Plastic pollution in the deep sea: A geological perspective
Focus study published in this month's Geology
2021-05-04
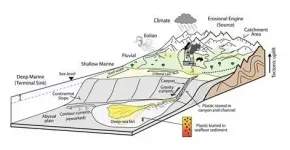
(Press-News.org) Boulder, Colo., USA: A new focus article in the May issue of Geology summarizes research on plastic waste in marine and sedimentary environments. Authors I.A. Kane of the Univ. of Manchester and A. Fildani of the Deep Time Institute write that "Environmental pollution caused by uncontrolled human activity is occurring on a vast and unprecedented scale around the globe. Of the diverse forms of anthropogenic pollution, the release of plastic into nature, and particularly the oceans, is one of the most recent and visible effects."
The authors cite multiple studies, including one in the May issue by Guangfa Zhong and Xiaotong Peng, discussed in a previous GSA press release when it was published online ahead of print (26 Jan. 2021). Zhong and Peng were surprised to find plastic waste in a deep-sea submarine canyon located in the northwestern South China Sea.
"Plastic is generally considered to be the dominant component of marine litter, due to its durability and the large volume produced," write Kane and Fildani. "Nano- and microplastics are a particularly insidious form of anthropogenic pollutant: tiny fragments and fibers may be invisible to the naked eye, but they are ingested with the food and water we consume and absorbed into the flesh of organisms."
One of their vital questions is, "If some plastics can survive for >1000 years in terrestrial environments, how long do they last in ocean trenches that are kilometers deep, dark, cold, and at high pressure? How long does it take microplastic to break down into microplastics and nanoplastics in the deep sea?"
"While it is incumbent on policy makers to take action now to protect the oceans from further harm, we recognize the roles that geoscientists can play," write Kane and Fildani. That includes using their deep-time perspective to address the societal challenges, their understanding of the present-day distribution on the seafloor and in the sedimentary record, using geoscience techniques to record the downstream effects of mitigation efforts, and to predict the future of seafloor plastics.
In summary, they write, "We understand ... the transient nature of the stratigraphic record and its surprising preservation, and the unique geochemical environments found in deep-sea sediments. Our source-to-sink approach to elucidate land-to-sea linkages can identify the sources and pathways that plastics take while traversing natural habitats and identify the context in which they are ultimately sequestered, and the ecosystems they affect. This will happen by working closely with oceanographers, biologists, chemists, and others tackling the global pollution problem."
INFORMATION:
FEATURED ARTICLE
Anthropogenic pollution in deep-marine sedimentary systems--A geological perspective on the plastic problem
I.A. Kane; A. Fildani: Geology, v. 49, p. 607-608, https://doi.org/10.1130/focus052021.1.
You can access the current issue of GEOLOGY at https://pubs.geoscienceworld.org/geology/issue. Representatives of the media may obtain complimentary articles by contacting Kea Giles at the e-mail address above. Please discuss articles of interest with the authors before publishing stories on their work, and please make reference to GEOLOGY in articles published. Non-media requests for articles may be directed to GSA Sales and Service, gsaservice@geosociety.org.
https://www.geosociety.org
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-05-04
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. -- As more people go online for shopping, understanding how they rely on e-commerce recommendation systems to make purchases is increasingly important. Penn State researchers now suggest that it's not just what is recommended, but how and why it's recommended, that helps to shape consumers' opinions.
In a study, the researchers investigated how people reacted to two product recommendation systems. The first system generated recommendations based on the user's earlier purchases -- often referred to as content-based recommendation systems. ...
2021-05-04
EL PASO, Texas -- For more than a year, researchers at The University of Texas at El Paso's Stanley E. Fulton Gait Research & Movement Analysis Lab in the College of Health Sciences have been using real-time 3D animation to investigate motor impairments in children who have autism spectrum disorder (ASD). Their aim is to understand how children with autism can learn motor skills, so that they can receive effective therapies.
The results of their study, titled "Children With Autism Exhibit More Individualized Responses to Live Animation Biofeedback Than Do Typically Developing Children," were recently published in the journal of Perceptual and Motor Skills. The paper's release coincides with National Autism Awareness Month in April.
"The greatest takeaway from this study is that when teaching ...
2021-05-04
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. -- Tweaking the look of a social media profile may subtly alter a person's reaction to the health messages that appear on that site, according to researchers. They add that these reactions could influence whether the users heed the advice of those messages.
In a study, the researchers found that people who gained a feeling of control when they customized an online website were more likely to perceive the health message as a threat to their freedom, lowering the chance that they will adopt the message's advice. On the other hand, when customization bolstered the users' sense of identity, they did not resent the message as much and were more willing to consider the ads' recommended behavioral changes, according to the researchers.
"In ...
2021-05-03
Ensuring that veterans have stable housing not only reduces homelessness but also slashes the cost of providing them with publicly funded health care, according to a national study led by University of Utah Health scientists. The researchers found that veterans who received temporary financial assistance (TFA) from the Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) to acquire or retain housing had fewer hospital visits and an average reduction in health care costs of $2,800 over a two-year period than veterans who did not receive this benefit.
The researchers say this model could help non-profit organizations and other federal, state, and local governments better serve homeless Americans who are not veterans.
"Getting ...
2021-05-03
Black and Latino neighborhoods in the 30 most populous U.S. cities had fewer pharmacies than white or diverse neighborhoods in 2007-2015, USC research shows, suggesting that 'pharmacy deserts'- like so-called food deserts-may be an overlooked contributor to persistent racial and ethnic health disparities.
Pharmacies are increasingly vital points of care for essential health services. In addition to filling prescriptions to treat chronic health conditions, pharmacists dispense emergency doses of naloxone to reverse opioid overdoses, contraceptives to prevent unplanned pregnancy and COVID-19 testing and vaccinations.
But ...
2021-05-03
More than 25% of the world's population (greater than 1.5 billion people) face the burden of soil-transmitted helminth (STH) infections, a species of intestinal parasite whose eggs develop in the soil before finding a new host. The main cause of this high infection rate is lack of access to adequate sanitation facilities (toilets) and the consequent contamination of the environment with human feaces. While universal access to adequate sanitation is one of the sustainable development goals, parasite burdens are still causing harm. Fortunately, deworming medicines are highly effective and safe. Researchers from Syracuse University, the World Health Organization, ...
2021-05-03
A year into the COVID-19 pandemic, mass vaccinations have begun to raise the tantalizing prospect of herd immunity that eventually curtails or halts the spread of SARS-CoV-2. But what if herd immunity is never fully achieved - or if the mutating virus gives rise to hyper-virulent variants that diminish the benefits of vaccination?
Those questions underscore the need for effective treatments for people who continue to fall ill with the coronavirus. While a few existing drugs show some benefit, there's a pressing need to find new therapeutics.
Led by The University of New Mexico's Tudor Oprea, MD, PhD, scientists ...
2021-05-03
An abnormal build up of carbohydrates -- sugars and starches -- in the kernels and leaves of a mutant line of corn can be traced to one misregulated gene, and that discovery offers clues about how the plant deals with stress.
That is the conclusion of Penn State researchers whose previous study discovered the Maize ufo1 gene responsible for creating the mutant corn line. They now are assessing its effects and potential for inclusion in breeding new lines of corn better able to thrive in a warming world. The finding of higher sugar levels in plant tissues in their latest study is just ...
2021-05-03
May 3, 2021
Using social values for profit cheapens them, a new study cautions.
Toronto - Businesses sometimes align themselves with important values such as a clean environment, feminism, or racial justice, thinking it's a win-win: the value gets boosted along with the company's bottom line.
But be careful, warns new research from the University of Toronto's Rotman School of Management.
Using these values primarily for self-interested purposes such as profit or reputation can ultimately undermine their special status and erode people's commitment to them.
"It sets a different norm for appropriate use of the value," says research author Rachel Ruttan, an assistant professor of organizational behaviour and human resources at the Rotman School, who ...
2021-05-03
When it comes to batteries, lithium-ion are the best we have as far as energy density and convenience.
For now.
The Washington University in St. Louis lab of Peng Bai, assistant professor in the Department of Energy, Environmental & Chemical Engineering in the McKelvey School of Engineering, has developed a stable sodium ion battery that is highly efficient, will be less expensive to make and is significantly smaller than a traditional lithium ion battery due to the elimination of a once-necessary feature.
"We've found that the minimal is maximum," ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Plastic pollution in the deep sea: A geological perspective
Focus study published in this month's Geology