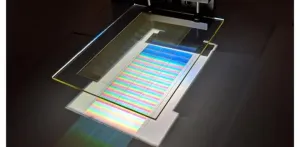
(Press-News.org) The energy available from sunlight is 10,000 times more than what is needed to supply the world's energy demands. Sunlight has two main properties that are useful in the design of renewable energy systems. The first is the amount power falling on a fixed area, like the ground or a person's roof. This quantity varies with the time of day and the season. The second property is the colors or spectrum of the sunlight.
One way to capture solar energy is to use solar cells that directly turn sunlight into electricity. In a solar module like those that people place on their roof, many cells are assembled on a rigid panel, connected to one another, sealed, and covered with protective glass. The solar cell works best when certain colors of sunlight fall on it, and when the whole area is covered by photocells. However, some panel area is needed to connect the cells, and the solar cell shape may not allow all of the remaining panel area to collect sunlight. These effects make the solar panel less efficient than it could be. Capturing as much of the sunlight on a solar panel as possible is critical to efficiently harnessing solar energy.
Researchers at the University of Arizona recently developed an innovative technique to capture the unused solar energy that illuminates a solar panel. END
Holograms increase solar energy yield
A newly developed holographic light collector boosts solar panel efficiency for an energy conversion increase of approximately five percent over the course of a year
2021-05-25
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Cocaine's effect on the brain: Fruit fly research shows impact at the cellular level
2021-05-25
New research from the Clemson University Center for Human Genetics has identified specific cell clusters in the brain of the common fruit fly affected by acute cocaine exposure, potentially laying the groundwork for the development of drugs to treat or prevent addiction in humans.
While cocaine's neurological effects are well known, the underlying genetic sensitivity to the drug's effects is not. In human populations, susceptibility to the effects of cocaine varies due to both environmental and genetic factors, making it challenging to study. Approximately 70 percent of genes in the fruit fly, Drosophila melanogaster, have human counterparts, providing researchers with a comparable model when studying ...
Researchers uncover mechanism related to severe post-COVID-19 disease in children
2021-05-25
BOSTON -- A multidisciplinary team from MassGeneral Hospital for Children (MGHfC), Brigham and Women's Hospital and other institutions have identified the mechanism of how an extremely rare but serious post-COVID-19 complication develops in children and adolescents. Led by MGHfC pediatric pulmonologist Lael Yonker, MD, researchers determined that viral particles remaining in the gut long after an initial COVID-19 infection can travel into the bloodstream, instigating the condition called Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children (MIS-C).
The syndrome can occur several weeks after an initial infection; symptoms include high fever, abdominal pain, vomiting, diarrhea, rash and extreme fatigue. The hyperinflammatory ...
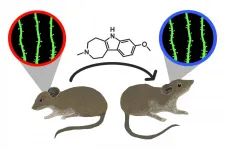
Non-hallucinogenic psychedelic analog reverses effects of stress in mouse study
2021-05-25
A novel compound similar in structure to the psychedelic drug ibogaine, but lacking its toxic and hallucinogenic effects, has been found to rapidly reverse the effects of stress in mice.
Researchers found that a single dose of tabernanthalog (TBG) can correct stress-induced behavioral deficits, including anxiety and cognitive inflexibility, and also promotes the regrowth of neuronal connections and restores neural circuits in the brain that are disrupted by stress. The study was published May 25 in Molecular Psychiatry.
"It was very surprising that a single treatment with a low dose had such dramatic effects within a day," said corresponding author ...
Dimensions of invasion success
2021-05-25
Invasive alien plants are plant species that grow in an environment outside their native habitat. If they successfully establish self-sustaining populations in these new environments - an event called "naturalization" - they can have considerable negative impacts on local ecosystems, economies, and societies. But not all alien plant species are equally effective in invading new habitats. Therefore, an international team of scientists, headed by Konstanz-based biologist Professor Mark van Kleunen, investigated different types of "invasiveness" and possible factors that determine invasion success of alien plants in Europe.
The new study, published in PNAS, describes ...
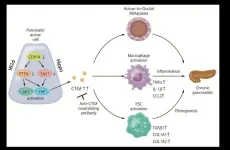
Unforeseen links to chronic pancreatitis found in cancer-related signals
2021-05-25
Osaka, Japan - Chronic inflammation of the pancreas is a debilitating disease with poorly understood causative factors. Now, researchers at Osaka University have identified the disturbed molecular pathways and revealed the underlying mechanisms that may inform an effective and much-needed therapeutic strategy.
The pancreas is an important organ with a dual role in digestion and the production of various hormones including insulin and glucagon that fine-tune blood sugar levels.
Chronic pancreatitis (CP) is characterized by inflammation of the gland ...
States' developmental disability services lacking for autistic adults and their families
2021-05-25
In the latest National Autism Indicators Report, researchers from Drexel University's A.J. Drexel Autism Institute examined surveys of family members of autistic adults who use Developmental Disability services, and found needs for additional supports like respite care and assistance to plan for crisis and emergencies, especially among families whose adult lived with them.
Data from the surveys showed over one quarter of families with autistic adults who use Developmental Disability services and live with family do not have enough services or supports for themselves, according to the report. And over half of these ...
A COVID-fighter's guide to T cells
2021-05-25
LA JOLLA--In a new paper, scientists from La Jolla Institute for Immunology (LJI) bring together research findings from COVID-19 researchers around the world. The results are striking: human T cells can target more than 1,400 sites on the SARS-CoV-2 virus.
"Our lab and many others have shown this very broad and diverse T cell response," says LJI Research Assistant Professor Daniela Weiskopf, Ph.D., co-author of the Cell Host & Microbe review.
This kind of research review, called a "meta-analysis," pools the results of multiple studies, and the researchers give close consideration to how the studies were conducted.
In the case of COVID-19, a global meta-analysis of T cell response studies is especially helpful because different patient populations ...
Study shows how fungi and bacteria can activate genes associated with head and neck cancer
2021-05-25
An in vitro study conducted by a group of researchers at São Paulo State University (UNESP) in Araraquara, Brazil, shows how fungi and bacteria can activate genes associated with head and neck tumors, as the metabolism of biofilms (communities in which these microorganisms self-organize in a structured and coordinated manner) stimulate tumor cells by favoring the cell signaling pathways required for tumor development and resistance to treatment. The findings include entirely novel information on the links between microbial biofilms and cell behavior in head and neck cancer.
The researchers discovered that metabolites secreted by biofilms, termed the secretome, can modulate the expression of proto-oncogenes and cell cycle genes associated with tumor cell growth and survival. Their analysis ...
Microbes metabolizing toxic substances were found in the burning coal seams of Kuzbass
2021-05-25
Geothermal ecosystems, such as volcanoes and hot terrestrial and deep-sea springs, are characterized by severe conditions. The temperatures are high and the environment could be extremely acidic or very alkaline. Moreover, there are chemically active compounds in them that can be fatal to living organisms, because they are capable of destroying the membrane of an ordinary cell.
"Exclusively very adapted microorganisms can exist here. They do not only have unique protective systems but are also able to get energy from chemical transformations of those substances that are available to them. Humans are actively using the ...
Serendipitous discovery could lead to treatment for strokes, cardiac arrest
2021-05-25
BOSTON - In a surprising discovery, researchers at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) identified a mechanism that protects the brain from the effects of hypoxia, a potentially lethal deprivation of oxygen. This serendipitous finding, which they report in Nature Communications, could aid in the development of therapies for strokes, as well as brain injury that can result from cardiac arrest, among other conditions.
However, this study began with a very different objective, explains senior author Fumito Ichinose, MD, PhD, an attending physician in the Department of Anesthesia, Critical Care and Pain Medicine at MGH, and principal investigator in ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
[Press-News.org] Holograms increase solar energy yieldA newly developed holographic light collector boosts solar panel efficiency for an energy conversion increase of approximately five percent over the course of a year