(Press-News.org) CHAMPAIGN, Ill. -- Advanced microscope technology and cutting-edge geological science are giving new perspectives to an old medical mystery: How do kidney stones form, why are some people more susceptible to them and can they be prevented?
In a new paper published in the journal Nature Reviews Urology, researchers from the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign, Mayo Clinic and other collaborators described the geological nature of kidney stones, outlined the arc of their formation, established a new classification scheme and suggested possible clinical interventions.
"The process of kidney stone formation is part of the natural process of the stone formation seen throughout nature," Illinois geology professor Bruce Fouke said. "We are bringing together geology, biology and medicine to map the entire process of kidney stone formation, step by step. With this road map in hand, more effective and targeted clinical interventions and therapies can now be developed."
Kidney stones are a painful problem that will strike one in 10 adults in their lifetime and send half a million people in the United States to emergency rooms each year, according to the National Kidney Foundation. Yet little is understood about the geology behind how kidney stones form, Fouke said.
Previous work from Fouke's group found that kidney stones form in the same way as geological stones in nature: Rather than crystalizing all at once, they partially dissolve and re-form multiple times, contrary to doctors' belief that they form suddenly and intact.
In the new work, the research team - brought together by the Mayo Clinic and Illinois Alliance for Technology-Based Healthcare - describes in detail the multiple phases kidney stones go through in forming, dissolving and re-forming, documented through high-resolution imaging technologies. The findings defy the typical classification schemes doctors use, which are based on bulk analyses of the type of mineral and the presumed location of formation in the kidney. Instead, the researchers developed a new classification scheme based on which phase of formation the stone is in and which chemical processes it is undergoing.
"If we can identify these phase transformations, what makes one step to go to another and how it progresses, then perhaps we can intervene in that progression and break the chain of chemical reactions happening inside the kidney tissues before a stone becomes problematic," said Mayandi Sivaguru, the lead author of the study and assistant director of core facilities at the Carl R. Woese Institute for Genomic Biology at Illinois.
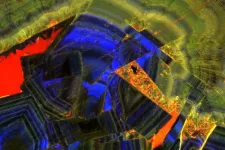
One particularly revelatory finding was in the very beginnings of kidney stone formation: Stones start as microspherules, or tiny droplets of mineral, which merge to form larger crystals throughout kidney tissues. Normally they are flushed out, but when they coalesce together to form larger stones that continue to grow, they can become excruciatingly painful and even deadly in some cases, Fouke said.
"Stone formation is part of a natural, healthy process within kidneys where these tiny mineral deposits are shuttled away and excreted from the body," Fouke said. "But then there is a tipping point when those same mineral deposits start to grow together too rapidly and are physically unable to leave the kidney."
As the stone goes through the formation process, more microspherules merge, lose their rounded shape and transform into much larger, perfectly geometric crystals. Stones go through multiple cycles of partially dissolving - shedding up to 50% of their volume, the researchers found - and then growing again, creating a signature pattern of layered crystals much like those of agates, coral skeletons and hot-spring deposits seen around the world.
"Looking at a cross-section of a kidney stone, you would never guess that each of the layers was originally a bunch of little balls that lined up and coalesced. These are revolutionary new ways for us to understand how these minerals grow within the kidney and provide specific targets for stone growth prevention," Fouke said.
The study authors outlined several possible clinical interventions and treatment targets based on this expanded knowledge of kidney stone formation. They hope that researchers and clinicians can explore and test these options, from drug targets to changes in diet or supplements that could disrupt the chemical and biological cascade driving kidney stone formation, Sivaguru said.
To aid in this testing, Fouke's group developed the GeoBioCell, a microfluidic cartridge designed to mimic the intricate internal structures of the kidney. The group hopes the device can accelerate not only research, but also clinical diagnostic testing and the evaluation of potential therapies, especially for the more than 70% of kidney stone patients with recurring stones.
"Ultimately, our vision is that every operating room would have a small geology lab attached. In that lab, you could do a very rapid diagnostic on a stone or stone fragment in a matter of minutes, and have informed and individualized treatment targets," Fouke said.
INFORMATION:
The Mayo-Illinois Alliance, the Mayo Clinic Center for Individualized Medicine, the Mayo Clinic O'Brien Urology Research Center and the Astrobiology Institute of the National Aeronautics and Space Administration supported this work.
Editor's note: To reach Bruce Fouke, call 217-244-5431; email fouke@illinois.edu. To reach Mayandi Sivaguru, email sivaguru@illinois.edu.
The paper "Human kidney stones: A natural record of universal biomineralization" is available online and from the U. of I. News Bureau.Editor's note: To reach Bruce Fouke, call 217-244-5431; email fouke@illinois.edu. To reach Mayandi Sivaguru, email sivaguru@illinois.edu.
The paper "Human kidney stones: A natural record of universal biomineralization" is available online and from the U. of I. News Bureau.
Reno, Nev. (May 25, 2021) - After a wildfire, soils in burned areas often become water repellent, leading to increased erosion and flooding after rainfall events - a phenomenon that many scientists have attributed to smoke and heat-induced changes in soil chemistry. But this post-fire water repellency may also be caused by wildfire smoke in the absence of heat, according to a new paper from the Desert Research Institute (DRI) in Nevada.
In this pilot study (exploratory research that takes place before a larger-scale study), an interdisciplinary team of scientists led by DRI Associate Research Professor of Atmospheric Science Vera Samburova, Ph.D., exposed samples of clean sand to smoke from burning Jeffrey pine needles and branches ...
Cells are the building blocks of life, present in every living organism. But how similar do you think your cells are to a mouse? A fish? A worm?
Comparing cell types in different species across the tree of life can help biologists understand how cell types arose and how they have adapted to the functional needs of different life forms. This has been of increasing interest to evolutionary biologists in recent years because new technology now allows sequencing and identifying all cells throughout whole organisms. "There's essentially a wave in the scientific community to classify all types of cells in a wide variety of different organisms," explained Bo Wang, an assistant professor of bioengineering at Stanford University.
In response to this opportunity, ...
A new study finds that fly ash--particles left over from burning coal--make up between 37 and 72 percent of all particulate organic carbon carried by the Yangtze River in China, or around 200,000 to 400,000 tons of carbon per year.
The study, which is the first of its kind, shows just how big an impact fossil fuel consumption has on Earth. Beyond pumping carbon dioxide into the atmosphere, coal burning dumps about as much particulate carbon into the Yangtze River as natural processes do.
The findings were published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS) on May 17.
"About one-fifth of the world's coal consumption occurs along this river," says Gen Li, postdoctoral ...
A new report by Skoltech scientists and their colleagues describes an organic material for the new generation of energy storage devices, which structure follows an elegant molecular design principle. It has recently been published in ACS Applied Energy Materials and made the cover of the journal.
While the modern world relies on energy storage devices more and more heavily, it is becoming increasingly important to implement sustainable battery technologies that are friendlier to the environment, are easy to dispose, rely on abundant elements only, and are cheap. Organic batteries are desirable ...
East Hanover, NJ. May 25, 2021. A team of experts in post-stroke neurorehabilitation confirmed that including prism adaptation treatment in standard of care for patients with post-stroke spatial neglect improved functional and cognitive outcomes according to the Functional Independence Measure®. The article, "Prism Adaptation Treatment Improves Inpatient Rehabilitation Outcome in Individuals with Spatial Neglect: A Retrospective Matched Control Study" (doi: 10.1016/j.arrct.2021.100130.
was published in Archives of Rehabilitation Research and Clinical Translation on May XX, 2021. It is available open access at https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2590109521000343
The ...
LED lightbulbs offer considerable advantages over other types of lighting. Being more efficient, they require much less electricity to operate. They do not give off unwanted heat the way old-school incandescent bulbs do, and the best of them long outlast even fluorescent lightbulbs.
But LEDs are not problem-free. Questions linger over suspected links between health concerns such as fatigue, mood disorders, and insomnia from overexposure to the blue-tinted light produced by today's standard LED bulbs. Plus, higher prices can prompt lightbulb shoppers to weigh other options.
A University of Houston research team led by Jakoah Brgoch, associate professor of chemistry in the College of Natural Sciences and Mathematics and principal investigator in the Texas Center for ...
ITHACA, N.Y. - It stands to reason that the more one is compensated for performing a task, the greater the incentive to do a good job and the better one feels about doing it.
But what if the task is writing an objective review of a company or service? Does the compensation blur the lines of objectivity?
Kaitlin Woolley, assistant professor of marketing in the Samuel Curtis Johnson Graduate School of Management, Cornell SC Johnson College of Business, wondered the same thing.
"You often receive emails after a purchase, offering you a chance to win a gift card to the company in ...
One in five women experience pain during intercourse. The latest edition of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, the bible of American psychiatrists, lists it under "genito-pelvic pain or penetration disorder." However, this type of pain is not purely psychological.
Provoked vestibulodynia is a condition experienced by approximately 8% of women in North America. It is characterized by severe pain at the vaginal opening during sexual intercourse or when inserting tampons. To reduce the burning sensation, many women apply lidocaine, an anesthetic ...
Boston, MA-- How does the switch to a high-deductible health plan affect children with asthma? A new study led by researchers at the Harvard Pilgrim Health Care Institute suggests that enrollment in a high-deductible health plan (HDHP) may not be associated with changes in asthma medication use or asthma exacerbations when medications are exempt from the deductible. The findings were published in JAMA Pediatrics on May 10.
To treat asthma, clinical guidelines recommend the use of controller medications, but adherence to these medications is generally suboptimal, putting those affected at risk for asthma exacerbations. High out-of-pocket costs have been associated with decreased controller medication use and adverse asthma outcomes for children and adults. ...
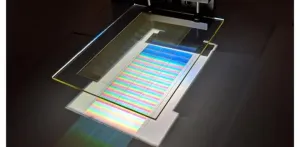
The energy available from sunlight is 10,000 times more than what is needed to supply the world's energy demands. Sunlight has two main properties that are useful in the design of renewable energy systems. The first is the amount power falling on a fixed area, like the ground or a person's roof. This quantity varies with the time of day and the season. The second property is the colors or spectrum of the sunlight.
One way to capture solar energy is to use solar cells that directly turn sunlight into electricity. In a solar module like those that people place on their roof, many cells are assembled on a rigid panel, connected to one another, sealed, and covered ...