Nanotechnology offers new hope for bowel cancer patients
2021-05-03
(Press-News.org) Bowel cancer survival rates could be improved if chemotherapy drugs were delivered via tiny nanoparticles to the diseased organs rather than oral treatment.
That's the finding from Indian and Australian scientists who have undertaken the first study, using nanoparticles to target bowel cancer, the third most common cancer in the world and the second most deadliest.
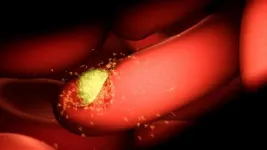
The researchers have shown in animal experiments that nanoparticles containing the chemotherapy drug Capecitabine (CAP) attach themselves directly to the diseased cells, bypassing healthy cells and therefore reducing toxic side effects as well as the size and number of tumours.
The scientists, from the Manipal Academy of Higher Education, Indian Institute of Science and the University of South Australia, have published their findings in the journal Carbohydrate Polymers.
UniSA Professor of Pharmaceutical Science, Sanjay Garg - the sole Australian researcher involved in the project - says that CAP (otherwise known as Xeloda) is the first-line chemotherapy drug for bowel cancer. He co-supervised the PhD scholar Reema Narayan, with Prof Usha Nayak from Manipal, India.
"Due to its short life, a high dose is necessary to maintain effective concentration, resulting in some harsh side effects when delivered conventionally, including severe hand and foot pain, dermatitis, nausea, vomiting, dizziness and loss of taste," Prof Garg says.
The side effects are exacerbated because the drug affects both healthy and diseased cells.
"A viable alternative to conventional therapy is targeted drug delivery using nanoparticles as smart carriers so that the drug can be delivered specifically to the tumour. This allows a smaller and less toxic dose," he says.
CAP delivered via nanoparticles reduces both the size and number of cancerous bowel tumours, results in fewer abnormal cells, improved red and white blood cell counts and less damage to other organs.
The targeted delivery system has a dual function: binding the receptors as well as releasing the drug to the tumour micro-environment.
"It has been a challenging project but we believe the platform technology developed can be applied to other cancers and chemotherapeutic drugs," Prof Garg says.
Approximately two million people are diagnosed with bowel cancer each year and half of those are not expected to survive, according to the World Health Organization.
The risk factors include consuming processed meat, red meat and alcoholic drinks and obesity.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-05-03
National Health and Medical Research Council, the European Research Council and the Victorian Government.
WEHI researchers have identified how natural human antibodies can block malaria parasites from entering red blood cells, potentially indicating how new protective therapies could be developed against this globally significant disease.
The research provides greater insight into how antibodies block the entry of Plasmodium vivax malaria parasites into young red blood cells called reticulocytes. It builds on an earlier discovery that the P. vivax latches onto the transferrin receptor 1 (TfR1) to enter cells.
The research, led by Associate Professor Wai-Hong Tham and PhD student Li-Jin Chan ...
2021-05-03
Many drug addicts take not only one substance but rather several. Scientists at the Max Planck Institute of Experimental Medicine in Göttingen have investigated the role that genes and the environment play in the development of such multiple substance consumption or polytoxicomania. Their results show that, in addition to genetic factors, the accumulation of several unfavourable environmental factors causes people to slip into such an extreme form of multiple drug use. Among the risk factors were sexual and physical abuse, living in a big city, and migration experience as well as the use ...
2021-05-03
Aromaticity, a concept usually used to explain the striking stability and unusual reactivity of certain carbon-based molecules, could inspire the design of new catalysts with novel uses, KAUST researchers have shown.
Chemists first came upon the anomalous behavior of aromatic molecules in the nineteenth century while studying benzene. The unexpected stability of this six-carbon cyclic structure comes down to its electrons.
In general, bonding electrons hold a specific pair of atoms together in a discrete chemical bond. But in benzene, six electrons form a delocalized ring across the molecule. A host of other molecules share this feature. "Many classic examples of organic and organometallic reactivity can be explained on this basis," says Théo Gonçalves, ...
2021-05-03
In material physics understanding how systems interact across the interfaces separating them is of central interest. But can physical models clarify similar concepts in living systems, such as cells? Physicists at the University of Geneva (UNIGE), in collaboration with the University of Zurich (UZH), used the framework of disordered elastic systems to study the process of wound healing - the proliferation of cell fronts which eventually join to close a lesion. Their study identified the scales of the dominant interactions between cells which determine this process. The results, published in the journal Scientific Reports, will allow better analysis of cell front behaviour, in terms of both wound healing and tumour development. In the future, this approach may offer personalised diagnostics ...
2021-05-03
Scientists are warning that drinking water supplies in parts of rural West Africa are being contaminated by lead-containing materials used in small community water systems such as boreholes with handpumps and public taps.
They analysed scrapings taken from the plumbing of 61 community water supply systems in Ghana, Mali and Niger. Eighty percent of the tested systems had at least one component that contained lead in excess of international guidance.
Lead is released into the water when the components corrode.
The study, by a research team from the University of Leeds, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill and Boston University, also took samples of the water from those 61 water distribution systems, ...
2021-05-03
Migratory waterbirds are particularly exposed to the effects of climate change at their breeding areas in the High Arctic and in Africa, according to a new study published in Bird Conservation International. The research team came to this conclusion after modelling climatic and hydrological conditions under current and future climate scenarios (in 2050) and comparing the impact on the distribution of 197 of the 255 waterbird species listed under the Agreement on the Conservation of African-Eurasian Migratory Waterbirds (AEWA). The international team was led by Wetlands International, BirdLife International, and the British Trust for Ornithology, involved researchers from various universities, including McGill. The results suggest that investing more in habitat conservation in the wider ...
2021-05-03
A team of researchers led by Nanyang Technological University, Singapore (NTU Singapore) has developed a device that offers a quicker and less invasive way to seal tears and holes in blood vessels, using an electrically-activated glue patch applied via a minimally invasive balloon catheter.
This device could eventually replace the need for open or keyhole surgery to patch up or stitch together internal blood vessel defects.
After inserting the catheter into an appropriate blood vessel, the glue patch - nicknamed 'Voltaglue' - can be guided through the body to where the tear is located and then activated using retractable electrodes to glue it shut in ...
2021-05-03
Symptoms of health anxiety are common already during childhood and adolescence - and if the children do not receive the correct help, the anxiety can become a permanent problem with serious personal and socio-economic consequences. This is shown by a new research result from Aarhus University and the University of Copenhagen.
Ida is 11 years old. Six months ago, her grandmother died of cancer after a long illness and since then Ida has become more and more anxious that she too will get cancer and die. The anxiety can be triggered when she passes by a hospital or sees people who look ill. ...
2021-05-03
What would it be like to produce fertilizer in your own basement? Leguminous plants, like peas, beans, and various species of clover, obtain the organic nitrogen they need for their growth from symbiotic soil bacteria via specialized structures in their roots. A team led by the cell biologist Prof. Dr. Thomas Ott from the University of Freiburg's Faculty of Biology has now detected a factor in the root cells that the plants need for the initial contact with these so-called root-associated bacteria, which live in the soil. They discovered a protein found only in legumes called symbiotic formin 1 (SYFO1) and demonstrated the essential role it plays in symbiosis. Together with the molecular biologist Prof. Dr. Robert Grosse University of Freiburg's Faculty of Medicine and the evolutionary ...
2021-05-03
In a number of biological processes, iron-sulfur clusters play a vital role, where they act as cofactors to enzymes. Research published in Angewandte Chemie now shows that cubic clusters can support unusual bonding states. This study shows that the cluster copes well with a multiple bond between iron and nitrogen--a structural motif that may be involved in biological nitrogen fixation.
Clusters made of iron and sulfur atoms are essential cofactors for a number of enzymes, especially in biological processes involving electron transfer. As an example, nitrogen-fixing bacteria use iron-sulfur clusters to convert ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Nanotechnology offers new hope for bowel cancer patients