INFORMATION:
Higher doses of neutralizing antibody could protect humans against HIV
2021-06-24
(Press-News.org) Although the Antibody Mediated Prevention (AMP) study that launched in 2016 failed to show significant efficacy in a pair of clinical trials, Denis Burton argues in a Perspective that the AMP study's results represent a landmark in AIDS research; they show - for the first time - that a broadly neutralizing antibody (bnAb) can protect humans against exposure to some strains of HIV. According to Burton, the AMP study's data - despite not showing a significant difference between the numbers of infected individuals in the treated groups versus those in the placebo groups - still have tremendous implications for future HIV vaccine design and passive bnAb use strategies. The AMP study evaluated the immunotherapeutic use of the recently discovered HIV bnAb VRC01. Here, using context from animal model studies, Burton discusses the data in the trial that indicate that broad protection against a variety of HIV strains may be achievable using higher serum titers of infused therapeutic antibody and how these insights could be used to improve future human HIV bnAb clinical trials. "Overall, it is likely that data from the AMP study will be mined for some time and will doubtless provide new insights into HIV infection and the role of neutralizing antibody in containing virus infection."
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
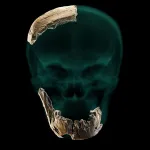
New fossil discovery from Israel points to complicated evolutionary process
2021-06-24
BINGHAMTON, N.Y. -- Analysis of recently discovered fossils found in Israel suggest that interactions between different human species were more complex than previously believed, according to a team of researchers including Binghamton University anthropology professor Rolf Quam.
The research team, led by Israel Hershkovitz from Tel Aviv University, published their findings in Science, describing recently discovered fossils from the site of Nesher Ramla in Israel. The Nesher Ramla site dates to about 120,000-140,000 years ago, towards the very end of the Middle Pleistocene time period.
The human fossils were found by Dr. Zaidner of ...
Scientists can predict and design single atom catalysts for important chemical reactions
2021-06-24
Researchers at Tufts University, University College London (UCL), Cambridge University and University of California at Santa Barbara have demonstrated that a catalyst can indeed be an agent of change. In a study published today in Science, they used quantum chemical simulations run on supercomputers to predict a new catalyst architecture as well as its interactions with certain chemicals, and demonstrated in practice its ability to produce propylene - currently in short supply - which is critically needed in the manufacture of plastics, fabrics and other chemicals. The improvements have potential for highly efficient, "greener" chemistry with a lower carbon footprint.
The demand for propylene is ...
A new type of Homo unknown to science
2021-06-24
The discovery of a new Homo group in this region, which resembles Pre-Neanderthal populations in Europe, challenges the prevailing hypothesis that Neanderthals originated from Europe, suggesting that at least some of the Neanderthals' ancestors actually came from the Levant.
The new finding suggests that two types of Homo groups lived side by side in the Levant for more than 100,000 years (200-100,000 years ago), sharing knowledge and tool technologies: the Nesher Ramla people who lived in the region from around 400,000 years ago, and the Homo sapiens who arrived later, some 200,000 years ago.
The new discovery also gives clues about a mystery in human evolution: How did genes of Homo sapiens penetrate the Neanderthal population that had presumably lived in Europe long before ...
Battle of the Pleiades against plant immunity
2021-06-24
Mythological nymphs reincarnate as a group of corn smut proteins to launch a battle on maize immunity. One of these proteins appears to stand out among its sister Pleiades, much like its namesake character in Greek mythology. The research carried out at GMI - Gregor Mendel Institute of Molecular Plant Biology of the Austrian Academy of Sciences - is published in the journal PLOS Pathogens.
Pathogenic organisms exist under various forms and use diverse strategies to survive and multiply at the expense of their hosts. Some of these pathogens are termed "biotrophic", as they are parasites that maintain their hosts alive. These biotrophic pathogens deregulate physiological processes in their hosts by suppressing their immune defenses and favoring disease development. ...
Vegetation growth in Northern Hemisphere stunted by water constraints in warming climate
2021-06-24
INDIANAPOLIS -- A first-of-its-kind large-scale study of vegetation growth in the Northern Hemisphere over the past 30 years has found that vegetation is becoming increasingly water-limited as global temperatures increase.
The results are significant since vegetation is one of the biggest factors when it comes to controlling water and carbon cycling across Earth, which influences global temperatures. The work by IUPUI and Indiana University Bloomington researchers Wenzhe Jiao, END ...
Primary lung cancers detected by LDCT are at lower risk of brain metastases
2021-06-24
(Denver)-Patients with primary lung cancer detected using low-dose computed tomography screening are at reduced risk of developing brain metastases after diagnosis, according to a study published in the Journal of Thoracic Oncology.
JTO is an official journal of the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer. The full study is available here: Impact of Low-Dose Computed Tomography Screening for Primary Lung Cancer on Subsequent Risk of Brain Metastasis - Journal of Thoracic Oncology (jto.org)
The researchers, led by Summer Han, PhD, from Stanford University School of Medicine in Palo ...
A low Omega-3 index is just as strong a predictor of early death as smoking
2021-06-24
A new research paper published in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition last week showed that a low Omega-3 Index is just as powerful in predicting early death as smoking. This landmark finding is rooted in data pulled and analyzed from the Framingham study, one of the longest running studies in the world.
The Framingham Heart Study provided unique insights into cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk factors and led to the development of the Framingham Risk Score based on eight baseline standard risk factors--age, sex, smoking, hypertension treatment, diabetes status, systolic blood pressure, total cholesterol (TC), and HDL cholesterol.
CVD is still the leading cause of death globally, and risk can be reduced by changing behavioral factors such as unhealthy diet, ...
New microscopy method reveals single childhood cancer cells in unprecedented detail
2021-06-24
A new technique to look at tumors under the microscope has revealed the cellular make-up of Wilm's tumors, a childhood kidney cancer, in unprecedented detail. This new approach could help understand how tumors develop and grow, and fuel research into new treatments for children's cancers.
Scientists at the Princess Máxima Center for pediatric oncology developed a new imaging technique and computational pipeline to study millions of cells in 3D tissue, revealing hundreds of features from each individual cell. Their research was published this month in Nature Biotechnology.
By offering a look at individual cells within an intact organ, the new technique helps scientists analyze the molecular profile of the cells, as well as their ...
Researchers find the adhesions that build the brain's networks
2021-06-24
DURHAM, N.C. - The brain's neurons tend to get most of the scientific attention, but a set of cells around them called astrocytes - literally, star-shaped cells - are increasingly being viewed as crucial players in guiding a brain to become properly organized.
Specifically, astrocytes, which form about half the mass of a human brain, seem to guide the formation of synapses, the connections between neurons that are formed and remodeled as we learn and remember.
A new study from Duke and UNC scientists has discovered a crucial protein involved in the communication and coordination between astrocytes as they build synapses. Lacking this molecule, called hepaCAM, astrocytes aren't as sticky as they ...
A 'tasty' protein may lead to new ways to treat metabolic and immune diseases
2021-06-24
GRAND RAPIDS, Mich. (June 24, 2021) -- The same taste-sensing molecule that helps you enjoy a meal from your favorite restaurant may one day lead to improved ways to treat diabetes and other metabolic and immune diseases.
TRPM5 is a specialized protein that is concentrated in the taste buds, where it helps relay messages to and from cells. It has long been of interest to researchers due to its roles in taste perception and blood sugar regulation.
Now, a team led by scientists at Van Andel Institute has published the first-ever high-resolution images of TRPM5, which reveal two areas that may serve as targets for new medications. The structures also may aid in the development of low-calorie alternative sweeteners that mimic sugar. The findings were published today in Nature ...