(Press-News.org) A new service piloted at Penn Medicine allowed a proportion of patients to avoid hospitalization by providing them with greater support after visiting the emergency department. The vast majority of the patients enrolled in the service - nearly 9 out of 10 - did not need to return to the hospital for care in the month that followed their initial visit. The study was published in Healthcare.
"The culture is shifting where we realize that hospitalization is not always the best option for patients - particularly patients with chronic illness," said one of the study's lead authors, Austin Kilaru, MD, an emergency physician at Penn Medicine. "We need to find better ways of helping patients not just get healthy in a hospital, but stay healthy at home - whenever they are ready to be there."
Increasingly, emergency departments care for greater shares of patients with acute symptoms and illnesses. Increased visits can lead to strain on hospitals, so Kilaru, co-author David Resnick, a senior innovation manager at Penn Medicine's Center for Health Care Innovation, and their team devised a method to open capacity in emergency departments and hospitals - by sending patients home with the right resources and support to help them recover safely.
The project, which began in 2018 within the Center for Health Care Innovation's annual Innovation Accelerator, was named Practical Alternative to Hospitalization (PATH). It contained two important elements.
First, the PATH team deployed an advanced practice provider (APP) to screen hospital bed requests to determine which patients met criteria for discharge to home. They considered the reasons for the patient's visit, their vital signs, medical history, and social support systems. If the patient's emergency physician agreed with enrolling in PATH, the APP developed a comprehensive plan in partnership with that physician and the patient's care team.
Patients enrolled in the program received personalized support at home. This included phone calls or text messages to assess their status, coordination of outpatient appointments, and additional diagnostic testing. This tailored plan might also include home nursing visits, physical or occupational therapy, or transportation assistance.
"We were concerned that emergency physicians would be reluctant to discharge patients who they would have normally hospitalized, but it turns out that they liked having the option of choosing our services," Kilaru said. "It's a new alternative to staying in the hospital or going home completely on their own. We were seen as an added support, acting in the best interests of patients and medical providers alike."
In this study's 14-day trial period set in a single hospital during December 2019, 52 patients met PATH's eligibility requirements (of 199 possible patients). More than half of them, 30, enrolled in the program, with most of the remainder still requiring hospitalization at the discretion of the treating emergency physician.
Many of the patients enrolled in the program for common conditions, such as chest pain, high blood sugar, and congestive heart failure. The study authors estimate that patients would have spent more than two days, on average, in the hospital and eight additional hours waiting in the emergency department. Only four patients needed to return to the hospital within 30 days of their initial visit, when the PATH team recognized that patients again required hospital-level care.
"Another concern in this pilot was that patients might have worsening illness at home and need to return to the emergency department," Kilaru said. "Fortunately, our patients did well and had good outcomes - even 30 days later. We created careful safeguards to select the right patients, so while a few patients did need to return, it was not unexpected, and we could help communicate key medical and social issues to the emergency department and hospital teams."
The study took place just a few months before the COVID-19 pandemic swept the East Coast. While the service was paused as a result, the pandemic created a surge of interest in shifting care from hospitals to home, like Penn Medicine's Cancer Care at Home. In addition, lessons from this study have been applied to efforts to manage COVID at Penn Medicine, including an "accelerated care pathway," where patients who only needed short hospital stays were identified in the emergency department, efficiently treated in the hospital, and followed closely at home.
"This could be promising for payers, health systems, and patients alike," Resnick said. "Payers benefit by having their members avoid costly inpatient stays. Patients benefit by having more safe days at home. And hospitals with busy emergency departments and full beds benefit by freeing up resources that can be utilized by the most sick and complex patients."
INFORMATION:
Other authors on this study include Danielle Flynn, Avanti Rangnekar, Madeline Snyder, Kehinde Oyekanmi, Denise Fitzpatrick, Zachary Meisel, David Asch, and Krisda Chaiyachati.
Leather is an ever growing multi-billion dollar industry requiring more than 3.8 billion bovine animals - equal to one for every two people on earth - to sustain production each year. And while the products - clothing, shoes, furniture and more - can be quite elegant and durable, the environmental impact of leather production has been severe, leading to deforestation, water and land overuse, environmental pollution, and greenhouse gas emissions.
Researchers at Tufts University School of Engineering set out to find an alternative to leather, with similar texture, flexibility and stiffness, yet focused on materials that are sustainable, non-toxic, and friendly to the environment. It turns out, we have been wearing that material ...
PITTSBURGH, May 5, 2021 - Subtle differences in the shape of the brain that are present in adolescence are associated with the development of psychosis, according to an international team led by neuroscientists at the University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine and Maastricht University in the Netherlands.
In results published today in JAMA Psychiatry, the differences are too subtle to detect in an individual or use for diagnostic purposes. But the findings could contribute to ongoing efforts to develop a cumulative risk score for psychosis that would allow for earlier detection and treatment, as well as targeted therapies. The discovery was made with the largest-ever ...
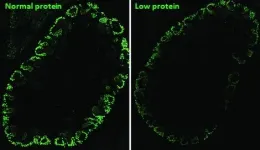
Besides being underweight, babies born to women whose diet lacked sufficient protein during pregnancy tend to have kidney problems resulting from alterations that occurred while their organs were forming during the embryonic stage of their development.
In a study published in PLOS ONE, researchers affiliated with the University of Campinas (UNICAMP) in the state of São Paulo, Brazil, discovered the cause of the problem at the molecular level and its link to epigenetic phenomena (changes in gene expression due to environmental factors such as stress, exposure to toxins or malnutrition, among others).
According to the authors, between 10% and 13% of the world population ...
Researchers from the University of Liverpool have shown the potential of repurposing an existing and cheap drug into a long-acting injectable therapy that could be used to treat Covid-19.
In a paper published in the journal Nanoscale, researchers from the University's Centre of Excellence for Long-acting Therapeutics (CELT) demonstrate the nanoparticle formulation of niclosamide, a highly insoluble drug compound, as a scalable long-acting injectable antiviral candidate.
The team started repurposing and reformulating identified drug compounds with the potential for COVID-19 therapy candidates within weeks of the first lockdown. Niclosamide is just one of the drug compounds identified and has been shown to be highly effective against SARS-CoV-2 in a number of laboratory studies.
Using ...
New Johns Hopkins University simulations offer an intriguing look into Saturn's interior, suggesting that a thick layer of helium rain influences the planet's magnetic field.
The models, published this week in AGU Advances, also indicate that Saturn's interior may feature higher temperatures at the equatorial region, with lower temperatures at the high latitudes at the top of the helium rain layer.
It is notoriously difficult to study the interior structures of large gaseous planets, and the findings advance the effort to map Saturn's hidden regions.
"By ...
The incorporation of boron into polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon systems leads to interesting chromophoric and fluorescing materials for optoelectronics, including organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDS) and field-effect transistors, as well as polymer-based sensors. In the journal Angewandte Chemie, a research team has now introduced a new anionic organoborane compound. Synthesis of the borafluorene succeeded through the use of carbenes.
Borafluorene is a particularly interesting boron-containing building block. It is a system of three carbon rings joined at the edges: two six-membered and one central five-membered ring, whose free tip is the boron atom. While neutral, radical, and cationic (positively ...
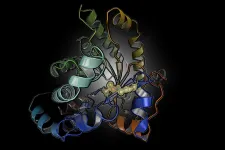
Proteins perform a vast array of functions in the cell of every living organism with critical roles in almost every biological process. Not only do they run our metabolism, manage cellular signaling and are in charge of energy production, as antibodies they are also the frontline workers of our immune system fighting human pathogens like the coronavirus. In view of these important duties, it is not surprising that the activity of proteins is tightly controlled. There are numerous chemical switches that control the structure and, therefore, the function of proteins in response to changing environmental conditions and stress. ...
Philadelphia, May 5, 2021--When Luke Terrio was about seven months old, his mother began to realize something was off. He had constant ear infections, developed red spots on his face, and was tired all the time. His development stagnated, and the antibiotics given to treat his frequent infections stopped working. His primary care doctor at Children's Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP) ordered a series of blood tests and quickly realized something was wrong: Luke had no antibodies.
At first, the CHOP specialists treating Luke thought he might have X-linked agammaglobulinemia (XLA), a rare immunodeficiency syndrome seen in children. However, as the CHOP research team continued investigating Luke's case, they realized Luke's condition was unlike any disease described ...
Pesticides have been used in European agriculture for more than 70 years, so monitoring their presence, levels and their effects in European soils quality and services is needed to establish protocols for the use and the approval of new plant protection products.
In an attempt to deal with this issue, a team led by the prof. Dr. Violette Geissen from Wageningen University (Netherlands) have analysed 340 soil samples originating from three European countries to compare the contentdistribution of pesticide cocktails in soils under organic farming practices and soils under conventional practices. This study was a combined effort of 3 EC funded projects addressing soil
quality: RECARE (http://www.recare-project.eu/), iSQAPER (http://www.isqaper-project.eu) ...
T-cells play a central role in our immune system: by means of their so-called T-cell receptors (TCR) they make out dangerous invaders or cancer cells in the body and then trigger an immune reaction. On a molecular level, this recognition process is still not sufficiently understood.
Intriguing observations have now been made by an interdisciplinary Viennese team of immunologists, biochemists and biophysicists. In a joint project funded by the Vienna Science and Technology Fund and the FWF, they investigated which mechanical processes take place when an antigen is recognized: ...