(Press-News.org) Liza Makowski, PhD, professor in the Department of Medicine and the UTHSC Center for Cancer Research, has long been interested in how the immune system is altered by obesity and how this impacts cancer risk and treatment.
"Obesity is complex, because it can cause both inflammation and activate counter-inflammation pathways leading to immunosuppression," Dr. Makowski said. "How obesity impacts cancer treatments is understudied."
Obese patients with breast cancer often have worse outcomes than non-obese patients. However, exciting developments are being made in other cancers that may also hold promise for treating breast cancer. In studies of a new type of immunotherapy drug, called a checkpoint inhibitor, obese patients appear to respond better, compared with their leaner counterparts in some cancers, such as melanoma, ovarian, certain lung, and kidney cancers. It is not clear if this finding is also true for breast cancer patients.
Dr. Makowski teamed up with Joe Pierre, PhD, assistant professor in Pediatrics and director of the UTHSC Center for Gnotobiotics, to investigate how obesity impacts immunotherapy and to identify potential biomarkers of success.
New findings they published in the June issue of Cell Reports have provided some clues to how breast cancer patients might respond.
Immunotherapies, such as immune checkpoint inhibitors, including atezolizumab (TECENTRIQTM, anti-PD-L1) or Pembrolizumab (KeytrudaTM, anti-PD-1), have been approved in 2019 and 2020, respectively, to treat some patients with triple negative breast cancer, a highly aggressive subtype. It is not currently known if obese breast cancer patients respond better to immunotherapies, similar to findings reported with melanoma. Clinical studies such as these are eagerly awaited by breast cancer patients and researchers.
Drs. Makowski and Pierre showed that obesity in mouse models led to accelerated tumor growth, compared to lean counterparts. Anti-PD-1 immune checkpoint blockade successfully blocked obesity-driven cancer progression. Anti-PD-1 increased immune cell numbers and effective anti-tumor markers. By comparing mice that didn't have tumors to mice with tumors, the team showed that the presence of the tumor exacerbated an environment allowing tumors to hide, resulting in high levels of immunosuppressive cells that were ineffective to reduce breast cancer.
Fortunately, these "sleepy cells" could be reprogrammed to reinvigorate anti-tumor immunity with anti-PD-1, despite persistent obesity. The group also worked to identify changes in the gut microbiome associated with obesity and a strong response to therapy.
The Makowski and Pierre labs are currently funded by the National Cancer Institute to further investigate why certain microbes may impact cancer therapies.
"Our gut is colonized by microbes including bacteria, fungi, and viruses, that may fundamentally impact our immune cells and our inherent ability to fight cancer in ways that we are only just beginning to understand," Dr. Pierre said.
INFORMATION:
Addional UTHSC investigators on the research team are: Tony N. Marion, PhD, professor in the Department of Microbiology, Immunology & Biochemistry; Hyo Young Choi, PhD, Department of Preventive Medicine; Neil Hayes, MD, MPH, professor of medicine, director of the UTHSC Center for Cancer Research, and division chief of Hematology and Oncology; and Ramesh Narayanan, PhD, professor in the Department of Medicine and the Division of Hematology and Oncology.
As Tennessee's only public, statewide, academic health system, the mission of the University of Tennessee Health Science Center is to bring the benefits of the health sciences to the achievement and maintenance of human health through education, research, clinical care, and public service, with a focus on the citizens of Tennessee and the region. The main campus in Memphis includes six colleges: Dentistry, Graduate Health Sciences, Health Professions, Medicine, Nursing, and Pharmacy. UTHSC also educates and trains medicine, pharmacy, and/or health professions students, as well as medical residents and fellows, at major sites in Knoxville, Chattanooga and Nashville. For more information, visit http://www.uthsc.edu. Find us on Facebook: facebook.com/uthsc, on Twitter: twitter.com/uthsc and on Instagram: instagram.com/uthsc.
"Fit for 55": under this heading, the EU Commission will specify the implementation of the European Green Deal on 14 July. This refers to the more ambitious climate policy announced, with 55 instead of 40 percent emission reduction by 2030 (relative to 1990), and net-zero emissions in 2050. Coordination between the 27 EU states is expected to be difficult since unanimity is usually required here for sweeping changes. An economic model study by the Berlin-based climate research institute MCC (Mercator Research Institute on Global Commons and Climate Change) and the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research (PIK) examines how to achieve good results under such conditions. The study has just been published in the renowned Journal of Environmental ...
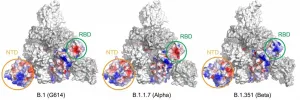
New SARS-CoV-2 variants are spreading rapidly, and there are fears that current COVID-19 vaccines won't protect against them. The latest in a series of structural studies of the SARS-CoV-2 variants' "spike" protein, led by Bing Chen, PhD, at Boston Children's Hospital, reveals new properties of the Alpha (formerly U.K.) and Beta (formerly South Africa) variants. Of note, it suggests that current vaccines may be less effective against the Beta variant.
Spike proteins, on the surface of SARS CoV-2, are what enable the virus to attach to and enter our cells, and all current vaccines are directed against them. The new study, published in Science on June 24, used cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) ...
LA JOLLA, CA--Researchers at La Jolla Institute for Immunology (LJI) have shed light on a process in immune cells that may explain why some people develop cardiovascular diseases.
Their research, published recently in Genome Biology, shows the key role that TET enzymes play in keeping immune cells on a healthy track as they mature. The scientists found that other enzymes do play a role in this process--but TET enzymes do the heavy lifting.
"If we can figure out what's going on with these enzymes, that could be important for controlling cardiovascular disease," ...
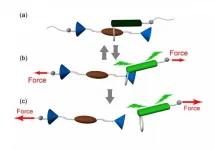
Scientists at Tokyo Institute of Technology design polymers infused with a stress-sensitive molecular unit that respond to external forces by switching on their fluorescence. The researchers demonstrate the fluorescence to be dependent on the magnitude of force and show that it is possible to detect both, reversible and irreversible polymer deformations, opening the door to the exploration of new force regimes in polymers.
Besides causing physical motion, mechanical forces can drive chemical changes in controlled and productive ways, allowing for desirable material properties. One way to go about this is by introducing a so-called mechanophore ...
Amphiphilic molecules, which aggregate and encapsulate molecules in water, find use in several fields of chemistry. The simple, additive-free connection of hydrophilic and hydrophobic molecules would be an efficient method for amphiphilic molecule synthesis. However, such connections, or bonds, are often fragile in water. Now, scientists at Tokyo Institute of Technology have developed an easy way to prepare water-stable amphiphiles by simple mixing. Their new catalyst- and reagent-free method will help create further functional materials.
Soaps and detergents are used to clean things like clothes and dishes. But how do they actually work? It turns out that they are made of long molecules ...
A study from UCLA neurologists challenges the idea that the brain recruits existing neurons to take over for those that are lost from stroke. It shows that in mice, undamaged neurons do not change their function after a stroke to compensate for damaged ones.
A stroke occurs when the blood supply to a certain part of the brain is interrupted, such as by a blood clot. Brain cells in that area become damaged and can no longer function.
A person who is having a stroke may temporarily lose the ability to speak, walk, or move their arms. Few patients recover fully and most are left with some disability, but the majority exhibit some degree of spontaneous recovery during the first few weeks after the stroke.
Doctors and scientists don't fully ...
A near-perfectly preserved ancient human fossil known as the Harbin cranium sits in the Geoscience Museum in Hebei GEO University. The largest of known Homo skulls, scientists now say this skull represents a newly discovered human species named Homo longi or "Dragon Man." Their findings, appearing in three papers publishing June 25 in the journal The Innovation, suggest that the Homo longi lineage may be our closest relatives--and has the potential to reshape our understanding of human evolution.
"The Harbin fossil is one of the most complete human cranial fossils in the world," says author Qiang Ji, a professor of paleontology of Hebei GEO University. "This fossil preserved many ...
WASHINGTON--Antacids improved blood sugar control in people with diabetes but had no effect on reducing the risk of diabetes in the general population, according to a new meta-analysis published in the Endocrine Society's Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.
Type 2 diabetes is a global public health concern affecting almost 10 percent of people worldwide. Doctors may prescribe diet and lifestyle changes, diabetes medications, or insulin to help people with diabetes better manage their blood sugar, but recent data points to common over the counter ...
What The Study Did: This study evaluated changes in hospitalization and death rates related to COVID-19 before and after U.S. states reopened their economies in 2020.
Authors: Pinar Karaca-Mandic, Ph.D., of the Carlson School of Management in Minneapolis, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamahealthforum.2021.1262)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest and funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
INFORMATION:
Media advisory: The full study ...
What The Study Did: Researchers examined the association of closures of childcare facilities with the employment status of women and men with children in the United States during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Authors: Yevgeniy Feyman, B.A., of the Boston University School of Public Health, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamahealthforum.2021.1297)
Editor's Note: The article includes funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author ...