INFORMATION:
Further information
For media enquiries contact University of Leeds press officer Lauren Ballinger via l.ballinger@leeds.ac.uk.
University of Leeds
The University of Leeds is one of the largest higher education institutions in the UK, with more than 38,000 students from more than 150 different countries, and a member of the Russell Group of research-intensive universities. The University plays a significant role in the Turing, Rosalind Franklin and Royce Institutes.
We are a top ten university for research and impact power in the UK, according to the 2014 Research Excellence Framework, and are in the top 100 of the QS World University Rankings 2021.
The University was awarded a Gold rating by the Government's Teaching Excellence Framework in 2017, recognising its 'consistently outstanding' teaching and learning provision. Twenty-six of our academics have been awarded National Teaching Fellowships - more than any other institution in England, Northern Ireland and Wales - reflecting the excellence of our teaching. http://www.leeds.ac.uk
Follow University of Leeds or tag us in to coverage: Twitter Facebook LinkedIn Instagram
Pandemic shift to home working could create UK tax crisis
2021-06-22
(Press-News.org) The shift to home working brought about by the pandemic could cost the UK economy up to £32bn a year in lost personal income tax.
Highly paid workers who live abroad but work in the UK will pay their income tax in their country of residence, rather than to HMRC - which researchers say could cost billions each year.
This new mobility of the workforce can also affect where corporate income tax is paid and value created, as well as VAT and where goods and services are purchased.
Professor Rita de la Feria, Chair in Tax Law in the University of Leeds' School of Law, co-led the new research with Dr Giorgia Maffini, Tax Policy expert, at PWC, London.
Their paper, The Impact of Digitalisation on Personal Income Taxes, is published in British Tax Review.
Professor de la Feria said: "The acceleration of digitalisation and the spread of remote working internationally as a result of the pandemic poses very significant challenges to personal income taxes.
"New mobile workers are likely to be at top of the income distribution, and even a small number could result in significant revenue losses to the UK, of between £6bn and £32bn.
"The likely effect will be a tightening of employment rules, introduction of new tax avoidance rules, and increased personal income taxes competition with countries fighting to attract new mobile workers.
"The impact of these labour changes is likely to be more significant in countries like the UK, which relies heavily on income tax - especially from a small number of high-income - and now potentially mobile - taxpayers.
"How big these challenges are, and how countries will react to them, will be a key issue in the coming years."
Total income tax paid in the UK in 2018-19 was £187 billion, with 35% paid by the 4.2 million higher rate taxpayers, and 31% from additional rate taxpayers.
An estimated 31% of UK jobs can be carried out remotely - of which an as-yet unknown share will be internationally mobile.
Assuming only higher and additional rate taxpayers are internationally mobile, the researchers say the potential loss in income tax would be between 2% and 10% of the total revenue - between £3.8bn and £19bn a year.
Including Social Security contribution losses of between £2.7bn and £13bn a year, the total income tax revenue loss would amount to between £6.5 billion and £32.5 billion a year.
The researchers say recent global tax discussions have focussed on solving challenges to corporation tax posed by digitalisation, but the pandemic-led shift to remote working could pose an even bigger crisis.
Professor de la Feria said: "This crisis has the potential for much wider economic and societal ramifications than the challenges to corporation tax. The challenges of adapting our tax systems to a digital economy are far from over; indeed, they have just started."
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
It's true: Stress does turn hair gray (and it's reversible)
2021-06-22
Legend has it that Marie Antoinette's hair turned gray overnight just before her beheading in 1791.
Though the legend is inaccurate--hair that has already grown out of the follicle does not change color--a new study from researchers at Columbia University Vagelos College of Physicians and Surgeons is the first to offer quantitative evidence linking psychological stress to graying hair in people.
And while it may seem intuitive that stress can accelerate graying, the researchers were surprised to discover that hair color can be restored when stress is eliminated, a finding that contrasts with a recent study in mice that suggested that stressed-induced gray hairs are permanent.
The ...
Some seafloor microbes can take the heat: And here's what they eat
2021-06-22
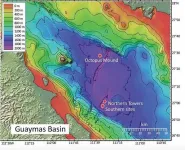
WOODS HOLE, Mass. -- It's cold in the depths of the world's oceans; most of the seafloor is at a chilly 4°C. Not so the seafloor of Guaymas Basin in the Gulf of California. Here, tectonic plates drift apart and heat from Earth's interior can rise up -- so far up that it bakes large areas of the seafloor sediments, turning buried organic matter into methane and other energy-rich compounds.
What kinds of organisms thrive in this oceanic hotspot? In two new studies, MBL Assistant Scientist END ...
Investigating a better treatment sequence for esophageal cancer
2021-06-22
Looking for better ways to treat patients with esophageal cancer, University of Colorado Cancer Center member Martin McCarter, MD, is investigating whether a new treatment sequence will result in better outcomes.
As they await the results of a group of clinical trials -- including one at the CU Cancer Center -- McCarter and other University of Colorado researchers (led by surgery resident Bobby Torphy, MD, PhD) looked at data from the National Cancer Database to see if they could identify other patients who have undergone the new sequence, and what the outcomes for those patients were. The group published a paper in the Annals of Surgical Oncology in April ...
Marine sediments explain how part of Brazil's Northeast region became semi-arid
2021-06-22
Rainfall associated with the Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ), the belt of converging trade winds and rising air that encircles the Earth near the Equator, affects the food and water security of approximately 1 billion people worldwide. They include about 11% of the Brazilian population, concentrated in four states of the Northeast region - Rio Grande do Norte, Ceará, Piauí, and Maranhão. Large swathes of these states have a semi-arid climate, and about half of all their annual rainfall occurs in only two months (March and April), when the tropical rain belt reaches its southernmost position, over the north of the Northeast region. During the rest of the year, the tropical ...
Switching from Western diet to a balanced diet may reduce skin, joint inflammation
2021-06-22
(SACRAMENTO, Calif.) -- The secret to healthier skin and joints may reside in gut microorganisms. A study led by UC Davis Health researchers has found that a diet rich in sugar and fat leads to an imbalance in the gut's microbial culture and may contribute to inflammatory skin diseases such as psoriasis. ...
New study: Eating prunes daily improves risk factors for heart disease and inflammation
2021-06-22
New research published in the Journal of Medicinal Food suggests eating prunes each day can improve risk factors for cardiovascular disease (CVD) including raising antioxidant capacity and reducing inflammation among healthy, postmenopausal women.
Cardiovascular disease is the number one cause of death worldwide posing a significant public health challenge.
The research led by San Diego State University reveals that prunes can positively affect heart disease risk.
"When you look at our prior research and the research of others combined with this new data, you'll see consistent ...
Experts highlight solutions to bolster long-term care workforce
2021-06-22
"Workforce issues are the most significant challenges facing the long-term care industry," states the opening editorial of a new special issue of The Gerontologist titled " END ...
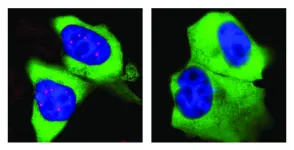
Flash mob in the nucleus
2021-06-22
Almost all cells in our body contain a nucleus: a somewhat spherical structure that is separated from the rest of the cell by a membrane. Each nucleus contains all the genetic information of the human being. So it serves as a kind of library - but one with strict requirements: If the cell needs the building instructions for a protein, it won't simply borrow the original information. Instead, a transcript of it is made in the nucleus.
The machinery required for this is very complex, not least because the transcripts are not simple copies. In addition to essential information, genes also contain numerous passages of meaningless "garbage". They are removed when the transcript is made. Biologists call this editorial revision ...
In many cases, MS starts long before the diagnosis
2021-06-22
Persons suffering from the autoimmune disease multiple sclerosis can develop various neurological symptoms caused by damage to the nervous system. Especially in early stages, these may include sensory dysfunction such as numbness or visual disturbances. In most patients, MS starts with recurring episodes of neurological disability, called relapses or demyelinating events. These clinical events are followed by a partial or complete remission. Especially in the beginning, the symptoms vary widely, so that it is often difficult even for experienced doctors to interpret them correctly to arrive at a diagnosis of MS.
Above-average numbers of medical appointments
It has been evident for some ...
Researchers find signs of inflammation in brains of people who died of COVID-19
2021-06-22
The most comprehensive molecular study to date of the brains of people who died of COVID-19 turned up unmistakable signs of inflammation and impaired brain circuits.
Investigators at the Stanford School of Medicine and Saarland University in Germany report that what they saw looks a lot like what's observed in the brains of people who died of neurodegenerative conditions such as Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's disease.
The findings may help explain why many COVID-19 patients report neurological problems. These complaints increase with the severity of infection with SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19. And they can persist as an aspect of "long COVID," a long-lasting disorder that sometimes ...