Health care use after COVID-19 diagnosis, home monitoring
2021-05-06
(Press-News.org) What The Study Did: Researchers compared health care use among patients with COVID-19 who were enrolled in a home monitoring program with similar patients who were not enrolled.
Authors: Anita D. Misra-Hebert, M.D., M.P.H., of the Cleveland Clinic, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamahealthforum.2021.0333)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest and funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
INFORMATION:
Media advisory: The full study and editor's note are linked to this news release.
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama-health-forum/fullarticle/ 10.1001/jamahealthforum.2021.0333?utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_term=050621
About JAMA Heath Forum: JAMA Health Forum has transitioned from an information channel to an international, peer-reviewed, online, open access journal that addresses health policy and strategies affecting medicine, health and health care. The journal publishes original research, evidence-based reports and opinion about national and global health policy; innovative approaches to health care delivery; and health care economics, access, quality, safety, equity and reform. Its distribution will be solely digital and all content will be freely available for anyone to read.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-05-06
New York, NY (May 6, 2021) -- Researchers have finally cracked the code of a bewildering pediatric disease that sets off a characteristic cytokine storm--a harmful immune system overaction resembling one that arises in COVID-19 cases--and can lead to catastrophic multisystem organ failure or neurodegeneration. Their study, which identifies the cause of the cytokine storm and possible treatments, was published in Nature Medicine in May.
The mystery of this disease, Langerhans-cell histiocytosis (LCH), runs deep. Its symptoms vary widely, and LCH has the ability to infiltrate almost any organ system, leaving most patients with long-term ...
2021-05-06
A team of researchers from UCLA, Cedars-Sinai and the Cystic Fibrosis Foundation has developed a first-of-its-kind molecular catalog of cells in healthy lungs and the lungs of people with cystic fibrosis.
The catalog, described today in the journal Nature Medicine, reveals new subtypes of cells and illustrates how the disease changes the cellular makeup of the airways. The findings could help scientists in their search for specific cell types that represent prime targets for genetic and cell therapies for cystic fibrosis.
"This new research has provided us with valuable insights into the cellular makeup of both healthy and diseased airways," said Dr. Brigitte Gomperts, a co-senior author of the study and a member of the Eli and Edythe Broad Center of Regenerative ...
2021-05-06
Obesity may be a stronger risk factor for death, severe pneumonia and the need for intubation in men than in women with COVID-19, according to a study published in the European Journal of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases.
An analysis of a cohort of 3530 COVID-19 patients showed that both moderate (BMI of 35/m2 or higher) and severe obesity (BMI of 40kg/m2 and higher) in men but only severe obesity in women (BMI of 40kg/m2 and higher) was associated greater risk of developing severe disease, needing intubation and dying from COVID-19 in hospital.
Previous research demonstrated that obesity is a risk factor for hospitalization, severe disease, and death in patients with COVID-19. ...
2021-05-06
Bacteria contain symmetry in their DNA signals that enable them to be read either forwards or backwards, according to new findings at the University of Birmingham which challenge existing knowledge about gene transcription.
In all living organisms, DNA code is divided into sections which provide information about a specific process. These must be read before the information can be used. Cells identify the start of each section using 'signposts', which scientists first identified in the 1960s.
It has always been assumed that these signposts enable genetic sequences ...
2021-05-06
The origins of a pretty smile have long been sought in the fearsome jaws of living sharks which have been considered living fossils reflecting the ancestral condition for vertebrate tooth development and inference of its evolution. However, this view ignores real fossils which more accurately reflect the nature of ancient ancestors.
New research led by the University of Bristol and the Naturalis Biodiversity Center published in Nature Ecology and Evolution reveals that the dentitions of living shark relatives are entirely unrepresentative of the last shared ancestor of jawed vertebrates.
The study reveals ...
2021-05-06
What The Study Did: This study estimates the association between Pfizer-BioNTech BNT162b2 vaccination and symptomatic and asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infections among health care workers more than seven days after getting a second vaccine dose.
Authors: Ronen Ben-Ami, M.D., of the Tel Aviv Sourasky Medical Center in Israel, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2021.7152)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
INFORMATION:
Media advisory: The full study ...
2021-05-06
What The Study Did: This study describes an association between the Pfizer-BioNTech BNT162b2 vaccine and decreased risk of symptomatic and asymptomatic infections with SARS-CoV-2 in hospital employees.
Authors: Li Tang, Ph.D., of the St. Jude Children's Research Hospital in Memphis, Tennessee, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2021.6564)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest and funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest ...
2021-05-06
The bulging, equator-belted midsection of Earth currently teems with a greater diversity of life than anywhere else -- a biodiversity that generally wanes when moving from the tropics to the mid-latitudes and the mid-latitudes to the poles.
As well-accepted as that gradient is, though, ecologists continue to grapple with the primary reasons for it. New research from the University of Nebraska-Lincoln, Yale University and Stanford University suggests that temperature can largely explain why the greatest variety of aquatic life resides in the tropics -- but also why it has not ...
2021-05-06
A key driver of patients' well-being and clinical trials for Parkinson's disease (PD) is the course the disease takes over time. However, nearly all that is known about the genetics of PD is related to susceptibility -- a person's risk for developing the disease in the future. A new study by investigators from Brigham and Women's Hospital published in Nature Genetics uncovers the genetic architecture of progression and prognosis, identifying five genetic locations (loci) associated with progression. The team also developed the first risk score for predicting ...
2021-05-06
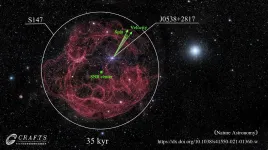
Pulsars - another name for fast-spinning neutron stars - originate from the imploded cores of massive dying stars through supernova explosion.
Now, more than 50 years after the discovery of pulsars and confirmation of their association with supernova explosions, the origin of the initial spin and velocity of pulsars is finally beginning to be understood.
Based on observations from the Five-hundred-meter Aperture Spherical radio Telescope (FAST), Dr. YAO Jumei, member of a team led by Dr. LI Di from National Astronomical Observatories of Chinese Academy of Sciences (NAOC), found the first evidence for three-dimensional (3D) spin-velocity alignment in pulsars.
The study was published in Nature Astronomy on May 6. It also marks the beginning of in-depth pulsar research with FAST.
For decades, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Health care use after COVID-19 diagnosis, home monitoring