(Press-News.org) People living with a child who attends school in-person have an increased risk of reporting evidence of COVID-19, but teacher masking, symptom screening, and other mitigation measures in schools may be able to minimize that excess risk, suggests a study led by researchers at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health.
For their study, the researchers analyzed nearly 600,000 responses from an ongoing Facebook-based COVID-19 symptom survey in the United States over two periods between November 2020 and February 2021 before vaccines were widely available in the U.S. The researchers found that those living with a child engaged in full-time, in-person pre-K-to-12 schooling were about 38 percent more likely to report COVID-19-like symptoms such as fever, cough, or difficulty breathing, compared to those living with a child schooled exclusively in a home setting.
A key finding was that school-based mitigation measures--the survey asked about 14 mitigation measures--were associated with less risk per mitigation measure. For example, 9 percent less risk of COVID-related illness per measure, and 7 percent less risk of a positive SARS-CoV-2 test per measure. Each additional mitigation measure reduced risk. Teacher masking and daily symptom screening appeared to be the strongest risk reducers.
The study was published online April 29 in Science.
The analysis included three outcomes as reported by survey respondents: COVID-19-like illness, i.e., fever and respiratory symptoms within the last 24 hours; loss of taste or small within the last 24 hours; and a positive COVID-19 test in the last 14 days.
The survey responses indicated that most pre-K-to-12 schools had some mitigation measures in place, such as mask mandates for teachers, daily screening of students and teachers for symptoms, and curtailment of extracurricular activities. The researchers found that when schools used seven or more mitigation measures, the excess risk associated with in-person schooling mostly disappeared--and completely disappeared when 10 or more mitigation measures were reported.
"These findings support the idea that mitigation measures at schools can greatly reduce the excess COVID-19 risk to adults living with children who attend school in-person," says study first author Justin Lessler, an associate professor in the Department of Epidemiology at the Bloomberg School.
The issue of in-person schooling has been much debated in the United States from the start of the COVID-19 pandemic, leading to different school policies across the country. This policy diversity effectively set in motion a "natural experiment" with schooling and COVID-19 risk in the U.S. population. A chief concern has been that children going to school every day, even if they are not very susceptible to COVID-19 themselves, may bring home the virus to parents and other adult family members who are at higher risk of disease.
To examine these issues, Lessler and colleagues used the COVID-19 Symptom Survey, an ongoing Facebook-based survey managed by Carnegie Mellon University's Delphi Group in collaboration with Facebook that garners about 250,000 responses per week. The researchers looked at responses during two recent periods--roughly from Thanksgiving to Christmas last year and mid-January to mid-February this year--from respondents in households where at least one child was enrolled in a school, from pre-kindergarten through high school. Of the 576,051 people in this group, about 49 percent, or 284,789, reported being in a household with a child attending pre-K-to-12 school in-person rather than online or homeschooled.
In their analysis, Lessler and colleagues examined how the in-person school group differed from the online or homeschooled group in terms of reported COVID-19-related symptoms and outcomes. They adjusted the results to account for obvious confounding factors such as differences in local COVID-19 rates.
In addition to the 38 percent increase in the odds of getting a COVID-19-related illness among respondents in households with an in-person-schooled child, the researchers found a 21 percent increase in the odds for the loss of taste or smell--one of the core symptoms of COVID-19--and a 30 percent increase in the odds for testing positive for SARS-CoV-2 infection in the previous two weeks.
The strength of these associations appeared to increase with grade level. At the K and pre-K level, the association with COVID-19 outcomes was not significant for all outcomes, but the strength of those associations rose steadily, peaking at the grade 9-12 level--where the excess risk of a recent positive SARS-CoV-2 test for household members was over 50 percent. These findings are consistent with past studies suggesting less susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2 infection and COVID-19 illness among younger children compared to older ones.
The survey data included responses about COVID-19 mitigation measures in schools attended by children in the respondent's household. These mitigation measures included mask mandates for teachers and students, extra space between desks, suspension of school clubs, sports, and other extracurricular activities, and daily symptom screening among teachers and students. Respondents with a child in their household attending school in person reported a mean of 6.7 mitigation measures at school--with significant variations in that figure across the country, from a mean of 4.6 measures in South Dakota schools to 8.9 in Vermont schools.
The analysis also suggested that most of the increased COVID-19-related risk was concentrated in schools with fewer than seven mitigation measures, and that in-person schooling was not associated with increased risk for any COVID-19-related outcomes among respondents living with children in schools with ten or more measures.
"Because the study is based on a self-reported symptom survey and a setting where we can't randomize students to different schooling modes and mitigation measures, it has limitations," Lessler says. "But having hundreds of thousands of respondents and the ability to control for geographic and individual-level characteristics helps make up for those limitations."
He and his colleagues plan to follow up with studies of how in-person schooling and school-based mitigation measures affect community-wide spread of COVID-19.
"Household COVID-19 risk and in-person schooling" was co-authored by Justin Lessler, M. Kate Grabowski, Kyra Grantz, Elena Badillo-Goicoechea, C. Jessica Metcalf, Carly Lupton-Smith, Andrew Azman, and Elizabeth Stuart.
INFORMATION:
Support for the research was provided by a Johns Hopkins University Discovery Award, Johns Hopkins University COVID-19 Modeling and Policy Hub Award, and the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services.
April 29, 2021 -An increasing number of digital mental health interventions are designed for adolescents and young people with a range of mental health issues, but the evidence on their effectiveness is mixed, according to research by Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health and Spark Street Advisors.
Computerized cognitive behavioral therapy was found effective for anxiety and depression in adolescents and young people holding promise for increasing access to mental health treatment for these conditions. However, the effectiveness of other digital interventions, including therapeutic video games, mobile apps, or social networking sites, and addressing a range of other mental health outcomes remain ...
Archeologists have learned a lot about our ancestors by rummaging through their garbage piles, which contain evidence of their diet and population levels as the local flora and fauna changed over time.
One common kitchen scrap in Africa -- shells of ostrich eggs -- is now helping unscramble the mystery of when these changes took place, providing a timeline for some of the earliest Homo sapiens who settled down to utilize marine food resources along the South African coast more than 100,000 years ago.
Geochronologists at the University of California, Berkeley, and the Berkeley ...
The European house mouse has invaded nearly every corner of the Americas since it was introduced by colonizers a few hundred years ago, and now lives practically everywhere humans store their food.
Yet in that relatively short time span -- 400 to 600 mouse generations -- populations on the East and West Coasts have changed their body size and nest building behavior in nearly identical ways to adapt to similar environmental conditions, according to a new study by biologists at the University of California, Berkeley.
To make these adaptations -- at least in the case of body size -- mice in the Western United States ...
Research has shed new light on the impact of humans on Earth's biodiversity. The findings suggest that the rate of change in an ecosystem's plant-life increases significantly during the years following human settlement, with the most dramatic changes occurring in locations settled in the last 1500 years.
An international research team studied fossilised pollen dating back 5000 years, extracted from sediments on 27 islands. By analysing the fossils they were able to build up an understanding of the composition of each island's vegetation and how it changed from the oldest to the most recent pollen samples.
The study was led by Dr Sandra Nogué, Lecturer in Palaeoenvironmental ...
Researchers at Karolinska Institutet in Sweden have discovered a mechanism through which meningitis-causing bacteria can evade our immune system. In laboratory tests, they found that Streptococcus pneumoniae and Haemophilus influenzae respond to increasing temperatures by producing safeguards that keep them from getting killed. This may prime their defenses against our immune system and increase their chances of survival, the researchers say. The findings are published in the journal PLoS Pathogens.
"This discovery helps to increase our understanding of the mechanisms these bacteria use to evade our normal immune defenses," ...
Scientists have been able to track how a multi-drug resistant organism is able to evolve and spread widely among cystic fibrosis patients - showing that it can evolve rapidly within an individual during chronic infection. The researchers say their findings highlight the need to treat patients with Mycobacterium abscessus infection immediately, counter to current medical practice.
Around one in 2,500 children in the UK is born with cystic fibrosis, a hereditary condition that causes the lungs to become clogged up with thick, sticky mucus. The condition tends to decrease life expectancy among patients.
In recent years, M. abscessus, a species of multi-drug resistant bacteria, has emerged as a significant global threat to individuals with cystic fibrosis and other lung diseases. ...
Considerable gap in evidence around whether portable air filters reduce the incidence of COVID-19 and other respiratory infections
There is an important absence of evidence regarding the effectiveness of a potentially cost-efficient intervention to prevent indoor transmission of respiratory infections, including COVID-19, warns a study by researchers at the University of Bristol.
Respiratory infections such as coughs, colds, and influenza, are common in all age groups, and can be either viral or bacterial. Bacteria and viruses can become airborne via talking, coughing or sneezing. The current global coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic is also spread primarily by airborne droplets, and to date has led to over three million deaths ...
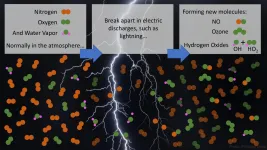
Lightning bolts break apart nitrogen and oxygen molecules in the atmosphere and create reactive chemicals that affect greenhouse gases. Now, a team of atmospheric chemists and lightning scientists have found that lightning bolts and, surprisingly, subvisible discharges that cannot be seen by cameras or the naked eye produce extreme amounts of the hydroxyl radical -- OH -- and hydroperoxyl radical -- HO2.
The hydroxyl radical is important in the atmosphere because it initiates chemical reactions and breaks down molecules like the greenhouse gas methane. OH is the main driver of many compositional changes in the atmosphere.
"Initially, we looked at these huge OH and HO2 signals found in the clouds and asked, what is wrong with our instrument?" said William ...
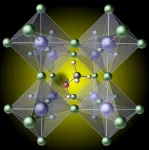
Researchers in the materials department in UC Santa Barbara's College of Engineering have uncovered a major cause of limitations to efficiency in a new generation of solar cells.
Various possible defects in the lattice of what are known as hybrid perovskites had previously been considered as the potential cause of such limitations, but it was assumed that the organic molecules (the components responsible for the "hybrid" moniker) would remain intact. Cutting-edge computations have now revealed that missing hydrogen atoms in these molecules can cause massive efficiency losses. The findings are published in ...
An international team led by Xiangming Xiao, George Lynn Cross Research Professor in the Department of Microbiology and Plant Biology, University of Oklahoma College of Arts and Sciences, published a paper in the April issue of the journal Nature Climate Change that has major implications on forest policies, conservation and management practices in the Brazilian Amazon. Xiao also is director of OU's Center for Earth Observation and Modeling. Yuanwei Qin, a research scientist at the Center for Earth Observation and Modeling, is the lead author of the study.
For the study described in the paper, "Carbon loss ...