(Press-News.org) A new study looking at the evolutionary history of the human oral microbiome shows that Neanderthals and ancient humans adapted to eating starch-rich foods as far back as 100,000 years ago, which is much earlier than previously thought.
The findings suggest such foods became important in the human diet well before the introduction of farming and even before the evolution of modern humans. And while these early humans probably didn't realize it, the benefits of bringing the foods into their diet likely helped pave the way for the expansion of the human brain because of the glucose in starch, which is the brain's main fuel source.
"We think we're seeing evidence of a really ancient behavior that might have been part encephalization -- or the growth of the human brain," said Harvard Professor Christina Warinner, Ph.D. '10. "It's evidence of a new food source that early humans were able to tap into in the form of roots, starchy vegetables, and seeds."
The findings come from a seven-year study published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences on Monday that involved the collaboration of more than 50 international scientists. Researchers reconstructed the oral microbiomes of Neanderthals, primates, and humans, including what's believed to be the oldest oral microbiome ever sequenced -- a 100,000-year-old Neanderthal.
The goal was to better understand how the oral microbiome -- a community of microorganisms in our mouths that help to protect against disease and promote health -- developed since little is known about its evolutionary history.
"For a long time, people have been trying to understand what a normal healthy microbiome is," said Warinner, assistant professor of anthropology in the Faculty of Arts and Sciences and the Sally Starling Seaver Assistant Professor at the Radcliffe Institute. "If we only have people today that we're analyzing from completely industrialized contexts and that already have high disease burdens, is that healthy and normal? We started to ask: What are the core members of the microbiome? Which species and groups of bacteria have actually co-evolved with us the longest?"
The scientists analyzed the fossilized dental plaque of both modern humans and Neanderthals and compared them to those of humanity's closest primate relatives, chimpanzees and gorillas, as well as howler monkeys, a more distant relative.
Using newly developed tools and methods, they genetically analyzed billions of DNA fragments preserved in the fossilized plaque to reconstruct their genomes. It's similar in theory to how archeologists painstakingly piece together ancient broken pots, but on a much larger scale.
The biggest surprise from the study was the presence of particular strains of oral bacteria that are specially adapted to break down starch. These strains, which are members of the genus Streptococcus, have a unique ability to capture starch-digesting enzymes from human saliva, which they then use to feed themselves. The genetic machinery the bacteria uses to do this is only active when starch is part of the regular diet.
Both the Neanderthals and the ancient humans scientists studied had these starch-adapted strains in their dental plaque while most of the primates had almost no streptococci that could break down starch.
"It seems to be a very human specific evolutionary trait that our Streptococcus acquired the ability to do this," Warinner said.
The findings also push back on the idea that Neanderthals were top carnivores, given that the "brain requires glucose as a nutrient source and meat alone is not a sufficient source," Warinner said.
Researchers said the finding makes sense because for hunter-gatherer societies around the world, starch-rich foods --underground roots, tubers (like potatoes), and forbs, as well as nuts and seeds, for example -- are important and reliable nutrition sources. In fact, starch currently makes up about 60 percent of calories for humans worldwide.
"Its availability is much more predictable across the annual season for tropical hunter-gatherers," said Richard W. Wrangham, Ruth B. Moore Professor of Biological Anthropology and one of the paper's co-authors. "These new data make every sense to me, reinforcing the newer view about Neanderthals that their diets were more sapien-like than once thought, [meaning] starch-rich and cooked."
The research also identified 10 groups of bacteria that have been part of the human and primate oral microbiome for more than 40 million years and are still shared today. While these bacteria may serve important and beneficial roles, relatively little is known about them. Some don't even have names.
Focusing on Neanderthals and today's humans, the analysis surprisingly showed the oral microbiome of both groups were almost indistinguishable. Only when looking at individual bacterial strains could they see some differences. For example, ancient humans living in Europe before 14,000 years ago during the Ice Age shared some bacterial strains with Neanderthals that are no longer found in humans today.
The differences and similarities from the study are all part of what makes us human, Warinner said. It also touches on the power of analyzing the tiny microbes that live in the human body, she said.
"It shows that our microbiome encodes valuable information about our own evolution that sometimes gives us hints at things that otherwise leave no traces at all," Warinner said.
INFORMATION:
ORLANDO, May 10, 2021 -University of Central Florida researchers are building on their technology that could pave the way for hypersonic flight, such as travel from New York to Los Angeles in under 30 minutes.
In their latest research published in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, the researchers discovered a way to stabilize the detonation needed for hypersonic propulsion by creating a special hypersonic reaction chamber for jet engines.
"There is an intensifying international effort to develop robust propulsion systems for hypersonic and supersonic flight that would allow flight through our atmosphere at very high speeds and also allow efficient entry and exit from planetary atmospheres," ...
In a newly published paper, Virginia Tech geoscientists have found that shallow wastewater injection -- not deep wastewater injections -- can drive widespread deep earthquake activity in unconventional oil and gas production fields.
Brine is a toxic wastewater byproduct of oil and gas production. Well drillers dispose of large quantities of brine by injecting it into subsurface formations, where its injection can cause earthquakes, according to Guang Zhai, a postdoctoral research scientist in the Department of Geosciences, part of the Virginia Tech College of Science, and a ...
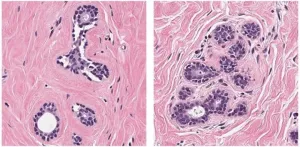
Breast cancer has recently overtaken lung cancer to become the most common cancer globally, END ...
Endometriosis, a disease found in up to 10 per cent of women, has been enigmatic since it was first described. A new theory developed by researchers at Simon Fraser University suggests a previously overlooked hormone -- testosterone -- has a critical role in its development. The research could have direct impacts on diagnosis and treatment of the disease, signaling hope for women with endometriosis worldwide.
The disease is caused by endometrial tissue growing outside of the uterus, usually in the pelvic area, where it contributes to pain, inflammation, and infertility. But why some women get it, and others do not, has remained unclear.
The new research is based on recent findings that women with endometriosis developed, as fetuses in their mother's womb, under conditions of relatively ...
Admit it: Daily commutes - those stops, the starts, all that stress - gets on your last nerve.
Or is that just me?
It might be, according to a new study from the University of Houston's Computational Physiology Lab. UH Professor Ioannis Pavlidis and his team of researchers took a look at why some drivers can stay cool behind the wheel while others keep getting more irked.
"We call the phenomenon 'accelerousal.' Arousal being a psychology term that describes stress. Accelarousal is what we identify as stress provoked by acceleration events, even small ones," said Pavlidis, ...
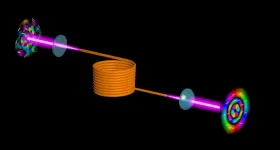
The use of multimode optical fibers to boost the information capacity of the Internet is severely hampered by distortions that occur during the transmission of images because of a phenomenon called modal crosstalk.
However, University of Rochester researchers at the Institute of Optics have devised a novel technique, described in a paper in Nature Communications, to "flip" the optical wavefront of an image for both polarizations simultaneously, so that it can be transmitted through a multimode fiber without distortion. Researchers at the University of South Florida and at the University of Southern California collaborated ...
Your local city park may be improving your health, according to a new paper led by Stanford University researchers. The research, published in END ...
After years of criticism for their lack of diversity, programs for high achievers may not be adequately serving their Black and low-income students, a new study shows.
"The potential benefits aren't equally distributed," said lead author and University of Florida College of Education professor Christopher Redding, Ph.D., who evaluated data from gifted programs in elementary schools nationwide. "The conversation up to this point has been about access, with less emphasis on how students perform once in gifted programs."
While academic achievement gains for students overall were modest -- going from ...
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. -- Log on to any app store, and parents will find hundreds of options for children that claim to be educational. But new research suggests these apps might not be as beneficial to children as they seem.
A new study analyzed some of the most downloaded educational apps for kids using a set of four criteria designed to evaluate whether an app provides a high-quality educational experience for children. The researchers found that most of the apps scored low, with free apps scoring even lower than their paid counterparts on some criteria.
Jennifer Zosh, associate professor of human development ...
Recurrent, metastatic breast cancer resists treatment and is usually fatal.
These tumors often have low numbers of immune cells in them, which renders immune therapies less effective for the disease.
This preclinical study suggests that drugs called CDK4 and CDK6 inhibitors may make immune-cell therapies an effective option for treating recurrent ER-positive metastatic breast cancer.
COLUMBUS, Ohio - A class of drugs that inhibits breast cancer progression when used with hormonal therapy might also boost the effectiveness of immune therapy in cases of recurrent, metastatic breast cancer, according to a new study led by researchers at The Ohio State University Comprehensive Cancer Center - Arthur G. James Cancer Hospital ...