High-risk, disadvantaged groups face barriers to preventing spread of COVID-19
Researchers urge greater focus on ensuring access to vaccines and precautionary measures
2021-05-06
(Press-News.org) Social factors such as education, financial stability, food security and the neighborhood where someone resides were strongly correlated with whether or not individuals with heart disease adopted measures to prevent the spread of COVID-19, including wearing masks and working from home, according to a study presented at the American College of Cardiology's 70th Annual Scientific Session. The researchers say the findings draw attention to longstanding challenges related to social determinants of health.
"Unless we look at COVID-19 through the lens of social determinants of health, we may not optimize our yield from interventions, and we might not be reaching the group of individuals who need these interventions the most," said Kobina Hagan, MD, a postdoctoral fellow at Houston Methodist Research Institute and the study's lead author.
The research is based on data from the COVID-19 Household Impact Survey, which assessed COVID-19 preventive strategies along with health and sociodemographic factors among more than 25,000 U.S. adults. The researchers analyzed responses from just over 2,000 survey respondents who reported a history of heart disease, heart attack or stroke. According to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, heart disease increases the risk of severe illness from COVID-19. The researchers grouped survey respondents into quartiles reflecting social risk factors based on income and financial security, employment, education, health insurance status, food insecurity and neighborhood quality.
The largest gap was seen in the degree to which respondents reported having flexibility in their work arrangements--defined as being able to work from home or cancel or postpone work activities. Compared to those with the most favorable social risk profile, those with the greatest social adversity were 46% less likely to report flexibility at work. Individuals with the greatest social adversity were also 31% less likely to engage in all social distancing measures (canceling or postponing social activities and avoiding crowded public places, restaurants and contact with high-risk people) and 17% less likely to engage in all personal protective measures (wearing a face mask, washing hands and keeping a 6-foot distance from those outside their household) compared to those with the most favorable social risk profile. These differences remained significant even after accounting for demographics and comorbidities.
The study was conducted before COVID-19 vaccines were available, at a time when public health experts primarily recommended social distancing and other measures to slow the disease's spread. However, similar trends are likely at play in the context of vaccine access, researchers said.
"I think we are repeating the same mistakes and expecting better results," Hagan said. "I hope we can come to a point where we as a society take social disparities into account in our decision making. We have to prioritize these socially disadvantaged individuals in our public policy programs, including vaccine delivery, to reduce the disparities in COVID-19 risk and outcomes."
Although the survey did not assess the reasons why respondents did or did not adopt COVID-19 mitigation measures, Hagan said many of the factors reflect circumstances that are often outside of a person's control, such as their ability to work from home. For measures that involve more personal choice, he suggested that low health literacy may play a role in the lower uptake of mitigation measures among disadvantaged groups.
"We as a society have ignored all the disparities and inequities that were happening during calmer times, even in cardiovascular disease," Hagan said. "2020 was a time when we could no longer ignore the disparities. We need to focus on holistic strategies to effectively fight this pandemic and ensure those not afforded the privilege of personal protection, social distancing and work flexibilities are prioritized with vaccine outreach to avoid further compounding existing health inequalities."
INFORMATION:
For resources on managing heart disease and COVID-19, visit CardioSmart.org/coronavirus.
This study will be simultaneously published in Circulation: Cardiovascular Quality & Outcomes.
Hagan will present the study, "Social Determinants of Health Disparities for COVID-19 Mitigation Measures Among Adults with Cardiovascular Disease in the United States," on Saturday, May 15, at 9:30 a.m. ET / 13:30 p.m. UTC.
ACC.21 will take place May 15-17 virtually, bringing together cardiologists and cardiovascular specialists from around the world to share the newest discoveries in treatment and prevention. Follow @ACCinTouch, @ACCMediaCenter and #ACC21 for the latest news from the meeting.
The American College of Cardiology envisions a world where innovation and knowledge optimize cardiovascular care and outcomes. As the professional home for the entire cardiovascular care team, the mission of the College and its 54,000 members is to transform cardiovascular care and to improve heart health. The ACC bestows credentials upon cardiovascular professionals who meet stringent qualifications and leads in the formation of health policy, standards and guidelines. The College also provides professional medical education, disseminates cardiovascular research through its world-renowned JACC Journals, operates national registries to measure and improve care, and offers cardiovascular accreditation to hospitals and institutions. For more, visit ACC.org.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-05-06
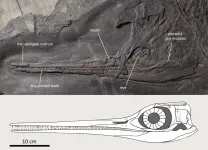
Middle Triassic ichthyosaurs are rare, and mostly small in size. The new Besanosaurus specimens described in the peer-reviewed journal PeerJ - the Journal of Life and Environmental Sciences - by Italian, Swiss, Dutch and Polish paleontologists provide new information on the anatomy of this fish-like ancient reptile, revealing its diet and exceptionally large adult size: up to 8 meters, a real record among all marine predators of this geological epoch. In fact, Besanosaurus is the earliest large-sized marine diapsid - the group to which lizards, snakes, crocodiles, and their extinct cousins belong to - with a long and narrow snout.
Besanosaurus leptorhynchus was originally discovered near Besano (Italy) three decades ago, during systematic excavations led by the Natural ...
2021-05-06
LUGANO, 6 May, 2021- Researchers have discovered a novel biomarker to identify male COVID-19 patients most at risk for ICU admission. The findings presented today at EADV's 2021 Spring Symposium, suggest that men with genetic characteristics (phenotypes) sensitive to the male sex hormone androgen, are more likely to experience severe COVID-19 disease.
Researchers were driven to study the association between the androgen receptor (AR) gene and COVID-19, after observing the disproportionate number of men hospitalised with COVID-19 presenting with androgenetic alopecia (a common form of hair-loss) compared to the expected number in a similar age-matched population (79% vs. 31-53%).
Androgenetic alopecia is known to be controlled by variations ...
2021-05-06
LUGANO, 6 May, 2021- New research investigating for the first time the effects of modified intermittent fasting (MIF) on the skin of people with psoriasis has yielded promising results. Preliminary study findings presented today at the EADV Spring Symposium, show a significant reduction in scaling and thickness in patients with mild psoriasis after following a MIF 5:2 diet (eating normally for 5 days and restricting calorie intake on 2 non-consecutive days).
Psoriasis is a chronic, systemic immune-mediated inflammatory disease that causes raised plaques and ...
2021-05-06
A premature start in life can cause problems even into teenage years. A study by the University of Basel and the University Children's Hospital Basel (UKBB) indicates that training motor skills in these children helps even when they are older.
Children that are born before the 37th week of pregnancy remain under close medical supervision while they are young. Any cognitive limitations often disappear after a few years. However, children who come into the world even before the 32nd week of gestation still exhibit differences even into their teenage years. In a new study, researchers led by Dr. Sebastian Ludyga ...
2021-05-06
(MAY 6, 2021) New York, NY - With around 30 percent of the U.S. population now fully vaccinated, the rate of daily vaccinations has started to slow, raising concerns that greater efforts and investments may be needed to reach higher coverage levels. A study published in the Journal of Infectious Diseases on May 6 shows the lives, hospitalizations, and costs that can be saved by even relatively small increases in vaccination coverage and reaching higher vaccination coverage levels sooner (e.g., by the end of the summer versus fall/winter).
The study was led by researchers from PHICOR (Public Health Informatics, Computational, and Operations Research) at CUNY Graduate School of Public ...
2021-05-06
Philadelphia, May 6, 2021 - Misunderstanding food date labeling is common and educational communications are needed to improve consumer understanding, according to a new study in the Journal of Nutrition Education and Behavior, published by Elsevier.
Does it mean "spoiled - throw it out," or "might not taste as good as it could anymore?" Food date labels (e.g., "USE By August 16") can play an important role in helping consumers make informed decisions about food, and ultimately prevent unsafe consumption and waste of food. Researchers surveyed 2,607 adults in the United States to assess consumer understanding of the streamlined 2-date ...
2021-05-06
PULLMAN, Wash. -- With state legislatures nationwide preparing for the once-a-decade redrawing of voting districts, a research team has developed a better computational method to help identify improper gerrymandering designed to favor specific candidates or political parties.
In an article in the Harvard Data Science Review, the researchers describe the improved mathematical methodology of an open source tool called GerryChain. The tool can help observers detect gerrymandering in a voting district plan by creating a pool, or ensemble, of alternate maps that also meet legal voting criteria. This map ensemble can show ...
2021-05-06
The identity of the skeletal remains of a member of the 1845 Franklin expedition has been confirmed using DNA and genealogical analyses by a team of researchers from the University of Waterloo, Lakehead University, and Trent University. This is the first member of the ill-fated expedition to be positively identified through DNA.
DNA extracted from tooth and bone samples recovered in 2013 were confirmed to be the remains of Warrant Officer John Gregory, engineer aboard HMS Erebus. The results matched a DNA sample obtained from a direct descendant of Gregory.
The remains of the officer were found on King William Island, Nunavut. "We now know that John Gregory was one of three expedition personnel who ...
2021-05-06
A team of engineers recommends expanding fast-charging stations for electric vehicles as campuses and businesses start planning for a post-pandemic world.
The recommendation is based on a study of charging patterns for electric vehicles on the University of California San Diego campus from early January to late May of 2020, after the university moved most of its operations online. Researchers say the findings can be applied to a broader range of settings.
"Workplace charging is a critical enabler of carbon-free transportation as the electrons consumed primarily come from solar power plants, as opposed to at-home charging, which occurs at night and relies more on fossil ...
2021-05-06
WASHINGTON, DC - MAY 6, 2021 - One out of every six adult workers (16%) in the United States are staying in jobs they might otherwise leave out of fear of losing their employer-sponsored health insurance, according to a new West Health-Gallup survey of more than 3,800 U.S. adults.
The survey finds the fear is even more pronounced among Black workers, who are 50% more likely to remain in an unwanted job than their White and Hispanic counterparts (21% to 14% and 16%, respectively).
But the most likely to stay in a job they would rather leave are those workers in households earning less than $48,000 a year -- roughly 3 in 10 (28%) say they will not leave and risk losing their health benefits. Workers in lower income households are nearly ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] High-risk, disadvantaged groups face barriers to preventing spread of COVID-19
Researchers urge greater focus on ensuring access to vaccines and precautionary measures