Diagramming the brain with colorful connections
2021-05-10
(Press-News.org) There are billions of neurons in the human brain, and scientists want to know how they are connected. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL) Alle Davis and Maxine Harrison Professor of Neurosciences Anthony Zador, and colleagues Xiaoyin Chen and Yu-Chi Sun, published a new technique in Nature Neuroscience for figuring out connections using genetic tags. Their technique, called BARseq2, labels brain cells with short RNA sequences called "barcodes," allowing the researchers to trace thousands of brain circuits simultaneously.
Many brain mapping tools allow neuroscientists to examine a handful of individual neurons at a time, for example by injecting them with dye. Chen, a postdoc in Zador's lab, explains how their tool, BARseq, is different:
"The idea here is that instead of labeling each neuron with a fluorescent dye, we fill it up with a unique RNA sequence, and we call this an RNA barcode. You can sequence the barcode to read out where that neuron sends its projection. You can label like tens of thousands of neurons, all at the same time, and you can still distinguish which axon comes from which neuron."
The latest generation of this tool, called BARseq2, adds a step to analyze a couple dozen natural neural genes through sequencing chemistry similar to what is used to light up artificial RNA barcodes. Chen says:
"These differences in gene expression usually reflect something that these neurons are doing. For example, if a neuron expresses certain receptors, you will be able to respond to whatever those receptors receive. So compared to anyone that doesn't have those receptors, they will respond differently to certain signals."
BARseq2 brings brain structure and function together. Sun, a former research technician in Zador's lab and now a New York University graduate student, compares the brain to a car. To truly understand how a car works, "you look at all aspects, from the physical and electrical properties to the way each piece links together. Similarly, to understand how the brain works, you have to look at all the different aspects of each neuron, including each neuron's location in the brain, gene expression, and connection to other neurons."
This project is part of a multi-institutional effort, the NIH-funded BRAIN Initiative Cell Census Network, to compile an atlas of every cell in human, mouse, and non-human primate brains. This work will allow scientists to tease apart how we produce complex behaviors and give researchers new tools to treat brain diseases.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-05-10
The COVID-19 pandemic has spurred genomic surveillance of viruses on an unprecedented scale, as scientists around the world use genome sequencing to track the spread of new variants of the SARS-CoV-2 virus. The rapid accumulation of viral genome sequences presents new opportunities for tracing global and local transmission dynamics, but analyzing so much genomic data is challenging.
"There are now more than a million genome sequences for SARS-CoV-2. No one had anticipated that number when we started sequencing this virus," said Russ Corbett-Detig, assistant professor of biomolecular engineering at UC Santa Cruz.
The sheer number of coronavirus genome sequences and their rapid accumulation makes it hard to place new sequences on a "family ...
2021-05-10
PHILADELPHIA-- New research performed in mice models at Penn Medicine shows, mechanistically, how the infant lung regenerates cells after injury differently than the adult lung, with alveolar type 1 (AT1) cells reprograming into alveolar type 2 (AT2) cells (two very different lung alveolar epithelial cells), promoting cell regeneration, rather than AT2 cells differentiating into AT1 cells, which is the most widely accepted mechanism in the adult lung. These study findings, published today in Cell Stem Cell, show that the long-held assumption that AT1 ...
2021-05-10
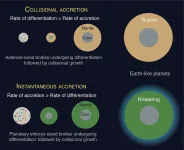
HOUSTON - (May 10, 2021) - The prospects for life on a given planet depend not only on where it forms but also how, according to Rice University scientists.
Planets like Earth that orbit within a solar system's Goldilocks zone, with conditions supporting liquid water and a rich atmosphere, are more likely to harbor life. As it turns out, how that planet came together also determines whether it captured and retained certain volatile elements and compounds, including nitrogen, carbon and water, that give rise to life.
In a study published in Nature Geoscience, Rice graduate student and lead author Damanveer Grewal and Professor Rajdeep Dasgupta show the competition between the time it takes for material to accrete into a protoplanet and the time the protoplanet ...
2021-05-10
ITHACA, N.Y. - Voyager 1 - one of two sibling NASA spacecraft launched 44 years ago and now the most distant human-made object in space - still works and zooms toward infinity.
The craft has long since zipped past the edge of the solar system through the heliopause - the solar system's border with interstellar space - into the interstellar medium. Now, its instruments have detected the constant drone of interstellar gas (plasma waves), according to Cornell University-led research published in Nature Astronomy.
Examining data slowly sent back from more than 14 billion miles away, Stella Koch Ocker, a Cornell doctoral student in astronomy, has uncovered the emission. "It's very faint and monotone, because ...
2021-05-10
Speech problems such as stammering or stuttering plague millions of people worldwide, including 3 million Americans. President Biden himself struggled with stuttering as a child and has largely overcome it with speech therapy. The cause of stuttering has long been a mystery, but researchers at Tufts University are beginning to unlock its causes and a strategy to develop potential treatments using a very curious model system - songbirds. In a study published today in Current Biology, the researchers were able to observe that a simple, reversible pharmacological treatment in zebra finches can stimulate rapid firing in a part of the brain that leads ...
2021-05-10
Numerous disease development processes are linked to epigenetic modulation. One protein involved in the process of modulation and identified as an important cancer marker is BRD4. A recent study by the research group of Giulio Superti-Furga, Principal Investigator and Scientific Director at the CeMM Research Center for Molecular Medicine of the Austrian Academy of Sciences, now shows that the supply of purines as well as the purine synthesis of a cell can influence BRD4 activity and thus play a role in the carcinogenesis process. The findings were published in Nature Metabolism.
Chromatin is a ...
2021-05-10
New Curtin University research has found a bias among scientists toward colourful and visually striking plants, means they are more likely to be chosen for scientific study and benefit from subsequent conservation efforts, regardless of their ecological importance.
Co-author John Curtin Distinguished Professor Kingsley Dixon from Curtin's School of Molecular and Life Sciences was part of an international team that looked for evidence of an aesthetic bias among scientists by analysing 113 plant species found in global biodiversity hotspot the Southwestern Alps and mentioned in 280 research papers published between 1975 and 2020.
Professor Dixon said the study tested whether there was a relationship between research focus on plant species and characteristics ...
2021-05-10
In cancer, a lot of biology goes awry: Genes mutate, molecular processes change dramatically, and cells proliferate uncontrollably to form entirely new tissues that we call tumors. Multiple things go wrong at different levels, and this complexity is partly what makes cancer so difficult to research and treat.
So it stands to reason that cancer researchers focus their attention where all cancers begin: the genome. If we can understand what happens at the level of DNA, then we can perhaps one day not just treat but even prevent cancers altogether.
This drive has led a ...
2021-05-10
In the last few years, several technology companies including Google, Microsoft, and IBM, have massively invested in quantum computing systems based on microwave superconducting circuit platforms in an effort to scale them up from small research-oriented systems to commercialized computing platforms. But fulfilling the potential of quantum computers requires a significant increase in the number of qubits, the building blocks of quantum computers, which can store and manipulate quantum information.
But quantum signals can be contaminated by thermal noise generated by the movement of electrons. To prevent this, superconducting quantum systems must operate at ultra-low temperatures - less ...
2021-05-10
NEW YORK, NY (May 10, 2021)--Scientists have discovered that many esophageal cancers turn on ancient viral DNA that was embedded in our genome hundreds of millions of years ago.
"It was surprising," says Adam Bass, MD, the Herbert and Florence Irving Professor of Medicine at Columbia University Vagelos College of Physicians and Surgeons and Herbert Irving Comprehensive Cancer Center, who led the study published May 10 in Nature Genetics.
"We weren't specifically searching for the viral elements, but the finding opens up a huge new array of potential cancer targets that I think will be extremely exciting as ways to enhance immunotherapy."
Fossil ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Diagramming the brain with colorful connections