(Press-News.org) BROOKLYN, New York, Wednesday, June 23, 2021 -- Owing to their tunable properties, hydrogels comprising stimuli-sensitive polymers are among the most appealing molecular scaffolds because their versatility allows for applications in tissue engineering, drug delivery and other biomedical fields.
Peptides and proteins are increasingly popular as building blocks because they can be stimulated to self-assemble into nanostructures such as nanoparticles or nanofibers, which enables gelation -- the formation of supramolecular hydrogels that can trap water and small molecules. Engineers, to generate such smart biomaterials, are developing systems that can respond to a multitude of stimuli including heat. Although thermosensitive hydrogels are among widely studied and well-understood class of protein biomaterials, substantial progress is also reportedly being made in incorporating stimuli-responsiveness including pH, light, ionic strength, redox, as well as the addition of small molecules.
A team of researchers at the END
'On/off' switches for self-assembling hydrogels could advance wound healing and more
2021-06-23
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Study finds abnormal response to cellular stress is associated with Huntington's disease
2021-06-23
Irvine, CA - June 23, 2021 - A new University of California, Irvine-led study finds that the persistence of a marker of chronic cellular stress, previously associated with neurodegenerative diseases such as amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and frontotemporal dementia (FTD), also takes place in the brains of Huntington's disease (HD) patients.
Chronic cellular stress results in the abnormal accumulation of stress granules (SGs), which are clumps of protein and RNAs that gather in the cell. Prior to this study, published in the Journal of Clinical ...
COVID-19 disruptions in sub-Saharan Africa will have substantial health consequences
2021-06-23
Boston, MA--Early in the COVID-19 pandemic, many African leaders implemented prevention measures such as lockdowns, travel bans, border closures, and school closures. While these efforts may have helped slow the spread of the virus on the continent and continue to be important for its containment, they inadvertently disrupted livelihoods and food systems and curtailed access to critical nutrition, health, and education services. A new series of studies by researchers from Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health and colleagues from the Africa Research, Implementation Science and Education (ARISE) Network finds that these disruptions may have serious ...
Study: Environmental risks exacerbated for vulnerable populations in small towns
2021-06-23
AMES, Iowa -- A new study of small Iowa towns found that vulnerable populations within those communities face significantly more public health risks than statewide averages.
The study, published this week in PLOS ONE, a peer-reviewed open access journal, was led by Benjamin Shirtcliff, associate professor of landscape architecture at Iowa State University.
He focused on three Iowa towns - Marshalltown, Ottumwa and Perry - as a proxy for studying shifting populations in rural small towns, in particular how vulnerable populations in these towns ...
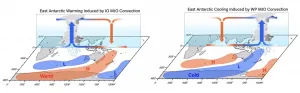
East Antarctic summer cooling trends caused by tropical rainfall clusters
2021-06-23
Our planet is warming due to anthropogenic greenhouse gas emissions; but the warming differs from region to region, and it can also vary seasonally. Over the last four decades scientists have observed a persistent austral summer cooling on the eastern side of Antarctica. This puzzling feature has received world-wide attention, because it is not far away from one of the well-known global warming hotspots - the Antarctic Peninsula.
A new study published in the journal Science Advances by a team of scientists from the IBS Center for Climate Physics at Pusan National University in South Korea, Nanjing University of Information Science and Technology, NOAA Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Laboratory, University Corporation for Atmospheric Research, Ewha Womans University, and National Taiwan ...
Being Anglo-Saxon was a matter of language and culture, not genetics
2021-06-23
A new study from archaeologists at University of Sydney and Simon Fraser University in Vancouver, has provided important new evidence to answer the question "Who exactly were the Anglo-Saxons?"
New findings based on studying skeletal remains clearly indicates the Anglo-Saxons were a melting pot of people from both migrant and local cultural groups and not one homogenous group from Western Europe.
Professor Keith Dobney at the University of Sydney said the team's results indicate that "the Anglo-Saxon kingdoms of early Medieval Britain were strikingly similar to contemporary Britain - full of people of different ancestries sharing a common language and culture".
The Anglo-Saxon (or early medieval) period in England runs from the 5th-11th centuries AD. Early Anglo-Saxon dates from ...
3,000-year-old shark attack victim found by Oxford-led researchers
2021-06-23
Newspapers regularly carry stories of terrifying shark attacks, but in a paper published today, Oxford-led researchers reveal their discovery of a 3,000-year-old victim - attacked by a shark in the Seto Inland Sea of the Japanese archipelago.
The research in Journal of Archaeological Science: Reports, shows that this body is the earliest direct evidence for a shark attack on a human and an international research team has carefully recreated what happened - using a combination of archaeological science and forensic techniques.
The grim discovery of the victim was made by Oxford researchers, J. Alyssa White and Professor Rick Schulting, while investigating evidence for violent trauma on the skeletal remains of prehistoric hunter-gatherers at ...
Western high-fat diet can cause chronic pain, according to UT Health San Antonio-led team
2021-06-23
SAN ANTONIO, June 23, 2021 - A typical Western high-fat diet can increase the risk of painful disorders common in people with conditions such as diabetes or obesity, according to a groundbreaking paper authored by a team led by The University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio, also referred to as UT Health San Antonio.
Moreover, changes in diet may significantly reduce or even reverse pain from conditions causing either inflammatory pain - such as arthritis, trauma or surgery - or neuropathic pain, such as diabetes. The novel finding could help treat chronic-pain patients by simply altering diet or developing drugs that block ...
Concepts from physics explain importance of quarantine to control spread of COVID-19
2021-06-23
By José Tadeu Arantes | Agência FAPESP – Mathematical models that describe the physical behavior of magnetic materials can also be used to describe the spread of the novel coronavirus that causes COVID-19.
This is the conclusion of a study conducted in Brazil by researchers affiliated with São Paulo State University (UNESP) in Rio Claro and Ilha Solteira and reported in an article published in Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications.
The study was part of a project led by Mariano de Souza, a professor at UNESP’s Rio Claro Physics Department, and of the PhD research of Isys Mello, whose thesis advisor is Souza, last author of the article. Another co-author is Antonio Seridonio, a professor at UNESP’s Ilha Solteira Physics ...
More seniors may have undiagnosed dementia than previously thought
2021-06-23
Only 1 in 10 older adults in a large national survey who were found to have cognitive impairment consistent with dementia reported a formal medical diagnosis of the condition.
Using data from the Health and Retirement Study to develop a nationally representative sample of roughly 6 million Americans age 65 or older, researchers at the University of Michigan, North Dakota State University and Ohio University found that 91% of people with cognitive impairment consistent with dementia told questioners they had a formal medical diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease or dementia.
"(The discrepancy) was higher than I was expecting," ...
Flavored e-cigarettes may affect the brain differently than non-flavored
2021-06-23
Flavoring can change how the brain responds to e-cigarette aerosols that contain nicotine, according to Penn State College of Medicine researchers. Andrea Hobkirk and her team used functional magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to understand how the brain's reward areas react to e-cigarette aerosol with and without flavor.
"There are nearly 12 million e-cigarette users in the United States," Hobkirk, an assistant professor of psychiatry and behavioral health at Penn State College of Medicine, said. "The vast majority use e-cigarettes with menthol, mint, fruity and dessert-type flavors. Although regulations that limit the sale of flavored e-cigarettes may help curb use among youth, they might also stop adults from using e-cigarettes as a smoking ...