarded or turned down every year due to concerns about organ quality and function. New insights into why these organs are considered unusable and how they function during external perfusion could help save lives by greatly increasing the number of livers that are transplantable.
After a liver is removed from a donor's body, it undergoes a process known as perfusion which flows blood or a blood replacement though the organ's blood vessels to keep them open and active before the transplantation surgery.
"Our new findings will allow us to design therapies that could be used during external perfusion to improve the quality of organs so that these livers can be transplanted instead of being discarded," ...