Regenerating damaged eyes with mussel protein and amniotic membrane
2021-06-15
(Press-News.org) The eye is the first sensory organ that recognizes the presence or shape of an object. The conjunctiva is a thin mucous membrane that covers the front half of the eyeball. It protects the eye by secreting mucus and tears for lubrication, and prevents microorganisms from entering. However, since it is exposed to the air, it is susceptible to damages by microorganisms, bacteria, or dust. In fact, if fibrovascular tissues are left to propagate on its surface, they can lead to diseases like pterygium, which can cause visual deterioration. To treat such conditions, an operation to remove and regenerate the damaged conjunctiva is performed. Recently, a Korean research team has developed a new method for performing sutureless amniotic membrane transplantation using the mussel adhesive protein.
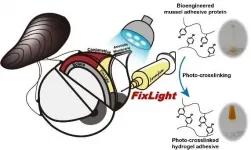
Professor Hyung Joon Cha's research team at POSTECH (Ph.D. candidate Seong-Woo Maeng, Dr. Tae Yoon Park) with the team led by Professor Woo Chan Park of the Department of Ophthalmology at Dong-A University College of Medicine (Dr. Ji Sang Min, currently at Kim's Eye Hospital of the Konyang University School of Medicine) have together applied a light-curable protein bioadhesive named FixLight to an animal model that simulated the transplantation of the amniotic membrane on an actual ocular surface. As a result, it was confirmed that the operation could be completed more than five times faster than the traditional suture method and the therapeutic effect of the conjunctival regeneration through stably bonded amniotic membranes could successfully replace the conventional procedure.
The amniotic membrane is the innermost membrane of the placenta that surrounds and protects the embryo. Since it contains many factors that promote epithelial regeneration, performing amniotic transplantation to reconstruct the ocular surface has been widely practiced. However, the current method stitches the membrane with sutures and fixes it to the surface of the eyeball, which leaves a scar. And since precise sutures are required due to the thinness of the amniotic membrane, the operation is considerably time-consuming.
To this, the POSTECH research team has developed a light-curable adhesive that exists in a liquid state when unexposed to light, but changes into a hydrogel within a few seconds when exposed to visible light of a specific wavelength. Going a step further this time, in joint effort with researchers from Dong-A University College of Medicine, the amniotic membrane was transplanted without sutures on the ocular surface of a rabbit model with conjunctiva defects using a light-curable bioadhesive.
The joint research team used a visible light-curable bioadhesive with liquid-solid photocrosslinking characteristics in the amniotic membrane transplantation surgery, focusing on the high transparency of the amniotic membrane. After evenly coating the liquid adhesive, the amniotic membrane was adhered to the defect site by crosslinking it with light of a specific wavelength. In an experiment using a rabbit conjunctiva defect model, the researchers observed stable tissue adhesion ability that showed no significant difference from suture-treated cases even on the wet surface of the eye. In addition, after epithelialization progressed over the transplanted amniotic membrane, the adhesive completely biodegraded and regenerated into an integrated epithelial tissue.
Professor Hyung Joon Cha of POSTECH explained, "We confirmed the effectiveness of a new amniotic membrane transplantation method for conjunctival reconstruction in an actual animal model using the mussel adhesive protein, an original biomaterial." He added, "It is anticipated to be highly useful as a safe bioadhesive to replace sutures in various medical fields."
FixLight - the visible light-curable protein bioadhesive - shows promise for commercialization in the near future as it has completed the technology transfer to Nature Gluetech Co., Ltd. and is awaiting clinical trials as a safe bioadhesive that can fully replace surgical sutures.
"The amniotic membrane transplantation is an important operation in ocular surface reconstruction and this visible light-curable bioadhesive enabled facile and rapid operation," remarked Professor Woo Chan Park of Dong-A University College of Medicine. "This technique shows promise to be applicable to other ophthalmological surgeries such as closing of incisions after cataract operation or other transplantations of the ocular surface, such as conjunctival autografting."
INFORMATION:
The findings from this research were published online in Advanced Healthcare Materials, an international journal on biomaterials. The study was carried out as part the Korea Health Technology R&D Project through the Korea Health Industry Development Institute funded by the Ministry of Health and Welfare, the Nano-New Materials Core Technology Development Program funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT, and the Marine Biotechnology Program of the Korea Institute of Marine Science & Technology Promotion funded by the Ministry of Oceans and Fisheries of Korea.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-06-15
INDIANAPOLIS - Much needs to be accomplished during the short time a primary care physician sees a patient. A new study from U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs, Regenstrief Institute and IUPUI researchers reports that electronic health records (EHRs) are not rising to the challenges faced by primary care physicians because EHRs have not been designed or tailored to their specific needs. The study, a review and analysis of research on the topic conducted from 2012 to 2020, recommends implementing a human factor approach for the design or redesign of EHR user interfaces.
"The human mind can do many things well. Digesting vast amounts of patient information while multitasking in time-constrained situations ...
2021-06-15
Women exposed to higher levels of air pollution during pregnancy have babies who grow unusually fast in the first months after birth, putting on excess fat that puts them at risk of obesity and related diseases later in life, new CU Boulder research shows.
The study of Hispanic mother-child pairs, published this week in the journal Environmental Health, is the latest to suggest that poor air quality may contribute at least in part to the nation's obesity epidemic, particularly among minority populations who tend to live in places with more exposure to toxic pollutants.
About one in four Hispanic youth in the United States ...
2021-06-15
ROCHESTER, Minn. -- Artificial intelligence (AI) may offer a way to accurately determine that a person is not infected with COVID-19. An international retrospective study finds that infection with SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, creates subtle electrical changes in the heart. An AI-enhanced EKG can detect these changes and potentially be used as a rapid, reliable COVID-19 screening test to rule out COVID-19 infection.
The AI-enhanced EKG was able to detect COVID-19 infection in the test with a positive predictive value -- people infected -- of 37% and a negative predictive value -- people not infected -- of 91%. When additional normal control subjects were added to reflect a 5% prevalence of COVID-19 -- similar ...
2021-06-15
CORVALLIS, Ore. - Research by Oregon State University suggests a pair of compounds originating from hops can help thwart a dangerous buildup of fat in the liver known as hepatic steatosis.
The findings, published today in eLife, are important because the condition affects roughly one-fourth of people in the United States and Europe. While heavy drinking is often associated with liver problems, people with little or no history of alcohol use comprise that 25%, which is why their illness is known as non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, or NAFLD.
Resistance to insulin, the hormone that helps control blood sugar levels, is a risk factor for NAFLD, ...
2021-06-15
COLUMBUS, Ohio - Adults who skip breakfast are likely to miss out on key nutrients that are most abundant in the foods that make up morning meals, a new study suggests.
An analysis of data on more than 30,000 American adults showed that skipping breakfast - and missing out on the calcium in milk, vitamin C in fruit, and the fiber, vitamins and minerals found in fortified cereals - likely left adults low on those nutrients for the entire day.
"What we're seeing is that if you don't eat the foods that are commonly consumed at breakfast, you have a tendency not to eat them the rest of the day. So those common breakfast nutrients become a nutritional gap," said Christopher Taylor, professor of medical dietetics in the College of Medicine at The Ohio State ...
2021-06-15
State-of-the-art video microscopy has enabled researchers at WEHI, Australia, to see the molecular details of how malaria parasites invade red blood cells - a key step in the disease.
The researchers used a custom-built lattice light sheet microscope - the first in Australia - to capture high-resolution videos of individual parasites invading red blood cells, and visualise the molecular and cellular changes that occur throughout this process. The research has provided critical new information about malaria parasite biology that may have applications for the development of much-needed new antimalarial medicines.
The research, which was published today in Nature Communications, was led by Ms Cindy Evelyn, Dr Niall Geoghegan, Dr Lachlan Whitehead, ...
2021-06-15
Makeup wearers may be absorbing and ingesting potentially toxic per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS), according to a new study published today in Environmental Science & Technology Letters. The researchers found high fluorine levels--indicating the probable presence of PFAS--in most waterproof mascara, liquid lipsticks, and foundations tested. Some of the products with the highest fluorine levels underwent further analysis and were all confirmed to contain at least four PFAS of concern. The majority of products with high fluorine, including those ...
2021-06-15
Many cosmetics sold in the United States and Canada likely contain high levels of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS), a potentially toxic class of chemicals linked to a number of serious health conditions, according to new research from the University of Notre Dame.
Scientists tested more than 200 cosmetics including concealers, foundations, eye and eyebrow products and various lip products. According to the study, 56 percent of foundations and eye products, 48 percent of lip products and 47 percent of mascaras tested were found to contain high levels of fluorine, which is an indicator of PFAS use in ...
2021-06-15
WASHINGTON (June 15, 2021)--Malicious COVID-19 online content -- including racist content, disinformation and misinformation -- thrives and spreads online by bypassing the moderation efforts of individual social media platforms, according to new research published in the journal END ...
2021-06-15
More than 50 species of tree snail in the South Pacific Society Islands were wiped out following the introduction of an alien predatory snail in the 1970s, but the white-shelled Partula hyalina survived.
Now, thanks to a collaboration between University of Michigan biologists and engineers with the world's smallest computer, scientists understand why: P. hyalina can tolerate more sunlight than its predator, so it was able to persist in sunlit forest edge habitats.
"We were able to get data that nobody had been able to obtain," said David Blaauw, the Kensall D. Wise Collegiate Professor of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science. "And ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Regenerating damaged eyes with mussel protein and amniotic membrane