Towards 2D memory technology by magnetic graphene
2021-05-06
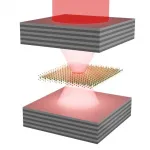
(Press-News.org) In spintronics, the magnetic moment of electrons (spin) is used to transfer and manipulate information. An ultra-compact 2D spin-logic circuitry could be built from 2D materials that can transport the spin information over long distances and also provide strong spin-polarization of charge current. Experiments by physicists at the University of Groningen (The Netherlands) and Colombia University (USA) suggest that magnetic graphene can be the ultimate choice for these 2D spin-logic devices as it efficiently converts charge to spin current and can transfer this strong spin-polarization over long distances. This discovery was published on 6 May in Nature Nanotechnology.
Spintronic devices are promising high-speed and energy-saving alternatives for the current electronics. These devices use the magnetic moment of electrons so-called spins ('up' or 'down') to transfer and store information. The ongoing scaling down of memory technology requires ever smaller spintronic devices and thus it seeks for atomically thin materials that can actively generate large spin signals and transfer the spin information over micrometre-long distances.
Graphene
For over a decade, graphene has been the most favourable 2D material for the transport of spin information. However, graphene cannot generate spin current by itself unless its properties are appropriately modified. One way to achieve this is to make it act as a magnetic material. The magnetism would favour the passage of one type of spin and thus create an imbalance in the number of electrons with spin-up versus spin-down. In magnetic graphene, this would result in a highly spin-polarized current.
This idea had now been experimentally confirmed by the scientists in the Physics of Nanodevices group led by prof. Bart van Wees at the University of Groningen, Zernike institute for advanced materials. When they brought graphene in close proximity to a 2D layered antiferromagnet, CrSBr, they could directly measure a large spin-polarization of current, generated by the magnetic graphene.
Spin-logic
In conventional graphene-based spintronic devices, ferromagnetic (cobalt) electrodes are used for injecting and detecting the spin signal into graphene. In contrast, in circuits built from magnetic graphene, the injection, transport and detection of the spins all can be done by the graphene itself, explains Talieh Ghiasi, first author of the paper. 'We detect an exceptionally large spin-polarization of conductivity of 14% in the magnetic graphene that is also expected to be efficiently tuneable by a transverse electric field.' This, together with the outstanding charge and spin transport properties of graphene allows for the realization of all-graphene 2D spin-logic circuitries where the magnetic graphene alone can inject, transport and detect the spin information.
Moreover, the unavoidable heat dissipation that happens in any electronic circuitry is turned to an advantage in these spintronic devices. 'We observe that the temperature gradient in the magnetic graphene due to the Joule heating is converted to spin current. This happens by the spin-dependent Seebeck effect that is also observed in graphene for the first time in our experiments,' says Ghiasi. The efficient electrical and thermal generation of spin currents by magnetic graphene promises substantial advances both for the 2D spintronic and spin-caloritronic technologies.
Graphene Flagship
The spin transport in graphene, furthermore, is highly sensitive to the magnetic behaviour of the outer-most layer of the neighbouring antiferromagnet. This implies that such spin transport measurements enable the read-out of the magnetisation of a single atomic layer. Thus, the magnetic graphene-based devices not only address the most technologically relevant aspects of magnetism in graphene for the 2D memory and sensory systems but also provide further insight into the physics of magnetism.
The future implications of these results will be investigated in the context of the EU Graphene Flagship, which works towards new applications of graphene and 2D materials.
INFORMATION:
Reference: T.S. Ghiasi, A.A. Kaverzin, A.H. Dismukes, D.K. de Wal, X. Roy and B. J. van Wees: Electrical and Thermal Generation of Spin Currents by Magnetic Bilayer Graphene. Nature Nanotechnology 6 May 2021
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-05-06
At extremely low temperatures, matter often behaves differently than in normal conditions. At temperatures only a few degrees above absolute zero (-273 degrees Celsius), physical particles may give up their independence and merge for a short time into a single object in which all the particles share the same properties. Such structures are known as Bose-Einstein Condensates, and they represent a special aggregate state of matter.
An international team of researchers led by physicists Dr Carlos Anton-Solanas and Professor Christian Schneider from the UNiversity of Oldenburg has now succeeded for the first time in generating this unusual quantum state in charge carrier complexes that are closely linked ...
2021-05-06
Hydrogen-based fuels should primarily be used in sectors such as aviation or industrial processes that cannot be electrified, finds a team of researchers. Producing these fuels is too inefficient, costly and their availability too uncertain, to broadly replace fossil fuels for instance in cars or heating houses. For most sectors, directly using electricity for instance in battery electric cars or heat pumps makes more economic sense. Universally relying on hydrogen-based fuels instead and keeping combustion technologies threatens to lock in a further fossil fuel dependency ...
2021-05-06
ROCHESTER, Minn. ? Heart disease can take a number of forms, but some types of heart disease, such as asymptomatic low ejection fraction, can be hard to recognize, especially in the early stages when treatment would be most effective. The ECG AI-Guided Screening for Low Ejection Fraction, or EAGLE, trial set out to determine whether an artificial intelligence (AI) screening tool developed to detect low ejection fraction using data from an EKG could improve the diagnosis of this condition in routine practice. Study findings are published in Nature Medicine.
Systolic low ejection fraction is defined as the heart's inability to contract strongly enough with each beat to pump at least 50% of the blood from ...
2021-05-06
What The Editorial Says: JAMA Health Forum debuts this week as a peer-reviewed, open-access, online journal focused on health policy, health care systems, and global and public health. The journal has transitioned from an online health policy channel and is the newest member of the family of JAMA Network specialty journals. The editor of JAMA Health Forum is John Z. Ayanian, M.D., M.P.P., of the University of Michigan in Ann Arbor, and the deputy editor is Melinda B. Buntin, Ph.D., of the Vanderbilt University School of Medicine in Nashville, Tennessee.
Authors: John Z. Ayanian, M.D., M.P.P., of the University of Michigan in Ann Arbor, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at ...
2021-05-06
What The Study Did: Researchers compared health care use among patients with COVID-19 who were enrolled in a home monitoring program with similar patients who were not enrolled.
Authors: Anita D. Misra-Hebert, M.D., M.P.H., of the Cleveland Clinic, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamahealthforum.2021.0333)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest and funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
INFORMATION:
Media advisory: The full study and editor's ...
2021-05-06
New York, NY (May 6, 2021) -- Researchers have finally cracked the code of a bewildering pediatric disease that sets off a characteristic cytokine storm--a harmful immune system overaction resembling one that arises in COVID-19 cases--and can lead to catastrophic multisystem organ failure or neurodegeneration. Their study, which identifies the cause of the cytokine storm and possible treatments, was published in Nature Medicine in May.
The mystery of this disease, Langerhans-cell histiocytosis (LCH), runs deep. Its symptoms vary widely, and LCH has the ability to infiltrate almost any organ system, leaving most patients with long-term ...
2021-05-06
A team of researchers from UCLA, Cedars-Sinai and the Cystic Fibrosis Foundation has developed a first-of-its-kind molecular catalog of cells in healthy lungs and the lungs of people with cystic fibrosis.
The catalog, described today in the journal Nature Medicine, reveals new subtypes of cells and illustrates how the disease changes the cellular makeup of the airways. The findings could help scientists in their search for specific cell types that represent prime targets for genetic and cell therapies for cystic fibrosis.
"This new research has provided us with valuable insights into the cellular makeup of both healthy and diseased airways," said Dr. Brigitte Gomperts, a co-senior author of the study and a member of the Eli and Edythe Broad Center of Regenerative ...
2021-05-06
Obesity may be a stronger risk factor for death, severe pneumonia and the need for intubation in men than in women with COVID-19, according to a study published in the European Journal of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases.
An analysis of a cohort of 3530 COVID-19 patients showed that both moderate (BMI of 35/m2 or higher) and severe obesity (BMI of 40kg/m2 and higher) in men but only severe obesity in women (BMI of 40kg/m2 and higher) was associated greater risk of developing severe disease, needing intubation and dying from COVID-19 in hospital.
Previous research demonstrated that obesity is a risk factor for hospitalization, severe disease, and death in patients with COVID-19. ...
2021-05-06
Bacteria contain symmetry in their DNA signals that enable them to be read either forwards or backwards, according to new findings at the University of Birmingham which challenge existing knowledge about gene transcription.
In all living organisms, DNA code is divided into sections which provide information about a specific process. These must be read before the information can be used. Cells identify the start of each section using 'signposts', which scientists first identified in the 1960s.
It has always been assumed that these signposts enable genetic sequences ...
2021-05-06
The origins of a pretty smile have long been sought in the fearsome jaws of living sharks which have been considered living fossils reflecting the ancestral condition for vertebrate tooth development and inference of its evolution. However, this view ignores real fossils which more accurately reflect the nature of ancient ancestors.
New research led by the University of Bristol and the Naturalis Biodiversity Center published in Nature Ecology and Evolution reveals that the dentitions of living shark relatives are entirely unrepresentative of the last shared ancestor of jawed vertebrates.
The study reveals ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Towards 2D memory technology by magnetic graphene