(Press-News.org) Granular materials, such as sand and gravel, are an interesting class of materials. They can display solid, liquid, and gas-like properties, depending on the scenario. But things can get complicated in cases of high-speed vehicle locomotion, which cause these materials to enter a "triple-phase" nature, acting like all three fundamental phases of matter at the same time.
As reported in the April 23, 2021 issue of the journal Science Advances, a team of engineers and physicists from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) and Georgia Institute of Technology (GIT) have proposed a new model, Dynamic Resistive Force Theory, or DRFT, to enable near real-time modeling of high-speed motion for arbitrarily shaped objects moving through granular media.
"Applications for this work include the predictive modeling of ground impacts, off-road vehicles, animal locomotion, and extraterrestrial rovers," notes Ken Kamrin, associate professor in the Department of Mechanical Engineering at MIT and the study's corresponding author.
Often, granular materials are modeled grain-by-grain, but this type of approach can be an expensive and slow affair. For instance, modeling one liter of beach sand for just a few seconds might take weeks to process on your average laptop computer.
Researchers have long sought faster ways to accurately model such materials -- and often their overall interest is focused on understanding one piece in the overall modeling puzzle: the net force that a granular material like sand exerts on larger moving bodies.
"This is why, over the past century, scientists and engineers have developed the discipline of 'terramechanics,' which helps predict the locomotive performance of vehicles -- mostly circular wheel and tanks treads -- in granular terrains, like deserts," Kamrin explains. "The majority of the methods used in this discipline remain empirical in nature with little room for customization. DRFT fills this gap and allows for modeling the motion of arbitrary objects moving at various speeds in sands."
DRFT is a joint effort between Kamrin and graduate student Shashank Agarwal (also of Mechanical Engineering at MIT) in collaboration with Daniel Goldman, Dunn Family Professor of Physics and graduate student Andras Karsai (both of School of Physics at GIT).
The research team unearthed the concept of DRFT after careful study of a continuum model of granular media, which -- unlike the grain-by-grain approach -- models the smooth flow of grains.
Their continuum analysis revealed an extended formula for the resistive forces that act on rapidly moving objects. While the static force response of granular media is already known as static RFT (Resistive Force Theory), DRFT's extended formulation includes two "key velocity-dependent effects" when calculating the force on each small piece of an object's surface. One contribution is due to the inertial effect of accelerating the granular media, and the other is, as Goldman explains, a "subtle structural modification," due to the changes in material strength that arise as the granular free-surface profile changes.
"Interestingly, when put together, DRFT captures diverse counterintuitive observations observed in granular locomotion, including the behaviors seen in circular and 'grousered' wheel locomotion, 'c-leg' robot locomotion, and possibly even the locomotion of desert animals like zebra-tailed lizards at high speeds," Goldman notes. "At the same time, DRFT illuminates the dominating physical phenomena occurring in rapid propulsion in grain beds."
"The research is of crucial importance for applications like path planning and optimal locomotor design for terrestrial, as well as extraterrestrial, applications, such as Mars and lunar rovers," adds Kamrin. "While this study specifically focuses on granular materials, it provides a blueprint for developing similar rapid, reduced-order models for other classes of materials like muds and slurries."
INFORMATION:
The Georgia Institute of Technology, or Georgia Tech, is a top 10 public research university developing leaders who advance technology and improve the human condition. The Institute offers business, computing, design, engineering, liberal arts, and sciences degrees. Its nearly 40,000 students, representing 50 states and 149 countries, study at the main campus in Atlanta, at campuses in France and China, and through distance and online learning. As a leading technological university, Georgia Tech is an engine of economic development for Georgia, the Southeast, and the nation, conducting more than $1 billion in research annually for government, industry, and society.
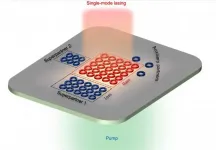
The field of photonics aims to transform all manner of electronic devices by storing and transmitting information in the form of light, rather than electricity. Beyond light's raw speed, the way that information can be layered in its various physical properties makes devices like photonic computers and communication systems tantalizing prospects.
Before such devices can go from theory to reality, however, engineers must find ways of making their light sources -- lasers -- smaller, stronger and more stable. Robots and autonomous vehicles that use LiDAR for optical sensing and ranging, manufacturing and material ...
Scientists are certain that dark matter exists. Yet, after more than 50 years of searching, they still have no direct evidence for the mysterious substance.
University of Delaware's Swati Singh is among a small group of researchers across the dark matter community that have begun to wonder if they are looking for the right type of dark matter.
"What if dark matter is much lighter than what traditional particle physics experiments are looking for?" said Singh, an assistant professor of electrical and computer engineering at UD.
Now, Singh, Jack Manley, a UD doctoral student, and collaborators at ...
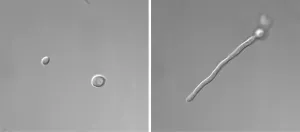
BUFFALO, N.Y. -- You might call Candida albicans a shape-shifter: As this fungus grows, it can multiply as single, oval-shaped cells called yeast or propagate in an elongated form called hypha, consisting of thread-like filaments.
This dual nature can help the pathogen survive in the body, where it can cause disease, including dangerous hospital-acquired infections.
But how does this switching ability occur?
New research identifies one factor that may contribute. In a study that will be published on May 5 in the journal mSphere, University at Buffalo biologists Guolei Zhao and Laura Rusche report that a protein called Sir2 may facilitate C. albicans' transition from ovoid yeast ...
WHAT:
A team of researchers funded by the National Institutes of Health has developed a new ultrasound technique to monitor the placenta for impaired fetal blood flow early in pregnancy. The technique, which uses conventional ultrasound equipment, relies on subtle differences in the pulsation of fetal blood through the arteries at the fetal and placental ends of the umbilical cord, potentially enabling physicians to identify placental abnormalities that impair fetal blood flow and, if necessary, deliver the fetus early. Like current ultrasound techniques, the new technique can also detect impaired flow of maternal blood through the placenta.
The study was conducted by John G. Sled, Ph.D., of The Hospital for Sick Children in Toronto, ...
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) images are usually meant to be static. But now, researchers from Mātai Medical Research Institute (Mātai), Stevens Institute of Technology, Stanford University, the University of Auckland and other institutions, report on an imaging technique that captures the brain in motion in real time, in 3D and in stunning detail, providing a potential diagnostic tool for detecting difficult-to-spot conditions such as obstructive brain disorders and aneurysms - before they become life threatening.
The new technique, called 3D amplified ...
The ant came in a small vial of ethanol, sealed in a plastic bag, and packed in a small cardboard box. It was addressed to Yale's Douglas B. Booher.
German entomologist Phillip Hoenle had discovered the ant, which he noted had some peculiar features, in a rain forest in Ecuador. Now he wanted Booher, a research associate in the Yale Center for Biodiversity and Global Change and the Department of Ecology & Evolutionary Biology, to confirm whether this trap ant was truly a new species. If so, Hoenle and Booher would have the honor of naming it.
Booher had imagined ...
BIRMINGHAM, Ala. - Last year, Charles O. Elson, M.D., demonstrated a potential preventive treatment for Crohn's disease, a form of inflammatory bowel disease. He used a mouse model that included immune-reactive T cells from patients with Crohn's disease in a flagellin peptide-specific immunotherapy. This study provided proof-of-principle that a flagellin-directed immunotherapy might provide similar benefits in patients.
Now University of Alabama at Birmingham researchers have moved a step closer to possible clinical testing of this treatment, say Elson and co-first authors Katie Alexander, Ph.D., ...
Researchers have created a probe that glows when it detects an enzyme associated with issues that can lead to blood clots and strokes.
The team of researchers, from the Department of Chemistry and the National Lung and Heart Institute at Imperial College London, demonstrated that their probe quickly and accurately detects the enzyme in modified E. Coli cells.
They are now expanding this proof-of-concept study, published in the Journal of the American Chemical Society and funded by the British Heart Foundation (BHF), with the hope of creating rapid tests for cardiovascular problems and a new way to track long-term conditions.
The build-up of plaque in the arteries - known as atherosclerosis - can lead to coronary artery ...
Biodiversity is of crucial importance to the marine ecosystem. The prohibition of trawling activities in the Hong Kong marine environment for two and a half years has significantly improved biodiversity, an inter-university study led by City University of Hong Kong (CityU) has found. Research results showed that the trawl ban could restore and conserve biodiversity in tropical coastal waters.
The research team was led by Professor Kenneth Leung Mei-yee, CityU's Director of the State Key Laboratory of Marine Pollution (SKLMP) and Chair Professor in the Department ...
Researchers at CRANN (The Centre for Research on Adaptive Nanostructures and Nanodevices), and the School of Physics at Trinity College Dublin, today announced that a magnetic material developed at the Centre demonstrates the fastest magnetic switching ever recorded.
The team used femtosecond laser systems in the Photonics Research Laboratory at CRANN to switch and then re-switch the magnetic orientation of their material in trillionths of a second, six times faster than the previous record, and a hundred times faster than the clock speed of a personal computer.
This discovery demonstrates the potential of the material for a new generation of energy efficient ultra-fast computers and data storage systems.
The researchers ...