HKU researchers identify promising new biologics for obesity-related diseases
2021-05-18
(Press-News.org) The research teams at the University of Hong Kong led by Professor Xuechen LI from the Research Division for Chemistry and Department of Chemistry, and Professor Yu WANG from the Department of Pharmacology and Pharmacy, reported a synthetic biotherapeutics with promising anti-tumour, insulin sensitising and hepatoprotective activities in the Journal of the American Chemical Society.
Obesity is a global pandemic associated with a significantly reduced life expectancy, it also increases the risk of type 2 diabetes, hypertension, coronary heart disease, stroke, chronic kidney disease and cancer. Adiponectin, as a protein hormone and adipokine, regulates glucose levels and improve lipid metabolism, and is a major player in the pathogenesis of obesity, insulin resistance and metabolic syndrome. Obese patients have low adiponectin levels, a condition known as hypoadiponectinemia, which contributes to increase risks of cardiovascular, metabolic diseases as well as aggressive development of malignancies with poor prognoses. Adiponectin supplementation is a long-sought-after strategy for the prevention and treatment of cancer and metabolic diseases, especially in obese patients. However, the adiponectin application in therapy has been hampered by the difficult production of human adiponectin.
The teams have been working on the development of synthetic compounds which can mimic the bioactivity of adiponectin over the past seven years. Finally, they developed an efficient synthetic approach to produce the adiponectin-derived glycopeptides that exhibit potent anti-tumour, insulin-sensitising and metabolic activities in various mouse models. The products hold greater potentials for clinical application in obesity and related medical complications, such as type 2 diabetes, hypertension, coronary heart disease, stroke, chronic kidney disease and cancer.
Professor Li and Professor Wang believe that this finding opens the door to explore the opportunity of using the synthetic glycopeptide as a potential adiponectin downsized mimic supplementary in clinical treatment. The apparent advantage of these synthetic glycopeptides is that they can be readily produced by chemical process. The two teams are continuing to apply for research grants which can support them to further evaluate the potential of these agents in preclinical studies for drug development.
INFORMATION:
The research paper: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/jacs.1c02382
Images download and captions: https://www.scifac.hku.hk/press
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-05-18
A team including Northwestern University astrophysicists has developed the most realistic, highest-resolution 3D simulation of star formation to date. The result is a visually stunning, mathematically-driven marvel that allows viewers to float around a colorful gas cloud in 3D space while watching twinkling stars emerge.
Called STARFORGE (Star Formation in Gaseous Environments), the computational framework is the first to simulate an entire gas cloud -- 100 times more massive than previously possible and full of vibrant colors -- where stars are born.
It also is the first simulation to simultaneously model star formation, evolution and dynamics while accounting for stellar feedback, including jets, radiation, wind and nearby supernovae activity. ...
2021-05-18
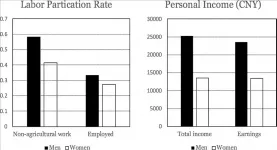
The challenges that many women face in today's labour market are well documented, from lower employment rates than men to lower rates of pay. Previous studies have considered how the burden of family care, which often falls largely on women's shoulders, has contributed to this imbalance. However, few of these studies have considered why women are the ones to bear that care burden.
A new study, published in the KeAi journal China Economic Quarterly International, has used data from China to investigate the impact of the concept of gender roles on women's employment and earnings.
Study author, Chuanchuan Zhang, of China's Zhejiang University, explains: "Traditionally, studies on women's labour supply ...
2021-05-18
Tsukuba, Japan - Aggression is common in many neuropsychiatric diseases, such as dementia, autism spectrum disorder, and schizophrenia. It causes many problems for patients and their families, but can be difficult to treat because little is known about what causes it. In a study published last month in Molecular Psychiatry, researchers from the University of Tsukuba revealed that variation in levels of interleukin 1β (IL-1β), a protein that mediates the inflammatory response, is associated with individual differences in aggressive behaviors in male mice.
In humans, levels ...
2021-05-18
[Outline]
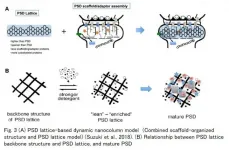
A research group led by Specially appointed professor, Dr. Tatsuo Suzuki of Shinshu University School of Medicine developed a new purification protocol for Postsynaptic density (PSD) lattice, a core structure of the PSD of excitatory synapses in the central nervous system. The components of the PSD lattice were identified by comprehensive shotgun mass spectrometry and categorized as either minimum essential component (MEC) or non-MEC proteins. Tubulin was found to be a major component of the MEC, with non-microtubule tubulin widely distributed on the purified PSD lattice. The presence of tubulin in and around PSDs was verified by post-embedding immuno-gold labeling ...
2021-05-18
Postpartum psychosis is a devastating, but rare, mental health problem that affects women in the first few weeks after giving birth. Symptoms vary widely, and can include high mood (mania), depression, confusion, hallucinations and delusions.
Although the disorder affects only one in every 1,000 women who have a baby, it is much more common in mothers with a history of bipolar disorder or schizoaffective disorder (a condition which has symptoms of schizophrenia and bipolar disorder), or women who have suffered a previous episode of postpartum psychosis.
There are currently no biological markers that help to identify women who ...
2021-05-18
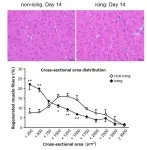
A study using a mouse model of eccentric contraction (*1) has revealed that icing injured muscles delays muscle regeneration. The discovery was made by a research group including Associate Professor ARAKAWA Takamitsu and then PhD. Student KAWASHIMA Masato from Kobe University's Graduate School of Health Sciences, and Chiba Institute of Technology's Associate Professor KAWANISHI Noriaki et al. In addition, the researchers illuminated that this phenomenon may be related to pro-inflammatory macrophages' (*2, 3, 4) ability to infiltrate damaged cells. This research raises questions as to whether or not severe muscle injuries (such as torn muscles) should be ...
2021-05-18
Robust data and genetic research are providing important evidence on a colony of wild African vervet monkeys that landed in Dania Beach more than 70 years ago and settled in a thick mangrove forest near the Fort Lauderdale-Hollywood International Airport in South Florida.
The non-native vervet monkey (Chlorocebus sabaeus) population living in this urban coastal region is well known and beloved among local residents and city officials; however, it is relatively unknown to primatologists. Despite wide public interest, there has been only one scientific study (early 1990s), suggesting that the monkeys escaped from a failed roadside zoo in the 1950s and 1970s. Until now, there was no confirmation about ...
2021-05-18
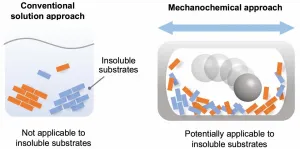
Scientists from Hokkaido University have developed a rapid, efficient protocol for cross-coupling reactions, vastly expanding the pool of chemicals that can be used for the synthesis of useful organic compounds.
Chemical reactions are a vital process in the synthesis of products for a diversity of purposes. For the most part, these reactions are carried out in the liquid phase, by dissolving the reactants in a solvent. However, there are a significant number of chemicals that are partially or completely insoluble, and thus have not been used for synthesis. The starting materials required for the synthesis of many cutting-edge organic materials--such as organic semiconductors and luminescent materials--are often poorly soluble, leading to problems in solution-based synthesis. Therefore, ...
2021-05-18
Vaccines are turning the tide of the pandemic, but the risk of infection is still present in some situations. If you want to visit a friend, get on a plane, or go see a movie, there is no highly accurate, instant test that can tell you right then and there whether or not you have a SARS-CoV-2 infection. But new research from Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) could help get reliable instant tests on the market.
A study led by Michal Hammel and Curtis D. Hodge suggests that a highly sensitive lateral flow assay - the same type of device used in home pregnancy tests - could be developed using pairs of rigid antibodies that bind to the SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein. Such a test would only require a small drop of mucus or saliva, could give results ...
2021-05-18
The first-ever discovery of an extraterrestrial radioactive isotope on Earth has scientists rethinking the origins of the elements on our planet.
The tiny traces of plutonium-244 were found in ocean crust alongside radioactive iron-60. The two isotopes are evidence of violent cosmic events in the vicinity of Earth millions of years ago.
Star explosions, or supernovae create many of the heavy elements in the periodic table, including those vital for human life, such as iron, potassium and iodine.
To form even heavier elements, such as gold, uranium and plutonium it was thought that a more violent event may be needed, such as two neutron stars merging.
However, a study led by Professor Anton Wallner from The Australian National University (ANU) suggests ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] HKU researchers identify promising new biologics for obesity-related diseases