(Press-News.org) Annapolis, MD; May 26, 2021--A new study has mounted perhaps the most intricate, detailed look ever at the diversity in structure and form of bees, offering new insights in a long-standing debate over how complex social behaviors arose in certain branches of bees' evolutionary tree.
Published today in Insect Systematics and Diversity, the report is built on an analysis of nearly 300 morphological traits in bees, how those traits vary across numerous species, and what the variations suggest about the evolutionary relations between bee species. The result offers strong evidence that complex social behavior developed just once in pollen-carrying bees, rather than twice or more, separately, in different evolutionary branches--but researchers say the case is far from closed.
Diego Sasso Porto, Ph.D., has been studying the structure and form, or morphology, of bees for more than a decade, and his latest effort ventures into a longstanding conundrum about bee evolution. Corbiculate bees--those that possess corbicula, or pollen baskets, on their hind legs--encompass honey bees, stingless bees, bumble bees, and orchid bees. Among them, honey bees and stingless bees are the only groups with highly complex social behaviors, such as forming large colonies with queens, workers, and drones. Bumble bees display less complex sociality, and orchid bees are mostly solitary. Traditional morphological analyses have long indicated that honey bees and stingless bees are most closely related and that complex social behavior developed in their common ancestor before the groups diverged. However, in the 1990s, emergent techniques in molecular genetic analysis began to show that stingless bees and bumble bees were the more closely related "sister" groups, which would mean that honey bees and stingless bees each developed their complex social behavior independently, after their ancestral paths diverged.
Ever since, these different lines of evidence have persisted as a notorious case of incongruence between molecular and morphological data sets in animals. Porto, now a postdoctoral researcher in the Department of Biological Sciences at Virginia Tech, made his foray into the debate amid his doctoral work at the University of São Paulo in Brazil, under the guidance of Eduardo Almeida, Ph.D., co-author on the new study.
"The main criticism from some molecular researchers against morphology, and even from morphologists themselves, was we don't have enough data," Porto says. "This work was a big effort to try to get the best morphological data set we could ever get for this group of bees, and we tried several analyses to see if the problem is with morphological data itself or the way we interpret morphological data."
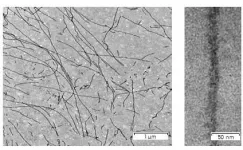
Porto evaluated past morphological studies of bees and then conducted new analysis of specimens from 53 species, dissecting each, imaging anatomical structures under optical and scanning electron microscopes, and ultimately scoring all of the specimens across 289 different traits. Often minute or even microscopic in detail, these traits ranged from the number of teeth on a bee's mandibles to the arrangement of barbs on its stinger.
With this massive trove of morphological data in hand, Porto applied multiple types of computerized statistical analyses to evaluate the possible phylogenies, or "family trees," that delineate the relationships among bee species. The results strongly support previous morphological findings, that honey bees (tribe Apini) and stingless bees (Meliponini) are most closely related. "The evidence from our dataset, if we just take it at plain sight, is really strong. We have a lot of traits supporting this," says Porto.
But, he sought to further explore the discrepancy between what molecular genetic analysis shows and what his own morphological data supports. To do so, Porto ran his data through a separate analysis that evaluated how well the morphological data could fit with the evolutionary tree supported by molecular analysis--that Meliponini and Bombini (bumble bees) are most closely related. As expected, it was not a great fit--a bit like putting a square peg in a round hole--but they were not completely incompatible, he says.
In their report in Insect Systematics and Diversity, Porto and Almeida offer a few hypotheses for evolutionary processes that could explain the continuing discrepancy in lines of evidence about corbiculate bee evolution.
"Morphological data is telling us one story, and molecular data is telling us another story. We are not going anywhere if we just keep these conflicting discussions," says Porto. "So, our decision was ... let's try to interpret the alternative scenario with our data. If the hypothesis given by molecular data is true, how can we interpret our strong morphological evidence for the other hypothesis?"
One possible explanation, they say, is that, if bumble bees and stingless bees share a common ancestor that first branched away from honey bees, they then rapidly diverged in a short time frame and evolved separately for much longer, gradually obscuring the shared traits bumble bees and stingless bees once had. Moreover, the earliest ancestor of stingless bees is believed to have been relatively small, and "miniaturization" is known to drive structural simplifications in anatomical traits, which would have further contributed to erasing similarities between bumble bees and stingless bees.
However, these possibilities don't explain why stingless bees then evolved to become more morphologically similar to honey bees, but Porto and Almeida posit that similar functional roles or similar social behaviors among stingless bees and honey bees could have driven them to evolve in similar ways.
Testing these hypotheses is what Porto says he would like to explore next--and encourages other researchers to do, as well. "It would be really good to have maybe the same data set, but including more specimens from fossils, and run the analysis again," he says.
INFORMATION:
"Corbiculate bees (Hymenoptera: Apidae): Exploring the limits of morphological data to solve a hard phylogenetic problem" will be published online on May 26, 2021, in Insect Systematics and Diversity. Journalists may request advance copies of the article via the contact below or download the published paper after 10 a.m. on May 26 at https://doi.org/10.1093/isd/ixab008.
CONTACT: Joe Rominiecki, jrominiecki@entsoc.org, 301-731-4535 x3009
ABOUT: ESA is the largest organization in the world serving the professional and scientific needs of entomologists and people in related disciplines. Founded in 1889, ESA today has more than 7,000 members affiliated with educational institutions, health agencies, private industry, and government. Headquartered in Annapolis, Maryland, the Society stands ready as a non-partisan scientific and educational resource for all insect-related topics. For more information, visit http://www.entsoc.org.
Insect Systematics and Diversity publishes research on systematics, evolution, and biodiversity of insects and related arthropods, including comparative and developmental morphology, conservation, behavior, taxonomy, molecular phylogenetics, paleobiology, natural history, and phylogeography. For more information, visit https://academic.oup.com/isd, or visit http://www.insectscience.org to view the full portfolio of ESA journals and publications.
Travelling elephants pay close attention to scent trails of dung and urine left by other elephants, new research shows.
Scientists monitored well-used pathways and found that wild African savannah elephants - especially those travelling alone - were "highly attentive", sniffing and tracking the trail with their trunks.
This suggests these scents act as a "public information resource", according to researchers from the University of Exeter and Elephants for Africa.
More research is now needed to find out whether humans can create artificial elephant trails to divert elephants away from farms and villages, where conflict with humans can cause devastation to communities.
Alternatively, scent trails could be placed to improve the efficiency of routes ...
HOUSTON - Researchers at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center have discovered a novel function for the metabolic enzyme medium-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase (MCAD) in glioblastoma (GBM). MCAD prevents toxic lipid buildup, in addition to its normal role in energy production, so targeting MCAD causes irreversible damage and cell death specifically in cancer cells.
The study was published today in Cancer Discovery, a journal of the American Association for Cancer Research. Preclinical findings reveal an important new understanding of metabolism in GBM and support the development of MCAD inhibitors as a novel treatment strategy. The researchers currently are working to develop targeted therapies against the enzyme.
"With ...
Alzheimer's disease is the most common neurodegenerative disorder in which neurons gradually die off, leading to dementia. The exact mechanism and causes of this disorder have not yet been identified. However, it is known that amyloid plaques form in the brains of patients. Plaques consist of amyloid fibrils, which are special filamentous assemblies formed by amyloid proteins.
'The number of patients with neurodegenerative disorders will continue to grow in the future. Thanks to the success of humanity in the treatment of cancer and cardiovascular diseases, more and more people are living into their 80s. At this age, the risk of developing neurodegenerative disorders, including Alzheimer's disease, becomes very high. Unfortunately, no cures for these diseases have yet ...
Killer flies can reach accelerations of over 3g when aerial diving to catch their prey - but at such high speeds they often miss because they can't correct their course.
These are the findings of a study by researchers at the Universities of Cambridge, Lincoln, and Minnesota, published today in the Journal of the Royal Society Interface.
Killer flies (Coenosia attenuata) perform high-speed aerial dives to attack prey flying beneath them, reaching impressive accelerations of up to 36 m/s2, equivalent to 3.6 times the acceleration due to gravity (or 3.6g). This happens because they beat their wings as they fall, combining the acceleration of powered flight with the acceleration of gravity.
This is an impressive feat: diving Falcons, the fastest animals that predate ...
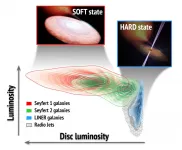
The researchers Juan A. Fernández-Ontiveros, of the Istituto Nazionale di Astrofisica (INAF) in Rome and Teo Muñoz-Darias, of the Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias (IAC), have written an article in which they describe the different states of activity of a large sample of supermassive black holes in the centres of galaxies. They have classified them using the behaviour of their closest "relations", the stellar mass black holes in X-ray binaries. The article has just been published in the journal Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society (MNRAS).
Black holes range in mass from objects which have only a few ...
Mercury pollution is an issue of global concern due to its toxic effects. High levels have already been measured in Arctic organisms - with worrying effects on ecosystems and the food chain. So far, the Greenland Ice Sheet has not been taken into account as a part of the Arctic mercury cycle. Now, researchers led by Jon Hawkings of the German Research Centre for Geosciences in Potsdam and Florida State University show that meltwaters in the southwest of Greenland transport considerable amounts of mercury into the Arctic Ocean. Due to the large quantities detected, the researchers assume that they are of geological origin. They present their measurements in the current issue of Nature Geoscience.
Mercury: poison for humans and the environment - ...
LAWRENCE -- For two weeks in June 2020, a massive dust plume from Saharan Africa crept westward across the Atlantic, blanketing the Caribbean and Gulf Coast states in the U.S. The dust storm was so strong, it earned the nickname "Godzilla."
Now, researchers from the University of Kansas have published a new study in the Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society parsing the mechanism that transported the dust. Their results explain a phenomenon that could occur more frequently in the years ahead due to climate change, affecting human health and transportation systems.
African dust darkened the skies of the Caribbean and American Gulf States thanks to a trio of atmospheric patterns, ...
Mitochondria are the cell's power plants and produce the majority of a cell's energy needs through an electrochemical process called electron transport chain coupled to another process known as oxidative phosphorylation. A number of different proteins in mitochondria facilitate these processes, but it's not fully understood how these proteins are arranged inside mitochondria and the factors that can influence their arrangement.
Now, scientists at the University of Copenhagen have used state-of-the-art proteomics technology to shine new light on how mitochondrial proteins gather into electron transport chain complexes, and further into so-called supercomplexes. The research, which is published in Cell Reports, also examined ...
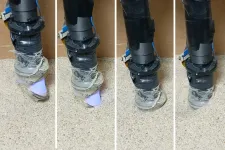
Over the years, robots have gotten quite good at identifying objects -- as long as they're out in the open.
Discerning buried items in granular material like sand is a taller order. To do that, a robot would need fingers that were slender enough to penetrate the sand, mobile enough to wriggle free when sand grains jam, and sensitive enough to feel the detailed shape of the buried object.
MIT researchers have now designed a sharp-tipped robot finger equipped with tactile sensing to meet the challenge of identifying buried objects. In experiments, the aptly named ...
A mathematical model which can predict landslides that occur unexpectantly has been developed by two University of Melbourne scientists, with colleagues from GroundProbe-Orica and the University of Florence.
Professors Antoinette Tordesillas and Robin Batterham led the work over five years to develop and test the model SSSAFE (Spatiotemporal Slope Stability Analytics for Failure Estimation), which analyses slope stability over time to predict where and when a landslide or avalanche is likely to occur.
In a study published in Scientific Reports, the research team was ...