(Press-News.org) A major hurdle to developing new and effective treatments for drug addiction is better understanding how exactly it manifests itself before, during and after chronic use. In a paper published online in the April 21, 2021 issue of the journal eNeuro, an international team of researchers led by scientists at University of California San Diego School of Medicine describe the creation of two unique collections of more than 20,000 biological samples collected from laboratory rats before, during and after chronic use of cocaine and oxycodone.
Developed by the Preclinical Addiction Research Consortium, located in the Department of Psychiatry at UC San Diego School of Medicine and at Skaggs School of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences, the new cocaine and oxycodone biobanks include samples from 20 different organs, plus urine, blood and feces.
"To create new treatments for drug addiction, we need to better identify the biomarkers of addiction and the biological targets of therapy," said senior author Olivier George, PhD, associate professor in the Department of Psychiatry. "These biobanks using an animal model help serve that purpose, providing deeper insight -- and potential therapeutic targets -- regarding the paths and pathologies of cocaine and oxycodone addiction."
Cocaine is among the world's most commonly used illicit drugs. In 2016, the National Survey on Drug Use and Health estimated approximately 2 million people age 12 and older in the United States were current users--a bit less than 1 percent of the total U.S. population. Fatal cocaine overdoses (in combination with an opioid) are rising, from 3,822 in 1999 to 15,883 in 2019.
Oxycodone is an opioid, a class of highly addictive drugs that also includes heroin, morphine and fentanyl. Opioid abuse is a major, ongoing public health crisis. In 2019, almost 71,000 drug overdose deaths occurred in the U.S. -- more than 70 percent involving an opioid, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Finding new ways to treat and reduce addiction requires well-validated, long-term models of how cocaine and oxycodone impact and impair biological systems and functions. Researchers used a heterogeneous rat model that reflects the genetic diversity of humans and have been characterized as vulnerable or resistant to cocaine and oxycodone behaviors.
Biological samples were collected before exposure to drugs, during intoxication, during acute withdrawal and after protracted abstinence. These samples were compared against age-matched control animals never exposed to the drugs.
Samples from more than 1,000 animals were taken, including tissue from brains, kidneys, livers, spleen, ovary, testes and adrenal glands, and preserved in methods that will allow researchers to conduct a variety of future assessments, including epigenomics, neuroanatomy, microbiomics and biomarker discovery. The samples are freely available to non-profit research institutions at cocainebiobank.org or oxycodonebiobank.org.
INFORMATION:
Co-authors include: Lieselot L.G. Carrette, UC San Diego and Ghent University; Giordano de Guglielmo, Marsida Kallupi, Lisa Maturin, Molly Brennan, Brent Boomhower, Sharona Sedighim, Lani Tieu, McKenzie J. Fannon, Nathan Velarde, Adam Kimbrough, Sierra Simpson, Francisco Ramirez Jr., Apurva S. Chitre, Bonnie Lin, Oksana Polesskaya, and Abraham A. Palmer, UC San Diego; Dana Conlisk and Jenni Kononoff, TSRI; Lauren C Smith and Kokila Shankar, UC San Diego and TSRI; and Leah Solberg Woods, Wake Forest University.
Corn is America's top agricultural crop, and also one of its most wasteful. About half the harvest--stalks, leaves, husks, and cobs-- remains as waste after the kernels have been stripped from the cobs. These leftovers, known as corn stover, have few commercial or industrial uses aside from burning. A new paper by engineers at UC Riverside describes an energy-efficient way to put corn stover back into the economy by transforming it into activated carbon for use in water treatment.
Activated carbon, also called activated charcoal, is charred biological material that has been treated to create millions of microscopic pores that increase how much the material can absorb. It has many industrial ...
How often have you laid in bed scrolling through news stories, social media or responding to a text? After staring at the screen, have you ever found that it is harder to fall asleep?
It's widely believed that the emitted blue light from phones disrupts melatonin secretion and sleep cycles. To reduce this blue light emission and the strain on eyes, Apple introduced an iOS feature called Night Shift in 2016; a feature that adjusts the screen's colors to warmer hues after sunset. Android phones soon followed with a similar option, and now most smartphones have some sort of night mode function that claims ...
The process designed to harvest on Earth the fusion energy that powers the sun and stars can sometimes be tricked. Researchers at the U.S. Department of Energy's (DOE) Princeton Plasma Physics laboratory have derived and demonstrated a bit of slight-of-hand called "quasi-symmetry" that could accelerate the development of fusion energy as a safe, clean and virtually limitless source of power for generating electricity.
Fusion reactions combine light elements in the form of plasma -- the hot, charged state of matter composed of free electrons and atomic nuclei that makes up 99 percent of the visible universe ...
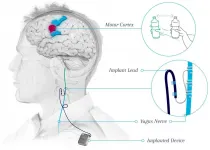
LOS ANGELES -- Every year, more than 795,000 people in the United States have a stroke. Of these, approximately 80% lose arm function and as many as 50-60% of this population still experience problems six months later.
Traditionally, stroke patients try to regain motor function through physical rehabilitation, where patients re-learn pre-stroke skills, such as eating motions and grasping. However, most patients eventually plateau and stop improving over time.
Now, results of a clinical trial published in The Lancet gives patients new hope in their recovery.
Patients who received a novel treatment that combines vagus nerve stimulation (VNS) and rehabilitation showed ...
A new study performed in human lung airway cells is one of the first to show a potential link between exposure to organophosphate pesticides and increased susceptibility to COVID-19 infection. The findings could have implications for veterans, many of whom were exposed to organophosphate pesticides during wartime.
Exposure to organophosphate pesticides is thought to be one of the possible causes of Gulf War Illness, a cluster of medically unexplained chronic symptoms that can include fatigue, headaches, joint pain, indigestion, insomnia, dizziness, respiratory disorders and memory problems. More than 25% of Gulf War veterans are estimated to experience this condition.
"We have identified a basic mechanism linked with inflammation that could increase susceptibility to COVID-19 infection ...
During infection, SARS-CoV-2 binds to a cellular receptor known as angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) before entering a cell and replicating. Because it is not well established whether common blood pressure medications can increase the levels of ACE2, there has been some concern that patients taking these medications might be more susceptible to COVID-19.
In a new study, researchers led by Hans Ackerman, MD, DPhil, in the Laboratory of Malaria and Vector Research (LMVR) at the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, found that mice treated with an ACE inhibitor blood pressure medication showed increased levels of ACE2. However, mice that received both an ACE inhibitor and a different blood pressure medicine known as an angiotensin ...
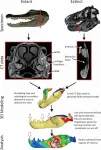
Tyrannosaurus rex dinosaurs chomped through bone by keeping a joint in their lower jaw steady like an alligator, rather than flexible like a snake, according to a study being presented at the END ...
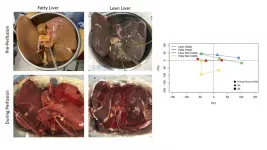
Thousands of livers donated for transplantation are discarded or turned down every year due to concerns about organ quality and function. New insights into why these organs are considered unusable and how they function during external perfusion could help save lives by greatly increasing the number of livers that are transplantable.
After a liver is removed from a donor's body, it undergoes a process known as perfusion which flows blood or a blood replacement though the organ's blood vessels to keep them open and active before the transplantation surgery.
"Our new findings will allow us to design therapies that could be used during external perfusion to improve the quality of organs so that these livers can be transplanted instead of being discarded," ...
New research suggests a simple step could help millions of people reduce their risk of heart disease: make sure to get enough vitamin D. Elucidating linkages between skin pigmentation, vitamin D and indicators of cardiovascular health, the new study, combined with evidence from previous research, suggests vitamin D deficiency could contribute to the high rate of heart disease among African Americans.
"More darkly-pigmented individuals may be at greater risk of vitamin D deficiency, particularly in areas of relatively low sun exposure or high seasonality of sun exposure," said S. Tony Wolf, PhD, a postdoctoral fellow at the Pennsylvania State University and the study's lead author. "These ...
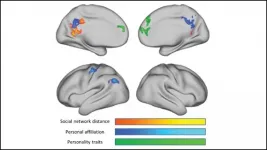
The brain encodes information about our relationships and the relationships between our friends using areas involved in spatial processing, according to new research published in JNeurosci.
Humans maintain hundreds of social relationships, requiring the brain to catalogue countless details about each person and their connections to other people. But it is not known how exactly the brain stores all of this information.
To uncover how the brain encodes social network structure, Peer et al. used Facebook data to map out participants' social connections. Then the researchers measured their brain activity with fMRI as they thought about people from their network. Thinking about a connection generated ...