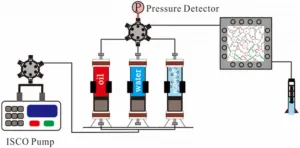
Preformed gel particles tested for enhanced oil recovery
A joint paper went out in Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering
2021-06-16
(Press-News.org) A joint paper went out in Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering.
Petroleum, being a liquid compound, has very good migratory properties, and recovery methods take account of that - using various methods, oilers displace petroleum through cavities and vugs and extract it. However, sometimes oil is "locked" in low-permeability reservoirs, and water displacement used in such cases poses a high risk of reservoir flooding and workplace emergencies.
Many teams work on blocking high-permeability areas in order to make extraction a more controlled and safe process. In particular, there have yet been no efficient agents for reservoirs with high temperatures (up to 140 C) and mineralization (up to 250 grams per liter). Experts from Kazan Federal University, Southwest Petroleum University, Sinopec, and Curtin University joined forces to test novel gel particles in such conditions. The new technique improves on earlier such attempts made by other teams.
Co-author, Senior Research Associate Yuan Chengdong comments, "We'll continue to test our technique on oil deposits in China, where reservoirs with salinity of over 290 grams per liter are quite common. Previous tryouts showed that an increase in recovery can amount to 100 thousand tons. This proves that the reagents are efficient and are very stable under high temperature and high salinity."
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-06-16
Professor Hermann Ehrlich places a piece of sponge in an alkaline, copper-containing ammonia solution that simulates a copper bath from the manufacture of circuit boards for electronic components. About 12 hours later the sponge has turned blue - when dry it is stronger than before, but still very light. "At a pH value of 9 the fibers of the spongin open and the organic compounds of the protein change," explains Prof. Hermann Ehrlich. The copper contained in the ammonia solution reacts immediately with the organic components of the spongin, especially with the amino acid residues, and forms the mineral atacamite. "Like a string, nanometer-sized crystals grow along with the spongin fiber," explains the scientist. ...
2021-06-16
Olives, well-known for their characteristic bitter taste, are in high demand owing to the popularity of the oil that's derived from them. The health benefits of olive oil are well known, ranging from antiviral, anti-cancer, to even anti-hypertensive effects. These benefits are attributed to "oleuropein," the most abundant olive secoiridoid found in olives.
An efficient method to enhance the quality of plant products is by using molecular methods to manipulate their genes and enhancing their yield. With olives, however, this is still a challenge, because of a lack of sufficient genome data.
So far, the genomes of two European olive varieties have been sequenced. But to fully decipher ...
2021-06-16
Lack of data on contraception uptake prior to the pandemic means no clear picture of the impact Covid-19 had on contraception use
Study from Warwick Medical School highlights need to maintain access to contraception during disasters
Researchers recommend making more contraception prescription-free and discuss the benefits and pitfalls of telehealth
Limited data on the uptake of contraception prior to and during crises such as the Covid-19 pandemic could mean unforeseen issues for sexual and reproductive health services, research from the University of Warwick concludes.
It identifies additional barriers that women faced in accessing contraception during the Covid-19 lockdown, including disruption to sexual health services and fears about contracting the virus, as ...
2021-06-16
New research shows the UK's COVID-19 management decisions were based on an outdated pandemic modelling structure and suggests a more resilient approach would have been more effective.
In the initial months of the pandemic, regular updates using graphs showing how the R number was behaving was the mainstay of the Government's strategy for tackling COVID-19.
This type of infection transmission is usually mathematically-based on dividing the population into 'compartments'. Such an approach has been criticised for its limited scope and inability to capture critical factors, such as the ...
2021-06-16
Results show BAT's Modern Oral nicotine pouches have a comparable toxicant profile to NRTs, which are currently considered the least risky of all nicotine products*†
The Modern Oral products have far fewer and significantly lower levels of toxicants‡ than cigarette smoke
Data demonstrates how BAT is building A Better Tomorrow™ by providing evidence to show how we are reducing the health impact of our business and delivering Tobacco Harm Reduction
London, 16 June: New research published today indicates that BAT's modern oral (MO) products in the form of tobacco-free nicotine pouches have a toxicant profile that is comparable to nicotine replacement therapies (NRTs) and much lower than traditional oral ...
2021-06-16
CHAPEL HILL, NC - UNC School of Medicine scientists led a collaboration of researchers to demonstrate a potentially powerful new strategy for treating cystic fibrosis (CF) and potentially a wide range of other diseases. It involves small, nucleic acid molecules called oligonucleotides that can correct some of the gene defects that underlie CF but are not addressed by existing modulator therapies. The researchers used a new delivery method that overcomes traditional obstacles of getting oligonucleotides into lung cells.
As the scientists reported in the journal Nucleic Acids Research, they demonstrated the striking effectiveness of their approach in cells derived from a CF patient and in mice.
"With our oligonucleotide delivery platform, we were able to restore the activity of ...
2021-06-16
Stuttgart/Boulder - It is not the first time that spiders have served as biological models in the research field of soft robotics. The hydraulic actuation mechanisms they apply to move their limbs when weaving their web or hunting for prey give them powers many roboticists and engineers have drawn inspiration from.
A team of researchers at the Max Planck Institute for Intelligent Systems in Germany and at the University of Boulder in Colorado in the US has now found a new way to exploit the principles of spiders' joints to drive articulated robots without any bulky components and connectors, which weigh down the robot and reduce portability and speed. Their slender and lightweight simple ...
2021-06-16
Magnetic-spin interactions that allow spin-manipulation by electrical control allow potential applications in energy-efficient spintronic devices.
An antisymmetric exchange known as Dzyaloshinskii-Moriya interactions (DMI) is vital to form various chiral spin textures, such as skyrmions, and permits their potential application in energy-efficient spintronic devices.
Published this week, a Chinese-Australia collaboration has for the first time illustrated that DMI can be induced in a layered material tantalum-sulfide (TaS2) by intercalating iron atoms, and can further be tuned by gate-induced proton intercalation.
REALIZING AND TUNING DMI IN VAN-DER-WAALS MATERIAL TaS2
Searching ...
2021-06-16
WASHINGTON --Just a small number of cells found in tumors can enable and recruit other types of cells nearby, allowing the cancer to spread to other parts of the body, report END ...
2021-06-16
It sounds like a plot from a Quentin Tarantino movie -- something sets off natural killers and sends them on a killing spree.
But instead of characters in a movie, these natural killers are part of the human immune system and their targets are breast cancer tumor cells. The triggers are fusion proteins developed by Clemson University researchers that link the two together.
"The idea is to use this bifunctional protein to bridge the natural killer cells and breast cancer tumor cells," said Yanzhang (Charlie) Wei, a professor in the College of Science's Department of Biological Sciences. "If the two cells are brought close enough together through this receptor ligand connection, the natural killer cells can release what I call killing machinery to have the tumor cells killed."
It's ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Preformed gel particles tested for enhanced oil recovery
A joint paper went out in Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering