Scientists discover five new species of listeria, improving food safety
2021-05-18
(Press-News.org) ITHACA, N.Y. - While examining the prevalence of listeria in agricultural soil throughout the U.S., Cornell University food scientists have stumbled upon five previously unknown and novel relatives of the bacteria.
The discovery, researchers said, will help food facilities identify potential growth niches that until now, may have been overlooked - thus improving food safety.
"This research increases the set of listeria species monitored in food production environments," said lead author Catharine R. Carlin, a doctoral student in food science. "Expanding the knowledge base to understand the diversity of listeria will save the commercial food world confusion and errors, as well as prevent contamination, explain false positives and thwart foodborne outbreaks."
One of the novel species, L. immobilis, lacked motility, or the ability to move. Listeria move a lot. Among scientists, motility was thought to be common among listeria closely related to L. monocytogenes, a well-known foodborne pathogen - and used as a key test in listeria detection methods. This discovery effectively calls for a rewrite of the standard identification protocols issued by food safety regulators, Carlin said.
As listeria species are often found co-existing in environments that support the growth of L. monocytogenes, food facilities will monitor for all listeria species to verify their sanitation practices.
Listeria monocytogenes can have profound pathogenic influence on food processing plants and those plants must be kept clean. Listeriosis has a mortality rate of 20% to 30% - even with a patient taking antibiotics, according to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention estimate that 1,600 people in the U.S. get listeriosis annually and nearly 260 die.
"This paper describes some unique characteristics of listeria species that are closely related to listeria monocytogenes, which will be important from an evolutionary perspective and from a practical standpoint for the food industry," said co-author Martin Wiedmann, the professor in food safety and food science. "Likely, some tests will need to be re-evaluated."
Understanding the different listeria species is key to comprehending their similarities. "This will help us to get better about identifying listeria monocytogenes," Wiedmann said, "and not misidentifying it as something else."
Since 2010, Wiedmann's research group has discovered 13 of the 26 species classified in the genus listeria.
"When you're inspecting the environments of food processing plants or restaurants, you need to know the pathogenic listeria from the non-pathogenic species," Wiedmann said. "You need to tell the good guys from the bad guys."
INFORMATION:
The research published May 17 in the International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-05-18
WASHINGTON, May 18, 2021 -- What are the most delicate and valuable things you have handled? How would you feel if your daily job involved handling human eggs and any mistakes would affect someone's life?
Typical egg collection requires a healthy woman to go through weeks of hormone therapy and then undergo an operation to retrieve eggs. These hard-earned and precious eggs are fertilized in vitro, and the best embryos are selected for future transfer.
But not all transfers succeed, which gives rise to the practice of freezing the extra embryos from an IVF cycle for future ...
2021-05-18
WASHINGTON, May 18, 2021 -- The COVID-19 pandemic made it clear technological innovations were urgently needed to detect, treat, and prevent the SARS-CoV-2 virus. A year and a half into this epidemic, waves of successive outbreaks and the dire need for new medical solutions -- especially testing -- continue to exist.
In the Journal of Vacuum Science & Technology B, researchers from the University of Florida and Taiwan's National Chiao Tung University report a rapid and sensitive testing method for COVID-19 biomarkers.
The researchers, who previously demonstrated ...
2021-05-18
WASHINGTON, May 18, 2021 -- The COVID-19 pandemic has reinforced the pressing need to mitigate a fast-developing virus as well as antibiotic-resistant bacteria that are growing at alarming rates worldwide.
Photodynamic therapy (PDT), or using light to inactivate viruses, bacteria, and other microbes, has garnered promising results in recent decades for treating respiratory tract infections, such as pneumonia, and some types of cancer.
In Applied Physics Reviews, by AIP Publishing, researchers at Texas A&M University and the University of São Paulo in Brazil ...
2021-05-18
Academic institutions need to do much more to support faculty members with disabilities and to create an environment in which they can thrive, argues a commentary published May 18 in the journal Trends in Neurosciences. The paper was written by Justin Yerbury, a cell and molecular neurobiologist who has amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), and his wife, Rachel Yerbury, a research psychologist.
"We want people to understand how tough life is for people with a disability," says Justin Yerbury (@jjyerbury), a professor at the University of Wollongong in Australia. "When you add academia on top of ...
2021-05-18
Twice as many eligible patients got screened for hepatitis C when it was already ordered for them compared to those who had to request it, according to a new study by researchers at the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania. Additionally, the patients in the study - whose average age was 63 - completed their screenings much more often when they were contacted via mail as opposed to electronic messaging. The study was published today in BMJ.
"We think that sending the lab order with outreach was so successful because it ...
2021-05-18
University of California scientists have discovered genetic data that will help food crops like tomatoes and rice survive longer, more intense periods of drought on our warming planet.
Over the course of the last decade, the research team sought to create a molecular atlas of crop roots, where plants first detect the effects of drought and other environmental threats. In so doing, they uncovered genes that scientists can use to protect the plants from these stresses.
Their work, published today in the journal Cell, achieved a high degree of understanding of the root functions because it combined genetic data from different cells of tomato roots grown both indoors and outside.
"Frequently, ...
2021-05-18
Bottom Line: The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) recommends that adults ages 45 to 75 be screened for colorectal cancer, lowering the age for screening that was previously 50 to 75. The USPSTF also recommends that clinicians selectively offer screening to adults 76 to 85 years of age. Colorectal cancer is the third leading cause of cancer death for both men and women in the United States. In 2016, 26% of eligible adults had never been screened and nearly one-third were not up to date with screening in 2018. The USPSTF routinely makes recommendations about the effectiveness of preventive care services and this statement replaces its 2016 recommendation.
To access the embargoed study: ...
2021-05-18
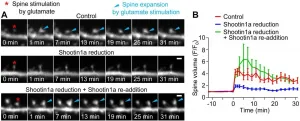
Ikoma, Japan - In neurons, changes in the size of dendritic spines - small cellular protrusions involved in synaptic transmission - are thought to be a key mechanism underlying learning and memory. However, the specific way in which these structural changes occur remains unknown. In a study published in Cell Reports, researchers from Nara Institute of Science and Technology (NAIST) have revealed that the binding of cell adhesion molecules with actin, via an important linker protein in the structural backbone of synapses, is vital for this process of structural plasticity.
Actin proteins make up an important part of a cell's structure, or cytoskeleton, and allow for dynamic changes in this structure by forming ...
2021-05-18
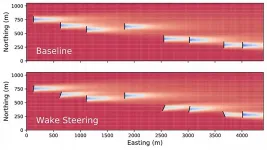
WASHINGTON, May 18, 2021 -- Wake steering is a strategy employed at wind power plants involving misaligning upstream turbines with the wind direction to deflect wakes away from downstream turbines, which consequently increases the net production of wind power at a plant.
In Journal of Renewable and Sustainable Energy, by AIP Publishing, researchers at the U.S. Department of Energy's National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) illustrate how wake steering can increase energy production for a large sampling of commercial land-based U.S. wind power plants.
While some plants showed less potential for wake steering due to unfavorable meteorological conditions or turbine layout, several wind power plants were ideal candidates ...
2021-05-18
What The Study Did: Telemedicine use grew rapidly during the COVID-19 pandemic but there was geographic variation in its use so researchers in this study examined the association of county-level telemedicine use with community factors among people with commercial or Medicare Advantage insurance.
Authors: Ateev Mehrotra, M.D., M.P.H., of Harvard Medical School in Boston, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.10330)
Editor's Note: The article includes funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Scientists discover five new species of listeria, improving food safety