(Press-News.org) The researchers Juan A. Fernández-Ontiveros, of the Istituto Nazionale di Astrofisica (INAF) in Rome and Teo Muñoz-Darias, of the Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias (IAC), have written an article in which they describe the different states of activity of a large sample of supermassive black holes in the centres of galaxies. They have classified them using the behaviour of their closest "relations", the stellar mass black holes in X-ray binaries. The article has just been published in the journal Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society (MNRAS).
Black holes range in mass from objects which have only a few times the mass of the sun up to those with thousands of millions of solar masses. To understand their activity cycles from a global perspective has been the object of research for decades. Those of stellar mass are found in binary systems together with a companion star from which they suck out the gas which they need to sustain their activity, while the supermassive variety are found in the centres of the majority of galaxies and they feed on the gas, dust, and stars which are fall into the gravitational well of the galactic nucleus.
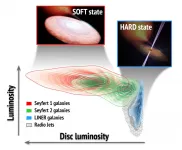
Stellar mass black holes evolve rapidly. Their activity cycles usually last a few months or years, during which they pass through different states, or phases. These are characterized by changes in the properties of their accretion discs (where the hot gas accumulates before falling into the black hole), their winds, and the jets of material which they produce. There are two principal states, the first dominated by the accretion disc, and the second by the jet. The 'soft' state is noted by the thermal emission by the plasma of the disc, while the jet is observed in the 'hard' state, when the disc cools down, and the emission at radio wavelengths becomes very intense.
Because they are much more massive, the supermassive black holes evolve much more slowly than their stellar mass equivalents. So, to show the presence of states and transitory phenomena in these would imply observing them for millions of years, because the changes during a human lifetime would be too small to measure. In addition, the nuclei of galaxies are regions with dense populations of stars, and the absorption of light by hydrogen and dust masks and hides the radiation from the accretion disc around the central black hole.
In this study Fernández-Ontiveros and Muñoz-Darias have used a sample of 167 active galaxies to be able to identify the possible accretions states of supermassive black holes with good statistics. The emission from the accretion disc cannot be detected directly, but the gas in the central region absorbs and processes the radiation in the form of spectral lines. Using the lines of oxygen and neon, which are observed in the mid-infrared, it is possible to test the presence of the disc in these object. "The study demonstrates the presence of accretion states in supermassive black holes, with properties very similar to those we know from stellar mass black holes, where the systems in the 'soft' state harbour a bright disc, and those in the 'hard' state show intense radio emission while the disc is very weak", explains Juan A. Fernández-Ontiveros, an INAF researcher who was trained at the IAC.
"This work opens a new window to understand the behaviour of material (gas) when it falls into black holes with a wide range of masses, and helps a more precise understanding of the activity cycles of the supermassive black holes which are in the centres of most galaxies", adds Teo Muñoz-Darias, a researcher at the IAC.
The figure illustrates how the population of active Seyfert-1 galaxies is typically dominated by the emission of the accretion disk ('soft' state), while the population of LINERs is much less luminous and is dominated by jets ('hard' state), which emit intensely in radio waves. The Seyfert-2 galaxies, on the other hand, do not show a homogeneous behaviour and while a good part behave in a similar way to the Seyfert-1, a large group of them are located in intermediate states. The latter are also observed in stellar black holes for short periods of time.
INFORMATION:
Article: Juan A. Fernández-Ontiveros & Teo Muñoz-Darias, "X-ray binary accretion states in Active Galactic Nuclei? Sensing the accretion disc of supermassive black holes with mid-infrared nebular lines". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, april 2021. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/mnras/stab1108
- Prepress: https://arxiv.org/abs/2104.09538
Mercury pollution is an issue of global concern due to its toxic effects. High levels have already been measured in Arctic organisms - with worrying effects on ecosystems and the food chain. So far, the Greenland Ice Sheet has not been taken into account as a part of the Arctic mercury cycle. Now, researchers led by Jon Hawkings of the German Research Centre for Geosciences in Potsdam and Florida State University show that meltwaters in the southwest of Greenland transport considerable amounts of mercury into the Arctic Ocean. Due to the large quantities detected, the researchers assume that they are of geological origin. They present their measurements in the current issue of Nature Geoscience.
Mercury: poison for humans and the environment - ...
LAWRENCE -- For two weeks in June 2020, a massive dust plume from Saharan Africa crept westward across the Atlantic, blanketing the Caribbean and Gulf Coast states in the U.S. The dust storm was so strong, it earned the nickname "Godzilla."
Now, researchers from the University of Kansas have published a new study in the Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society parsing the mechanism that transported the dust. Their results explain a phenomenon that could occur more frequently in the years ahead due to climate change, affecting human health and transportation systems.
African dust darkened the skies of the Caribbean and American Gulf States thanks to a trio of atmospheric patterns, ...
Mitochondria are the cell's power plants and produce the majority of a cell's energy needs through an electrochemical process called electron transport chain coupled to another process known as oxidative phosphorylation. A number of different proteins in mitochondria facilitate these processes, but it's not fully understood how these proteins are arranged inside mitochondria and the factors that can influence their arrangement.
Now, scientists at the University of Copenhagen have used state-of-the-art proteomics technology to shine new light on how mitochondrial proteins gather into electron transport chain complexes, and further into so-called supercomplexes. The research, which is published in Cell Reports, also examined ...
Over the years, robots have gotten quite good at identifying objects -- as long as they're out in the open.
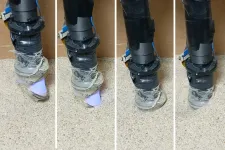
Discerning buried items in granular material like sand is a taller order. To do that, a robot would need fingers that were slender enough to penetrate the sand, mobile enough to wriggle free when sand grains jam, and sensitive enough to feel the detailed shape of the buried object.
MIT researchers have now designed a sharp-tipped robot finger equipped with tactile sensing to meet the challenge of identifying buried objects. In experiments, the aptly named ...
A mathematical model which can predict landslides that occur unexpectantly has been developed by two University of Melbourne scientists, with colleagues from GroundProbe-Orica and the University of Florence.
Professors Antoinette Tordesillas and Robin Batterham led the work over five years to develop and test the model SSSAFE (Spatiotemporal Slope Stability Analytics for Failure Estimation), which analyses slope stability over time to predict where and when a landslide or avalanche is likely to occur.
In a study published in Scientific Reports, the research team was ...
Discovered by Victor Hess in 1912, cosmic rays, relativisitic particles that shower Earth, contribute a signicant part of the energy density in the universe and carries unambiguous informations on various astrophysical processes . Yet until now, origin of cosmic rays is still a mystery.
A key problem in understanding the origin of cosmic rays is the searching for the acceleration site up to or even beyond Ultra-high energy (UHE). Such extreme accelerators are dubbed as PeVatrons. However, composed of subatomic particles, such as protons or atomic nuclei, cosmic rays are charged and lose ...
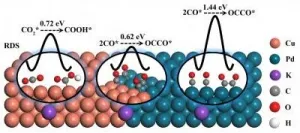
Using intermittent electric energy to convert excessive CO2 into C2 products, such as ethylene and ethanol, is an effective strategy to mitigate the greenhouse effect. Copper (Cu) is the only single metal catalyst which can converts CO2 into C2 products by electrochemical method, but with undesirable selectivity of C2 product. Therefore, how to improve the conversion efficiency of Cu-based catalysts for reducing CO2 to C2 product has attracted great attention.
Recently, a research team led by Prof. Min Liu from Central South University, China designed a Cu-Pd bimetallic electrocatalyst possessing CuPd(100) interface which can lower the energy barrier of C2 product generation. The electrocatalyst was obtained through using ...
WASHINGTON--People who eat too many refined carbs and fatty meats for dinner have a higher risk of heart disease than those who eat a similar diet for breakfast, according to a nationwide study published in the Endocrine Society's Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.
Cardiovascular diseases like congestive heart failure, heart attack and stroke are the number one cause of death globally, taking an estimated 17.9 million lives each year. Eating lots of saturated fat, processed meats and added sugars can raise your cholesterol and increase your risk of heart disease. Eating a heart-healthy diet with more whole carbohydrates like vegetables and grains and less meat can significantly offset the risk of cardiovascular disease.
"Meal timing along with food quality are important factors ...
The farming of livestock to feed the global appetite for animal products greatly contributes to global warming. A new study however shows that emission intensity per unit of animal protein produced from the sector has decreased globally over the past two decades due to greater production efficiency, raising questions around the extent to which methane emissions will change in the future and how we can better manage their negative impacts.
Despite what we know about the environmental cost of livestock production, the global appetite for animal products such as meat, eggs, and dairy continues to grow. The livestock sector is in fact the largest source of manmade methane emissions globally, and these emissions are projected ...
A team of international researchers has found that the Tsimane indigenous people of the Bolivian Amazon experience less brain atrophy than their American and European peers. The decrease in their brain volumes with age is 70% slower than in Western populations. Accelerated brain volume loss can be a sign of dementia.
The study was published May 26, 2021 in the Journal of Gerontology, Series A: Biological Sciences and Medical Sciences.
Although people in industrialized nations have access to modern medical care, they are more sedentary and eat a diet high in saturated fats. In contrast, the Tsimane ...